Host monitoring with Dynatrace
- Overview
- 1-min read
As soon as data about hosts is collected, Dynatrace Davis® AI starts baselining the data instantly. Each metric displayed on the host overview page is part of Davis AI source data used for automatically identifying potential performance issues at the infrastructure or full-stack level.
How to get there:
- Go to Hosts (previous Dynatrace) or
 Hosts Classic to list all the hosts (physical or virtual) in your environment that have OneAgent installed on them.
Hosts Classic to list all the hosts (physical or virtual) in your environment that have OneAgent installed on them. - Select a host name in the list to go to that host's overview page.
All relevant host metrics are shown on a single page, which is divided into several logical sections.
Notifications bar
The host notifications bar gives you a quick overview of the host state. Select a notification item to display more information.
Properties and tags
Select Properties and tags on the notifications bar to display the Properties and tags panel, which displays metadata about the selected host:
- Tags lists tags currently applied to the host. Select Add Tag to add a tag to the host metadata.
- Properties lists various host properties, such as OneAgent version, OS version, monitoring mode, IP addresses, and management zones.
Problems
- On the notifications bar, Problems indicates active and closed problems related to the selected host.
- Select Problems on the notifications bar to display the Problems panel, which lists the problems.
- Select a problem to display details.
- Select Go to problems to go to the Problems page filtered by the selected host.
Vulnerabilities
-
On the notifications bar, Vulnerabilities indicates the top detected vulnerabilities affecting the selected host.
-
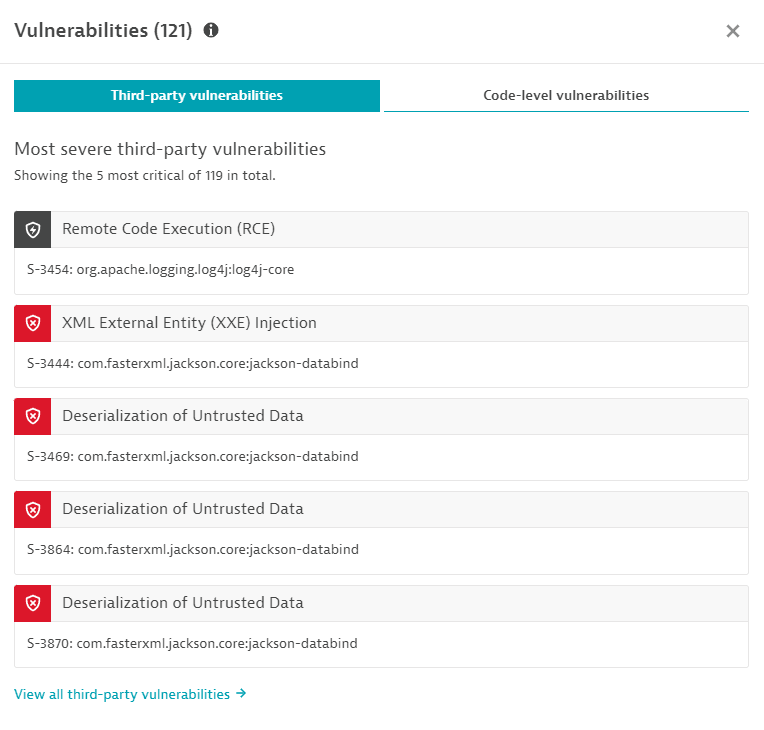
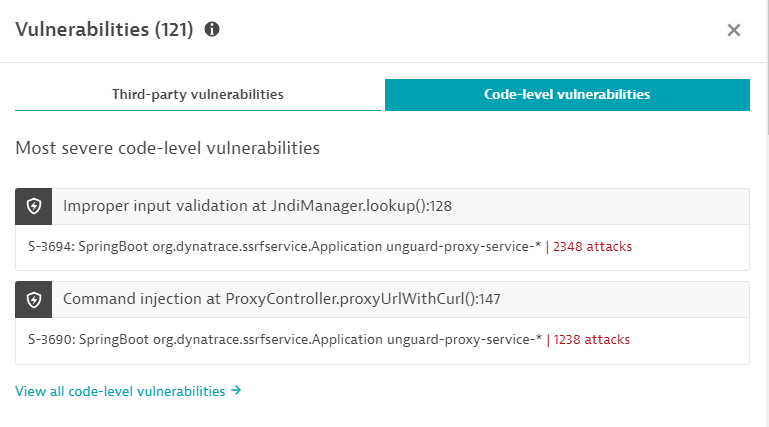
Select Vulnerabilities on the notifications bar to display the Vulnerabilities panel, which lists the most severe third-party vulnerabilities and code-level vulnerabilities related to this host.
- Select a vulnerability in the list to view the details and understand the severity and impact of a vulnerability within your environment.
- For a complete list of the detected vulnerabilities affecting this host, select Show all third-party vulnerabilities/Show all code-level vulnerabilities.
Example third-party vulnerabilities:
Example code-level vulnerabilities:
If you're missing the security permissions for the selected management zone, the Vulnerabilities tab on the notification bar shows Not analyzed.
Availability
-
On the notifications bar, Availability indicates the percentage of time that the host was online and responsive to requests. Dynatrace detects and shows operating system shutdowns (including reboots) and periods when a host is offline (for example, if the host is down unexpectedly).
-
Select Availability on the notifications bar to display the Host availability panel, which charts host availability over time.
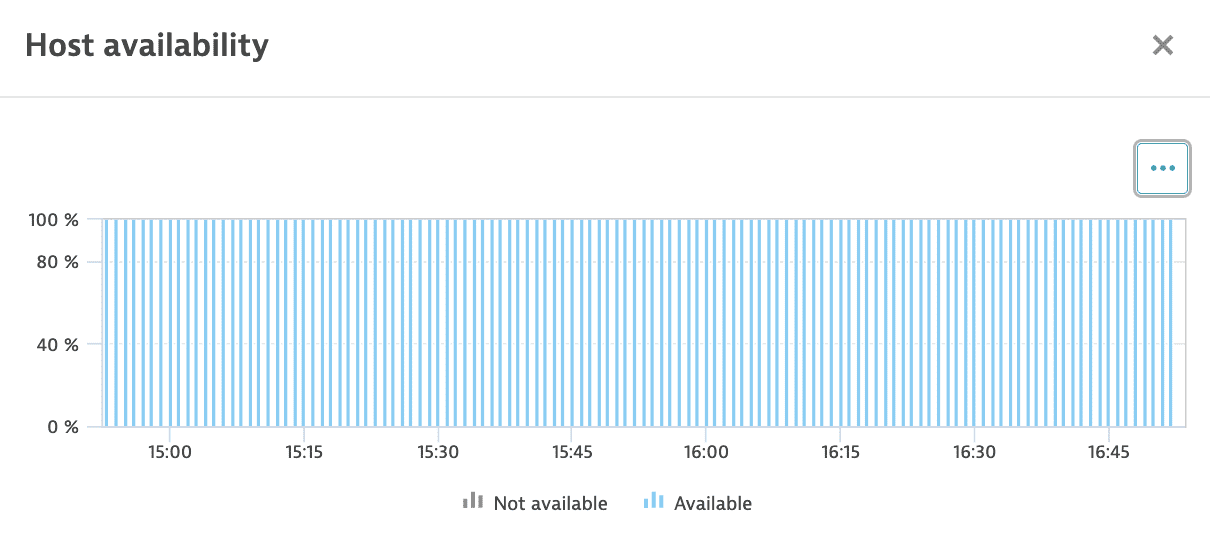
For details, see Host availability.
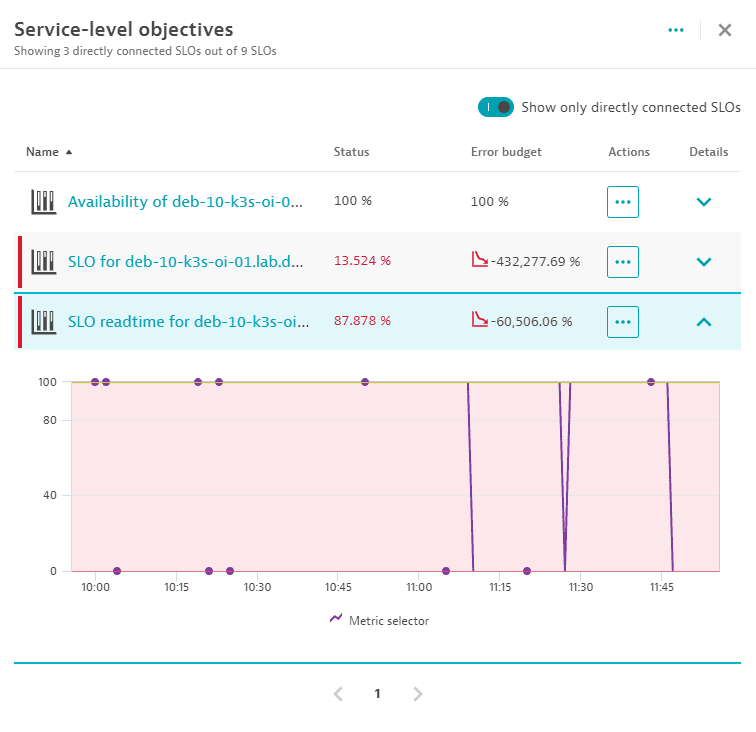
SLOs
- On the notifications bar, SLOs indicates the current number of SLOs related to the selected host.
- Select SLOs on the notifications bar to display the Service-level objectives panel, which lists SLOs that are directly or indirectly connected to the host.
Directly connected SLOs
-
An SLO is directly connected to a host when the entity selector of an SLO meets the following criteria:
- The entity type is set to
"HOST". - The entity ID is set to the host ID.
- The entity type is set to
-
To see only SLOs that are directly connected to the host, make sure that Show only directly connected SLOs is turned on.
Indirectly connected SLOs
-
An SLO isn't directly connected to a host when, in the entity selector of an SLO, no entity ID is provided.
Example: When generic values, such as
type("HOST"),tag("slo")are provided, the query results in all SLOs for all hosts, including the current host. -
To see SLOs that are not directly connected to the host, turn off Show only directly connected SLOs.
Options
-
Select Details to view a chart of the respective SLO metrics.
-
In Actions, select
- View in Data Explorer to see SLO metrics in Data Explorer.
- Pin to Dashboard to pin the SLO to your dashboard. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
- SLO definition to edit the SLO in Service-level objective definitions.
- Clone to clone the SLO.
- Create alert to create an alert for the SLO.
No SLOs
If no SLOs are found, you can
-
Select a different timeframe in the upper-right corner.

-
Select Add SLO to create an SLO in the SLO wizard.
Example SLO panel
Performance
Incoming connections
The Incoming connections section displays a table of hosts that are upstream from the selected host.
- Select any host to go to that host's overview page.
- Select > Analyze process connections to display the Process connections page, where you can view the incoming and outgoing connections.
Outgoing connections
The Outgoing connections section displays a table of hosts that are downstream from the selected host.
- Select any host to go to that host's overview page.
- Select > Analyze process connections to display the Process connections page, where you can view the incoming and outgoing connections.
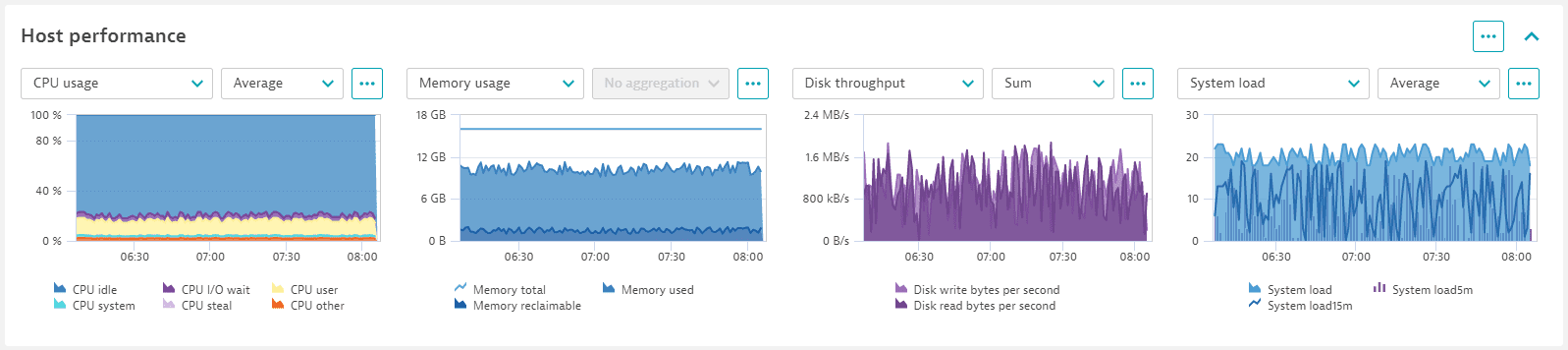
Host performance
Go to the Host performance section for quick insights with relevant metrics: CPU, memory, and network metrics, with different metric aggregations for the selected timeframe. Timeline browsing lets you pinpoint selected anomalies in all metric charts simultaneously, making it easier to understand the relationships between the various infrastructure components at a specific point in time.
It is easy to inspect maximum or minimum peaks in resource consumption, as each metric chart allows the selection of a different aggregation. Custom metrics can also be displayed instead of the default metrics, allowing inspection of specific relationships across metrics that might be critical for any specific host configuration.
Leverage these charts
Select in the upper-right corner of a chart to:
- Show in Data Explorer—Opens Data Explorer for the associated query, so you can view the associated query, explore the data more in-depth, adjust the chart settings, and pin the chart to your own dashboard.
- Pin to dashboard—Pins a copy of the selected chart to any classic dashboard you can edit. For example, if certain hosts are particularly important to your business, create a dashboard designated to monitoring only those hosts, and then pin charts from their host overview pages to that dashboard, all with almost no typing. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
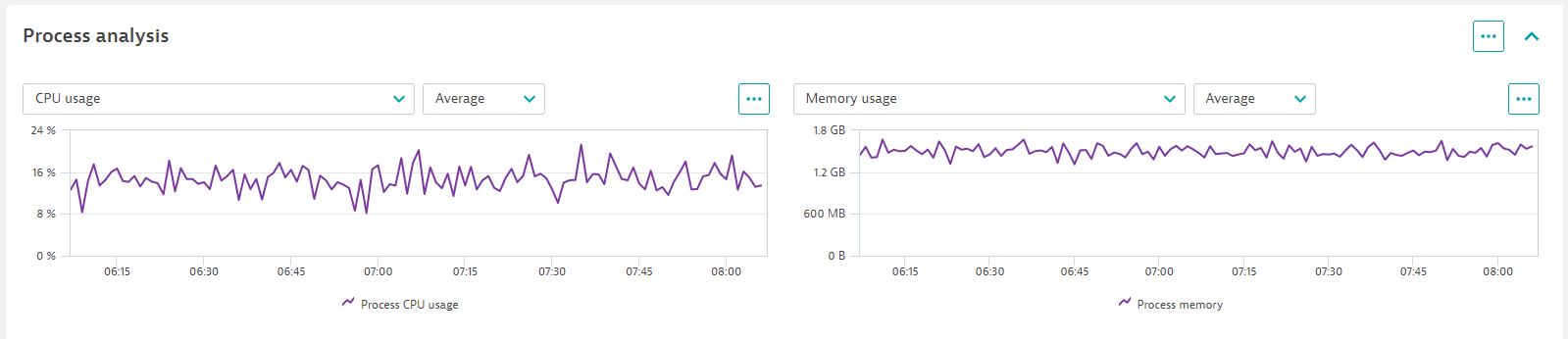
Process analysis
To get a better understanding of process behavior, go to the Process analysis section, which charts and lists processes running on the selected host. Select a process to drill down for details about that process on the host.
Leverage these charts
Select in the upper-right corner of a chart to:
- Show in Data Explorer—Opens Data Explorer for the associated query, so you can view the associated query, explore the data more in-depth, adjust the chart settings, and pin the chart to your own dashboard.
- Pin to dashboard—Pins a copy of the selected chart to any classic dashboard you can edit. For example, if certain hosts are particularly important to your business, create a dashboard designated to monitoring only those hosts, and then pin charts from their host overview pages to that dashboard, all with almost no typing. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
OS services analysis
This feature is available for Linux and Windows operating systems only.
The OS services analysis section lists the operating system services monitored for availability. For a service to be monitored, you need at least one policy with rules matching the properties of the service. For more information on creating monitoring policies for OS services, see OS services monitoring.
- Select any host to go to its overview page, then go to the OS services analysis section.
- Select a service name from the list to open the Service overview page, which displays the selected service's properties and a service availability chart.
To set up policies for OS services for Windows and Linux operating systems, select > OS services monitoring settings to display the OS services monitoring page.
Process instance snapshots
OneAgent version 1.237+
The Process instance snapshots section offers additional insights into the most resource-consuming processes running on your host and the processes defined for Process availability monitoring.
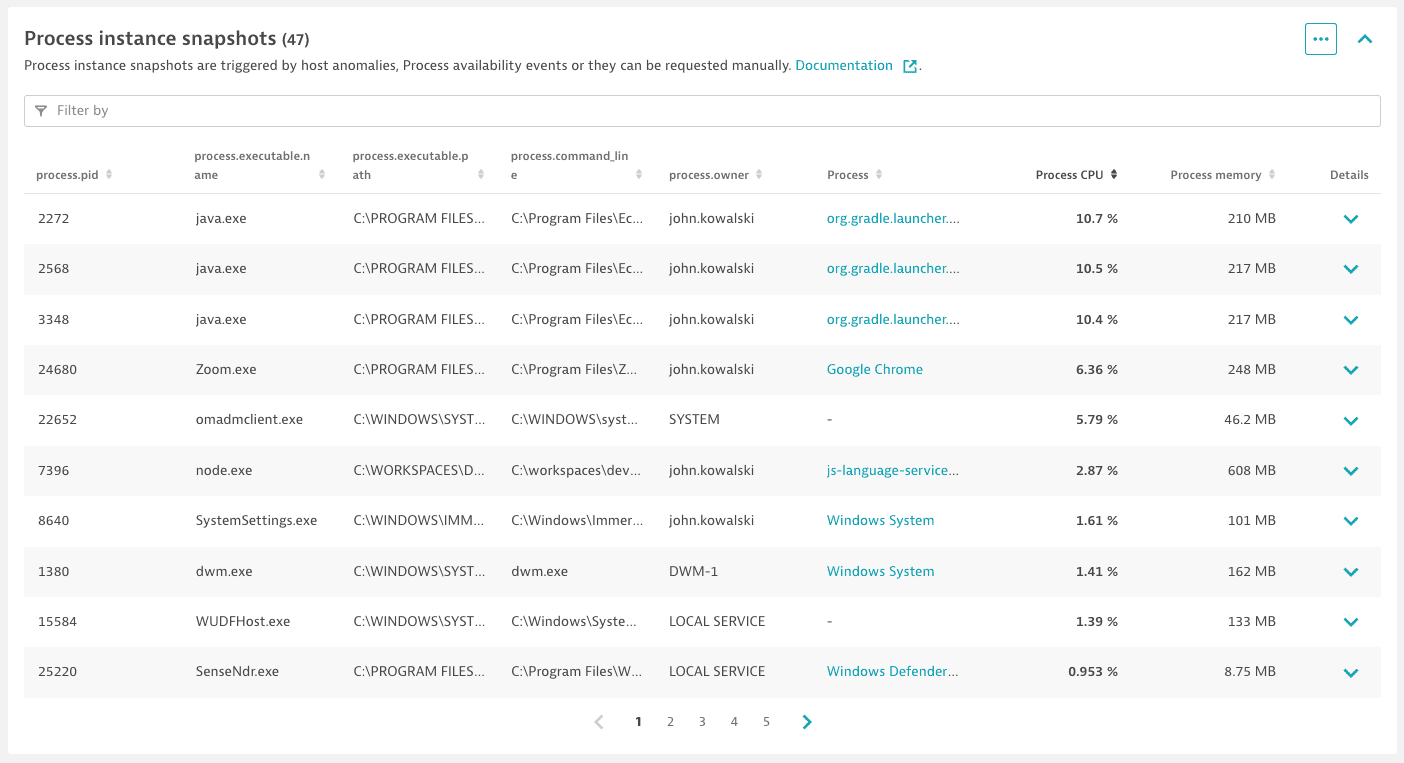
A single process instance snapshot is a set of monitoring data for processes. It contains data on the process CPU usage (%), Memory usage (B), Incoming network traffic (KB), and Outgoing network traffic (KB) measured at one-minute intervals. A single snapshot contains 20 minutes of monitoring data: 10 minutes preceding the trigger and 10 minutes after the trigger. Each host can report only 60 minutes of these metrics per day. A process is considered for the snapshot if its consumption of CPU, memory, or network is more than 1%.
A process instance snapshot is triggered by high CPU, memory, or network usage on your host. You can also request a process snapshot manually. Select in the upper-right corner of the section and select Request process snapshot now. Wait for a message confirming a successful snapshot trigger. Process snapshot data should appear after you reload the page within 90 seconds.
Additionally, for processes defined for Process availability monitoring, the snapshot shows how the processes behaved before they disappeared and if they reappeared within 10 minutes.
Enable process instance snapshots
You can enable process instance snapshots at a host or environment level.
- To enable it at the environment level, go to Settings, select Processes and containers > Process instance snapshots, and turn on Enable process instance snapshots.
- To define a host-level rule, go to a host overview page, select , go to Settings, select Process instance snapshots, and turn on Enable process instance snapshots.
- To define a host group level rule, go to the host group page at
https://your-environment/ui/settings/HOST_GROUP-NAME, select Process instance snapshots, and turn on Enable process instance snapshots.
On the same settings page, you can also lower the limit of processes reported in a single snapshot. The maximum/default setting is 100 processes.
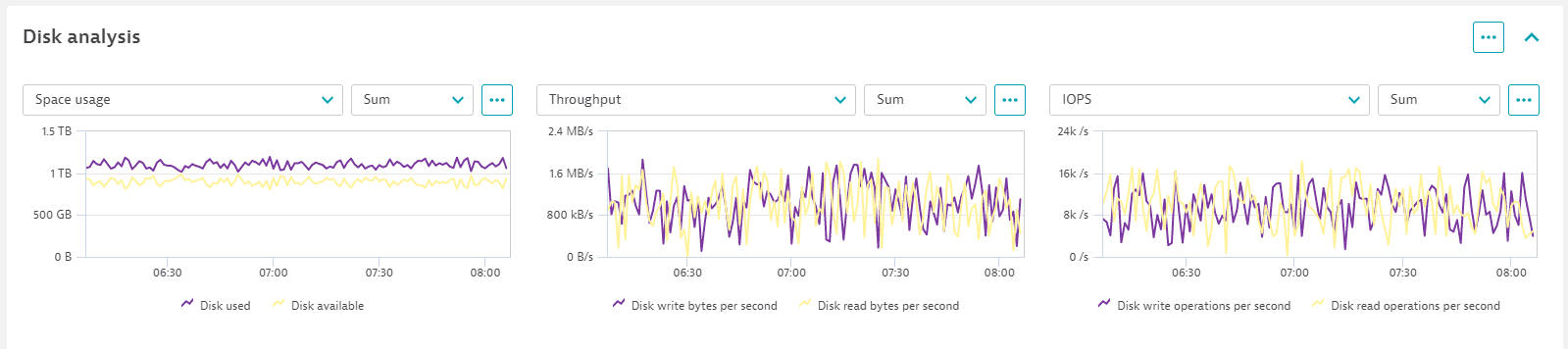
Disk analysis
To identify disk performance bottlenecks, go to the Disk analysis section , which displays all mount points for Linux systems and all volumes for Windows. At a glance, you can see the disk space usage and throughput metrics, in addition to other selected disk metrics, to allow rapid identification of any disk performance issues.
- On the host page, filter disks by disk name to focus on the selected disk
- Expand a disk entry to see details about the selected disk. Each disk instance displays separate detailed performance metrics, making it easy to spot any disk resource not performing optimally.
Each mount point (Linux) or volume (Windows) has its own performance metrics in addition to the combined metrics. This allows spotting a slow or erratic disk much easier. Alerts can be set for individual disks as for the combined charts.
Leverage these charts
Select in the upper-right corner of a chart to:
- Show in Data Explorer—Opens Data Explorer for the associated query, so you can view the associated query, explore the data more in-depth, adjust the chart settings, and pin the chart to your own dashboard.
- Pin to dashboard—Pins a copy of the selected chart to any classic dashboard you can edit. For example, if certain hosts are particularly important to your business, create a dashboard designated to monitoring only those hosts, and then pin charts from their host overview pages to that dashboard, all with almost no typing. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
Disk monitoring
Disk monitoring is a scheduled task that collects disk metrics from the agent. It starts automatically when OS agent detects a disk.
The available settings for disks are:
- Disk options: You can create exception rules to remove certain disks from the monitoring list and detect duplicate disks. For more details, see below or refer to Disk options.
- Disk anomaly detection rules: You can configure host anomaly detection, including problem and event thresholds, to meet your specific needs. For more details, refer to Host anomaly detection.
- Anomaly detection for infrastructure: Disk: You can use these settings to configure detection sensitivity, set alert thresholds, or disable alerting for disks. For more details, refer to Anomaly detection.
Limitations
-
Supported disk metrics
Infrastructure
Disk
Metric key Name and description Unit Aggregations Monitoring consumption builtin:host .disk .throughput .read Disk throughput read
File system read throughput in bits per second
bit /s autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .throughput .write Disk throughput write
File system write throughput in bits per second
bit /s autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .avail Disk available
Amount of free space available for user in file system. On Linux and AIX it is free space available for unprivileged user. It doesn't contain part of free space reserved for the root.
Byte autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .bytesRead Disk read bytes per second
Speed of read from file system in bytes per second
Byte /second autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .bytesWritten Disk write bytes per second
Speed of write to file system in bytes per second
Byte /second autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .free Disk available %
Percentage of free space available for user in file system. On Linux and AIX it is % of free space available for unprivileged user. It doesn't contain part of free space reserved for the root.
Percent (%) autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .inodesAvail Inodes available %
Percentage of free inodes available for unprivileged user in file system. Metric not available on Windows.
Percent (%) autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .inodesTotal Inodes total
Total amount of inodes available for unprivileged user in file system. Metric not available on Windows.
Count autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .queueLength Disk average queue length
Average number of read and write operations in disk queue
Count autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .readOps Disk read operations per second
Number of read operations from file system per second
Per second autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .readTime Disk read time
Average time of read from file system. It shows average disk latency during read.
Millisecond autoavgcountmaxminsum Host units builtin:host .disk .used Disk used
Amount of used space in file system
Byte autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .usedPct Disk used %
Percentage of used space in file system
Percent (%) autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .utilTime Disk utilization time
Percent of time spent on disk I/O operations
Percent (%) autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .writeOps Disk write operations per second
Number of write operations to file system per second
Per second autoavgmaxmin Host units builtin:host .disk .writeTime Disk write time
Average time of write to file system. It shows average disk latency during write.
Millisecond autoavgcountmaxminsum Host units -
OneAgent installer based deployment
- Network disks are supported for Linux hosts, AIX hosts, and since the release of OneAgent version 1.277, monitoring of network disks has been enabled also on Windows.
- SMB 1.0 is supported starting with OneAgent version 1.263.
-
OneAgent application-only deployment
-
Application-only OneAgents provide a reduced set of Disk I/O metrics, such as:
Disk read bytes per secondDisk write bytes per secondDisk read operations per secondWrite operations per second
-
Linux uses the file
/proc/diskstatsthat provides information about disk I/O activity on the system./proc/diskstatsdoes not provide any information about network mounts. -
Solaris doesn't provide any Disk I/O information.
-
AIX reports only the Disk I/O information about
Disk read bytes per secondandDisk write bytes per second.
-
Windows only The disk page shows only local disks with a letter and/or a mount point. For remote disks, the system recognizes and displays only the shares with CIFS protocol. For details, see https://dt-url.net/jw03uor.
Disable monitoring for specific disks
Set an exclusion filter to avoid problems with special mount points:
- Go to Settings > Preferences > Disk options.
- Select Add item to exclude the disk from the monitoring list.
- Provide your OS, disk path and file system type.
- Select Save changes.
Disk deduplication
Disk deduplication helps reduce redundancy in Network File System (NFS) mounts on a host. In some cases, the same NFS share may be mounted multiple times at different mount points or with different options. This can result in duplicate entries that affect monitoring accuracy. Disk deduplication identifies and removes these redundant mounts to ensure cleaner and more accurate disk data.
The system detects duplicate disks by comparing their IP addresses and available or used space. If two or more disks share the same IP and usage metrics, they are considered duplicates and are deduplicated accordingly.
You can turn disk deduplication on or off in Settings > Preferences > Disk options.
User impersonation on Windows
On Windows, OS agent impersonates a logged-on user to collect disk metrics from NFS shares. The agent uses the impersonated security context to query the NFS server for disk metrics.
Disk Edge alerting
OneAgent version 1.293+
Use Disk Edge to set up alerts for automatic detection of performance anomalies related to disk infrastructure.
Disk Edge provides automatic detection of performance anomalies related to disk infrastructure. Use these settings to tailor detection sensitivity to a specific disk's name and/or custom metadata. Defining custom properties can help with the post-processing of the event.
You can define policies on the host, host group, and environment levels.
- Go to Settings > Anomaly detection > Infrastructure > Disk Edge.
- Select Add policy.
- Define the policy.
- Policy name: The name under which your policy will be listed.
- Operating system: Detection rules can be specified for selected OS systems (if none are selected, settings will not be matched).
- Alerts: One rule can have up to seven alerts, one for each of the event types. See the table below.
- Disk name filters: Rules can be filtered by disk name.
- Host custom metadata conditions: Rules can be filtered by host custom metadata.
- Properties: Properties can be added to the sent event using the supported placeholders:
disk.all_mountpointsdisk.device_namedisk.mountpointdt.entity_hostdt.host_group.idhost.name
Event
Severity
Related OneAgent metric
Available disk space (%) below
Smaller value is more severe
DiskStats object field: availPercentage
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.free
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.free
Available disk space (MiB) below
Smaller value is more severe
DiskStats object field: avail
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.avail
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.avail
Available inodes (%) below
Smaller value is more severe
DiskStats object field: availINodesPercentag
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.inodes_avail
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.inodesAvail
Available inodes (number) below
Smaller value is more severe
Calculated from Diskstats: totalINodes * availINodesPercentage
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.inodes_avail * dt.host.disk.inodes_total
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.inodesTotal * builtin:host.disk.inodesAvail
Is read only file system
N/A
Disk object field: readOnly
Mintv2 metric: N/A
Timeseries: N/A
Read time (ms) exceeding
Larger value is more severe
Disk object field: readTime
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.read_time
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.readTime
Write time (ms) exceeding
Larger value is more severe
Disk object field: writeTime
Mintv2 metric: dt.host.disk.write_time
Timeseries: builtin:host.disk.writeTime
Infrastructure
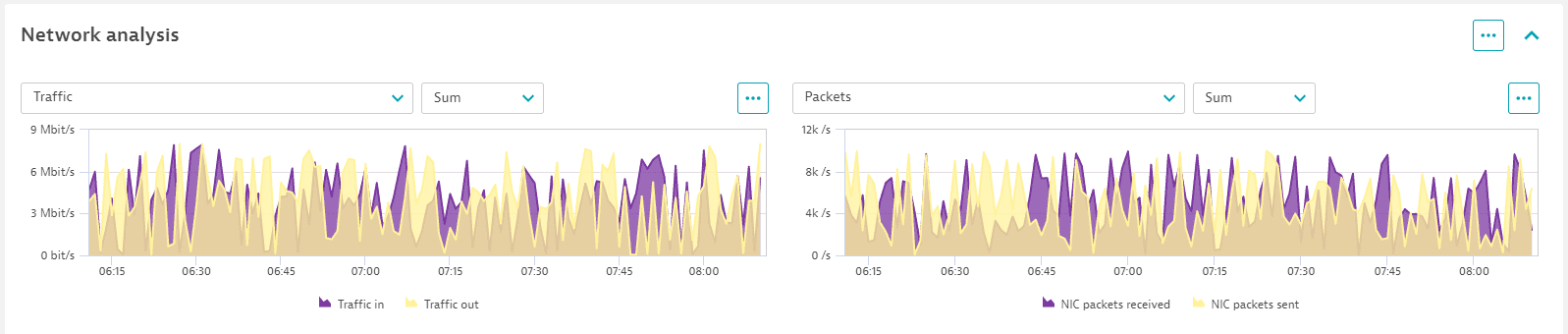
Network analysis
To spot network-related issues rapidly, go to the Network analysis section, which lists all network interfaces and combined metrics for all of them, in addition to individual metrics per network interface.
Use this section to:
- Identify packet loss, error packets, and other network issues
- Search for network interfaces by network name
- Identify network bottlenecks down to the specific adapter
Leverage these charts
Select in the upper-right corner of a chart to:
- Show in Data Explorer—Opens Data Explorer for the associated query, so you can view the associated query, explore the data more in-depth, adjust the chart settings, and pin the chart to your own dashboard.
- Pin to dashboard—Pins a copy of the selected chart to any classic dashboard you can edit. For example, if certain hosts are particularly important to your business, create a dashboard designated to monitoring only those hosts, and then pin charts from their host overview pages to that dashboard, all with almost no typing. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
Memory analysis
Use the Memory analysis section to analyze:
- Memory usage—total memory, memory used, and memory reclaimable
- Page faults—page faults per second
- Swap usage—swap total and swap used
Leverage these charts
Select in the upper-right corner of a chart to:
- Show in Data Explorer—Opens Data Explorer for the associated query, so you can view the associated query, explore the data more in-depth, adjust the chart settings, and pin the chart to your own dashboard.
- Pin to dashboard—Pins a copy of the selected chart to any classic dashboard you can edit. For example, if certain hosts are particularly important to your business, create a dashboard designated to monitoring only those hosts, and then pin charts from their host overview pages to that dashboard, all with almost no typing. For details, see Pin tiles to your dashboard.
Events
The events section displays recent host events that Davis AI has generated, with a clear timeline view to quickly identify critical events. The timeline view is interactive, filtering events around a specific moment, making it easier to isolate a particular event. In addition, different event types are color-coded for easier and faster identification and browsing.
- Show single card—Opens an Events card for the selected host.
Logs
The log viewer timeline is interactive, allowing a global timeline selection. Use it to identify issues around a specific log event and see how it relates to hosting performance or processes.
- The entire host page time selection will match what is selected in the log viewer. In this way, an error log can be easily compared to host performance metrics or process metrics around the time the log error took place. The same timeline selection will arrive on the event card.
- You can filter logs based on process group, status, log level, and other parameters, allowing searching, for example, just for error logs or for logs about a certain process.
Leverage this information
Select in the upper-right corner of the Logs section to:
- Go to Log Viewer—Opens the Log Viewer page filtered by the selected host.
- Create metric—Opens the Log metrics page with the Query value set to the selected host.
 Hosts Classic
Hosts Classic