What's new in Dynatrace SaaS version 1.312
- Release notes
- 10-min read
- Rollout start on Apr 8, 2025
This page showcases new features, changes, and bug fixes in Dynatrace SaaS version 1.312. It contains:
Digital Experience | RUM Web
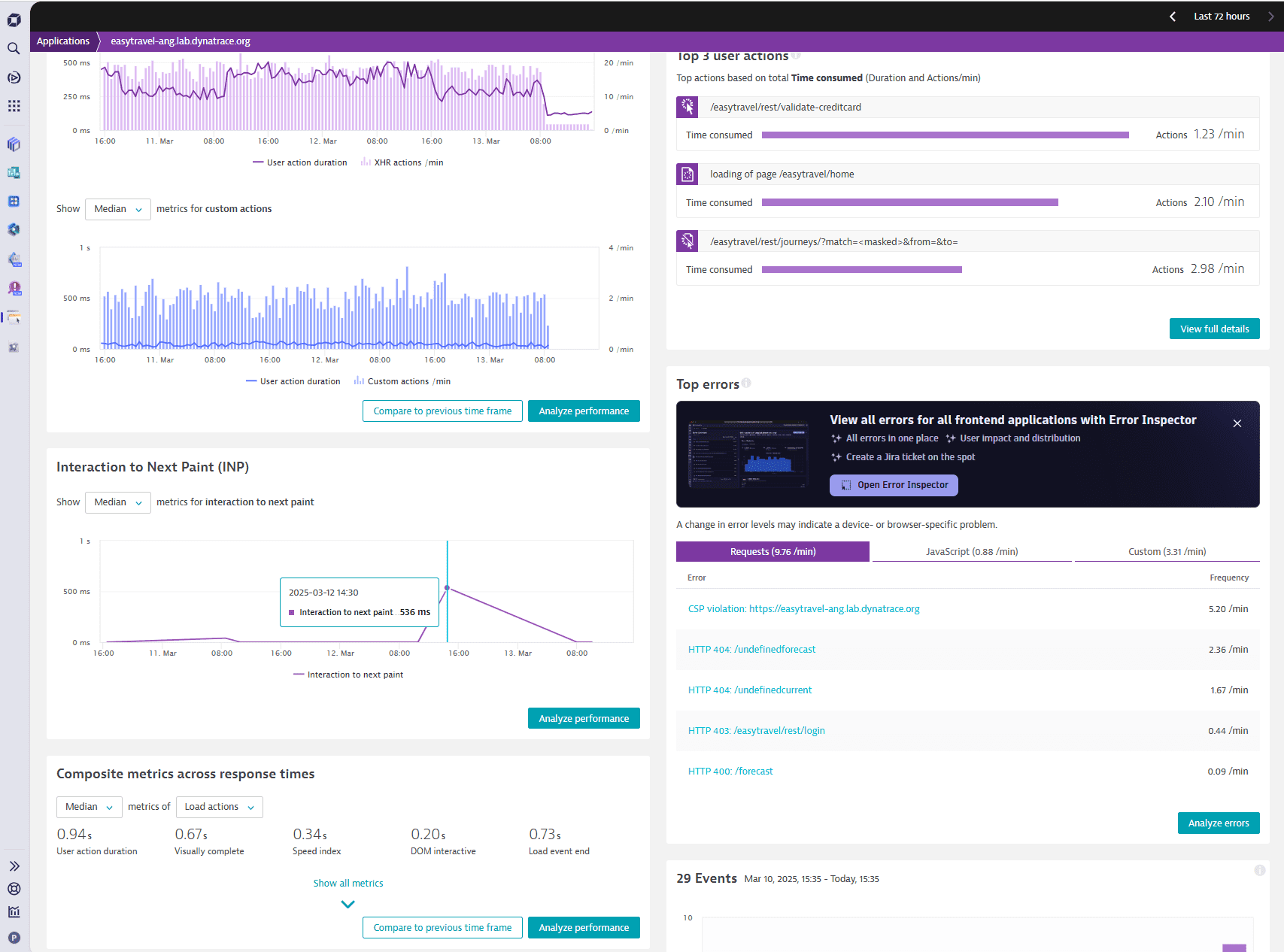
Monitor and analyze Interaction to Next Paint (INP) with ease
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) has replaced First Input Delay (FID) among Google’s Core Web Vitals. As of now, Dynatrace offers the capability to monitor and analyze INP for the websites monitored by our customers.
While FID was used to measure the responsiveness of the initial interaction on a page, INP allows to assess the latency across interactions on a page.
In Dynatrace (Classic and Managed), customers can put our built-in INP metric (builtin:apps.web.interactionToNextPaint) on dashboards (Dashboards Classic) across various dimensions, such as frontend applications, browsers, and locations.
In addition, a user can assess INP values via accessing the frontend application overview screen as well as page analysis screens and filter for pages with the worst INP values to initiate improvements.
Feature updates
Automations | SLOs
SLOs now support segments
The SLO definition now supports segments to either search for relevant entities or tailor the data considered for the SLI calculation.
- Defining segments as part of an SLO allows you to tailor generic SLI definitions to the relevant data based on the segment definition.
- Additionally, when visualized in a dashboard, the SLO takes a segment on the dashboard into account. This allows for a dynamic adjustment of the considered data points when evaluating an SLO.
Digital Experience | RUM Web
SRI for the RUM monitoring code
You can now leverage the subresource integrity (SRI) browser feature to ensure the integrity of the RUM monitoring code that is automatically injected or manually inserted into your web application.
For more information, see Use Subresource Integrity (SRI) for Real User Monitoring code.
Digital Experience | Synthetic
Added ephemeral storage limits to containerized location template
Containerized Synthetic location template now includes ephemeral storage requests and limits for each container.
Digital Experience | Synthetic
Synthetic Browser Monitors now support Kerberos authentication for private Synthetic locations
Private Synthetic locations on Linux, Windows, and Kubernetes can now be set up to execute Browser Monitors using Kerberos as an authentication protocol.
You can learn more about configuring a Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate in the Kerberos client setup for Linux/Windows and in the Kerberos authentication configuration for containerized locations.
Platform | Settings
New Settings page for external requests
The new and improved Settings page for external requests makes it even easier to allow outbound connections from AppEngine app functions and AppEngine ad-hoc functions.
You can find it in the Settings app under General in the Environment management group.
To learn more about the allowlist, see Allow external requests in the Dynatrace Developer documentation.
Application Security | Investigations
Add context to your investigations with reference time
You can now use the power of the reference time to keep track of the incident time and relative distance to it, when analyzing logs and events in  Investigations.
Investigations.
Setting the reference time will create a new virtual field for every timestamp field in your query results, which shows the time difference between the respective event time and the reference time you’ve defined.
Application Security | Vulnerabilities
Go support for RVA and RAP
Go technology is now available for Runtime Vulnerability Analytics (code-level vulnerability detection) and Runtime Application Protection (attack protection).
- To enable RVA monitoring for Go code-level vulnerabilities
- To enable RAP monitoring for attacks in Go technology
With this release, preview customers for Go technology (RVA and RAP) need to upgrade to OneAgent version 1.311 to reactivate this functionality. After that, no further configuration is necessary.
Account Management | Subscriptions and licensing
Cost allocation attributes now available for SAML
You can now add cost allocation attributes via SAML federation to account your costs to the correct product and cost center. The additional attributes can be configured as attribute mappings in the SAML configurations of your Dynatrace account.
Infrastructure Observability |  Discovery & Coverage
Discovery & Coverage
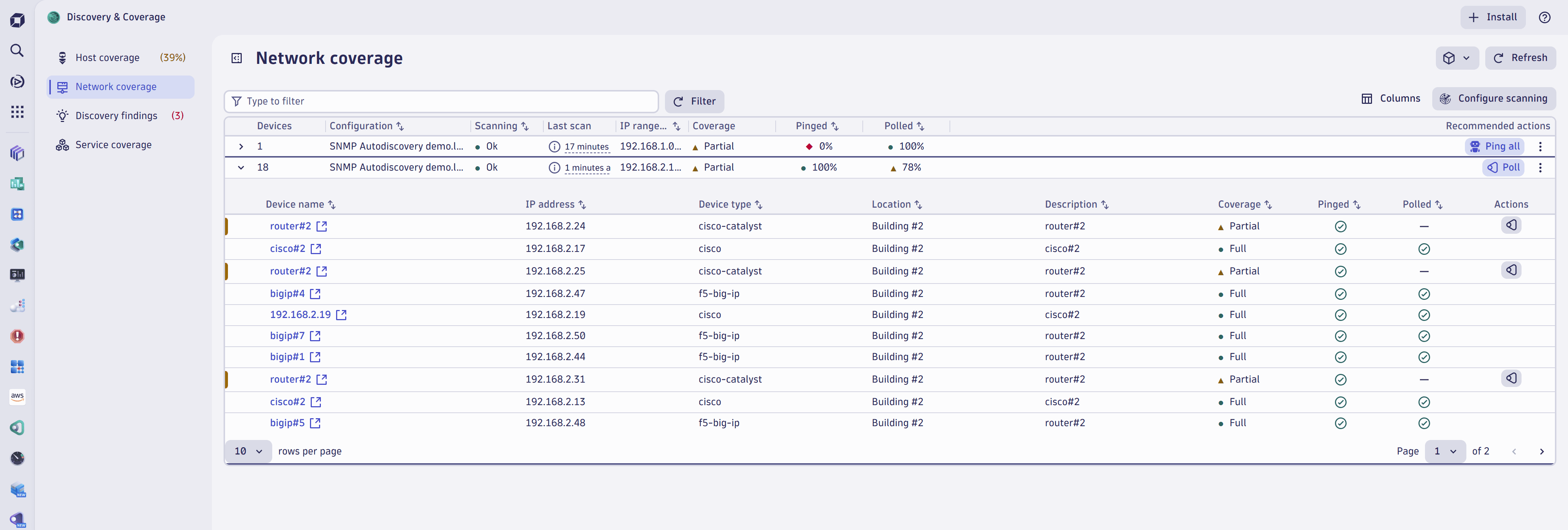
Leverage Discovery & Coverage app to accelerate SNMP network device observability
The  Discovery & Coverage app provides a streamlined observability onboarding experience for SNMP devices. It discovers device type and allows in-bulk extension and Network Availability Monitor enablement. An observation-level report is provided so that it can be compared with intents.
Discovery & Coverage app provides a streamlined observability onboarding experience for SNMP devices. It discovers device type and allows in-bulk extension and Network Availability Monitor enablement. An observation-level report is provided so that it can be compared with intents.
Breaking changes
Breaking change 
Permissions to make dashboards and notebooks visible to whole environment
To be able to make a document visible to the whole environment, a user is now required (as enforced in the document share dialog) to have all share-relevant permissions.
- This is a potential breaking change only in environments that use completely self-created policies.
- If the Standard user or Pro user policies are used, no action is required.
The share-relevant permissions a user needs to be able to share a document to the whole environment are as follows:
document:environment-shares:readdocument:environment-shares:writedocument:environment-shares:deletedocument:direct-shares:readdocument:direct-shares:writedocument:direct-shares:delete
Breaking change 
Scopes removed from Notebooks
In this release, the following scopes are removed from the  Notebooks app:
Notebooks app:
davis-copilot:conversations:execute: Refer to the CoPilot chat available outside the app for general questions. Existing functionality to generate notebook section with Davis CoPilot is not affected by this change.app-settings:objects:read: Internal scope, no workaround needed.
Please update your code sections accordingly. If you use code in your notebooks that relies on either of these scopes, this is a potential breaking change.
Upcoming changes
Kubernetes
Kubernetes dimension names change
The Kubernetes dimension names (dt.kubernetes.cluster.id, dt.kubernetes.workload.kind, dt.kubernetes.workload.name) won't be available starting with Dynatrace Operator version 1.8.0.
If you're still using them, update your configuration, queries, and other references to the new names as soon as possible.
| Deprecated name | New name |
|---|---|
dt.kubernetes.cluster.id | k8s.cluster.uid |
dt.kubernetes.workload.kind | k8s.workload.kind |
dt.kubernetes.workload.name | k8s.workload.name |
Fixes and maintenance
Resolved issues in this release
- Validation of DQL matcher queries in the classic log pipeline has been aligned with OpenPipeline, and incorrect queries in the form of
matchesPhrase({attribute.name},"*")are no longer allowed. (PPX-4419) - Fixed an issue where, in premium HA environments, the connection to Elasticsearch was initialized with the wrong IP addresses. (MGD-3242)
- Fixed an issue in the Calculated Service Metrics API that allowed the creation of unsupported metric "Capture full service call" (
CAPTURED_FULL_SERVICE_CALLS). (APPOBS-5311) - Hardened potentially failing tenant startup when a RUM app name for the default application was written multiple times. (DEM-7053)
Dynatrace API
To learn about changes to the Dynatrace API in this release, see Dynatrace API changelog version 1.312.