Monitor payment service to provide customer support and detect fraud
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
- 5-min read
- Published Nov 20, 2024
This guide is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information provided, it is recommended that you consult with a qualified legal professional to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
This use case from the financial industry involves a company that processes payments on behalf of online merchants. The company’s payment gateway relies on log data for various purposes to provide services to its customers (online merchants), address and troubleshoot complaints from end-users (online merchants customers), and detect and prevent fraud. The user flow includes the following steps for the payment service use case:
- A user makes a payment at a connected merchant’s website.
- The merchant requests the payment service to process the payment.
- The payment service processes the payment.
- The merchant receives the payment status from the payment service.
- The merchant shows the transaction outcome to its customer.
Logging payment transactions is essential for SLA compliance, platform performance, and troubleshooting. Payment logs very likely also contain sensitive information like personal data and financial data that must be kept secure. In cases where logs are collected from different sources (such as various merchants in this use case), utilizing OpenPipeline helps to consolidate data and to address security, privacy and compliance requirements.
Steps to consider to protect sensitive data and address your compliance requirements
If your logs contain personal information or other sensitive data, you may be subject to privacy or security requirements. Dynatrace does not require regulated personal information or sensitive data to provide value (and, per our Subscription Agreement, customers should not provide such data into the platform).
Start with reviewing the data that your logs collect. In this online store use case, this could include information such as a user’s IP address, email address, or ID. While this information may be necessary for certain use cases, you should decide whether you actually need this information for your specific purpose. Check whether your organization has guidelines on protecting sensitive data that you can use.
Key terms
Gain a deeper understanding of the different types of masking used in Log Management and Analytics compliance.
Masking at capture
At-capture masking requires identifying and masking sensitive parts of your log records before data is transferred to Dynatrace. To achieve this, you can choose OneAgent to collect your logs. OneAgent has a built-in mechanism for sensitive data masking that can be granularly configured on the host, host group, or environment level.
For details, refer to Mask your logs at capture or Protect personal data by not capturing it (masking at capture).
Masking at storage
When masking at storage is implemented, data is sent to the Dynatrace server for optimal analysis and is masked before it's stored.
For details, refer to Protect personal data by not storing it (masking at storage).
Masking on read/on display
When data is masked at display, it's stored in its original form but is accessible only to the users of your choice.
For details, refer to Protect personal data by not displaying it (masking at display).
Masking at ingest
With this method, you can mask the data once it reaches Dynatrace, by setting log processing rules. After data is processed, it is sent to storage and is available for further analysis. The key advantage of this method is the fact that it allows data flow from all log ingest channels.
For details, refer to Mask your logs at ingest.
Scenario 1
As a customer support representative, you need to assist customers’ payment-related inquiries.
When a merchant’s customer encounters payment issues and seeks support, the customer support representative investigates the situation by reviewing logs to determine what occurred. In this scenario, we exclude the payment processing logs and assume that the customer support representative already has information regarding the status of the payment request received from the merchant.
Scenario 2
As a security administrator, you want to identify and prevent potential financial fraud through our system.
Security administrators use detailed log records in Dynatrace to identify unusual patterns or anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. This proactive approach allows for quick intervention, protecting both the service and its users from potential losses. Additionally, comprehensive logs provide evidence for potential investigations and legal actions against fraudsters.
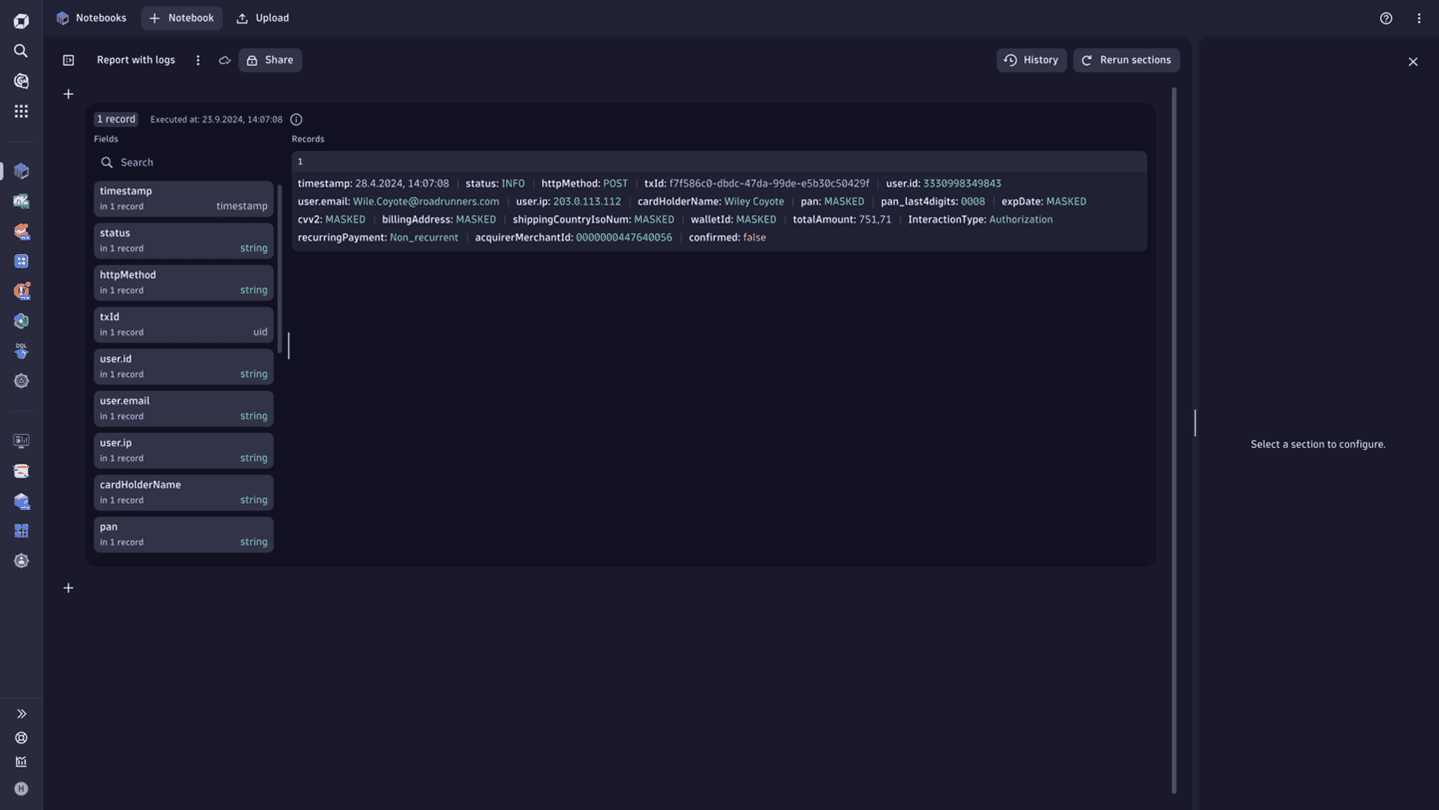
Example of raw data
Personal information contained in logs and methods of masking it
The table below lists some of the personal information that a log line might include and provides a link to the documentation that describes how to either mask the data, control access to this data, or help meet your compliance requirements in another way.
| Data Type | Log record field name | Needed for scenarios | Actions/mitigation | Learn more |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction ID | Acquirer MerchantReferenceNo | 1, 2 | No action required; will appear in the log line. | |
| Transaction timestamp | Timestamp | 1, 2 | No action required; will appear in the log line. | |
| User ID | user.id | 1, 2 | Apply proper retention periods and access controls for protecting PII. | Permissions in Grail, Customizable retention periods with buckets in Grail |
| User email address | user.email | 1, 2 | Apply proper retention periods and access controls for protecting PII. | Permissions in Grail, Customizable retention periods with buckets in Grail |
| User IP address | user.ip | 2 | Apply proper retention periods and access controls for protecting PII. | Permissions in Grail, Customizable retention periods with buckets in Grail |
| Credit card holder name | cardHolderName | 1, 2 | Apply proper retention periods and access controls for protecting PII. | Permissions in Grail, Customizable retention periods with buckets in Grail |
| Credit card Pan | pan | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Credit card expiration date | expDate | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Credit card CVV | cvv2 | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Credit card last 4 digits | pan_last4digits | 1, 2 | Apply proper retention periods and access controls for protecting PII. | Permissions in Grail, Customizable retention periods with buckets in Grail |
| Billing address | billingAddress | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Shipping country (ISO code) | shippingCountryIsoNum | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Wallet ID | walletId | No | Do not store using Mask at-ingest capabilities. | Mask your logs at ingest |
| Total amount | totalAmount | 1 | No action required; will appear in the log line. | |
| Payment processing attributes | InteractionType, RecuringPayment, confirmed, AcquireMerchantID | 1, 2 | No action required; will appear in the log line. |
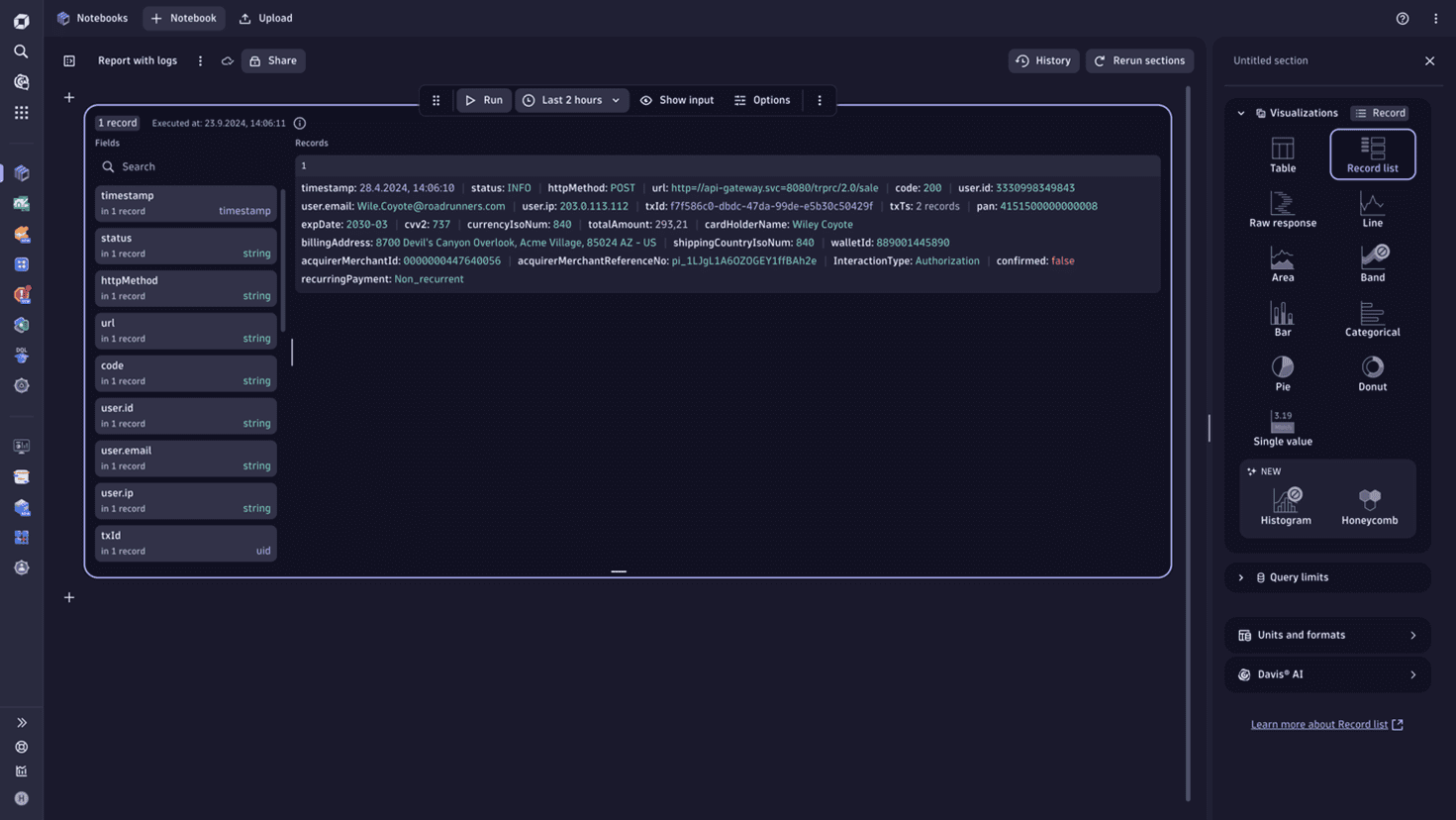
Example of sanitized data
The screenshot below shows how the ingested logs can look after some of the actions described in the table above are applied.