Getting started with Kubernetes experience
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
- 4-min read
To take advantage of the new Kubernetes experience, you can either add new Kubernetes clusters or enable existing Kubernetes clusters for the new experience.
Add new clusters
Start monitoring Kubernetes clusters with Dynatrace.
Enable existing clusters
Enable existing clusters that are already monitored with Kubernetes Classic for the new Kubernetes experience.
Prerequisites
- Dynatrace SaaS environment powered by Grail and AppEngine
- DPS license that includes the Kubernetes Platform Monitoring capability
- Sufficient permissions to use
 Kubernetes within your Dynatrace environment
Kubernetes within your Dynatrace environment - ActiveGate version 1.279+
FAQ
What if I don't have Dynatrace Platform Subscription (DPS) or I'm not on the SaaS platform powered by Grail?
You can’t access the new Kubernetes experience. You can continue to use Kubernetes Classic pages. We continue to support and innovate the existing product, but we encourage you to switch to the new platform to benefit from the latest platform innovations.
What if I do have DPS but miss the Kubernetes Platform Monitoring capability?
If you are already using DPS, reach out to your Dynatrace representative to add pricing for Kubernetes Platform Monitoring to your rate card. Customers who sign their DPS contract after February 2024 will have this capability included by default on their rate card.
Can I still use the Kubernetes classic pages after I activate clusters for the  Kubernetes?
Kubernetes?
Until further notice, the existing Kubernetes pages (Kubernetes Classic) will still be available and show the data for your Kubernetes clusters.
Do I need to change my rollout with Dynatrace Operator to use the  Kubernetes?
Kubernetes?
 Kubernetes doesn't require mandatory changes to the rollout. The minimum requirement is an ActiveGate version 1.279 or higher configured with Kubernetes Platform Monitoring ActiveGate capability. If you use Dynatrace Operator with default configurations (no specific ActiveGate image/tag), the ActiveGate is automatically upgraded, so that you don't need to take action.
Kubernetes doesn't require mandatory changes to the rollout. The minimum requirement is an ActiveGate version 1.279 or higher configured with Kubernetes Platform Monitoring ActiveGate capability. If you use Dynatrace Operator with default configurations (no specific ActiveGate image/tag), the ActiveGate is automatically upgraded, so that you don't need to take action.
You can use the onboarding screen in  Kubernetes to onboard new clusters. It will always use the latest Dynatrace Operator.
Kubernetes to onboard new clusters. It will always use the latest Dynatrace Operator.
Can I use the new experience for any Kubernetes environment?
 Kubernetes provides valuable insights for all Kubernetes distibutions supported by Dynatrace. There is no difference in supported distributions between
Kubernetes provides valuable insights for all Kubernetes distibutions supported by Dynatrace. There is no difference in supported distributions between  Kubernetes and Kubernetes Classic.
Kubernetes and Kubernetes Classic.  Kubernetes is optimized for customers with Kubernetes environments ranging up to 100.000 pods.
Kubernetes is optimized for customers with Kubernetes environments ranging up to 100.000 pods.
What permissions does a user need to access the  Kubernetes?
Kubernetes?
Users need a set of permissions to read and access relevant data from Grail to use  Kubernetes. You can find more details about required permissions in the reference section.
Kubernetes. You can find more details about required permissions in the reference section.
What is the impact on my DPS consumption if I monitor my Kubernetes clusters with the new experience?
-
Clusters monitored with Kubernetes Platform Monitoring will consume your DPS commit based on the Kubernetes Platform Monitoring price (cost per pod-hour) specified on your rate card.
-
Clusters monitored with Kubernetes Platform Monitoring and Application observability will consume your DPS commit based on the Kubernetes Platform Monitoring price (cost per pod-hour) and container-based Full-Stack price (cost per GiB-hour of used container memory) specified on your rate card.
-
Clusters monitored with Kubernetes Platform Monitoring and Full-Stack observability will consume your DPS commit based on the host-based Full-Stack price (cost per GiB-hour of host memory) specified on your rate card.
- Pods running on Full-Stack monitored Kubernetes hosts do not consume DPS Kubernetes Platform Monitoring.
- Pods that aren't running on Full-Stack monitored Kubernetes hosts (for example, pods stuck in Pending state) will still consume DPS Kubernetes Platform Monitoring.
- OneAgent version 1.301+ is required for including Kubernetes Platform Monitoring in the host-based Full-Stack package.
-
If you deactivate the new Kubernetes experience in the settings of your cluster, consumption of DPS Kubernetes Platform Monitoring will stop.
What are top-level workloads?
A top-level workload is the topmost controlling owner of a Pod. Possible top-level workload types are: Deployment, ReplicaSet, StatefulSet, DaemonSet, Job, CronJob, ReplicationController, DeploymentConfig. You can find a list of those workloads in the Top-level workloads menu entry.
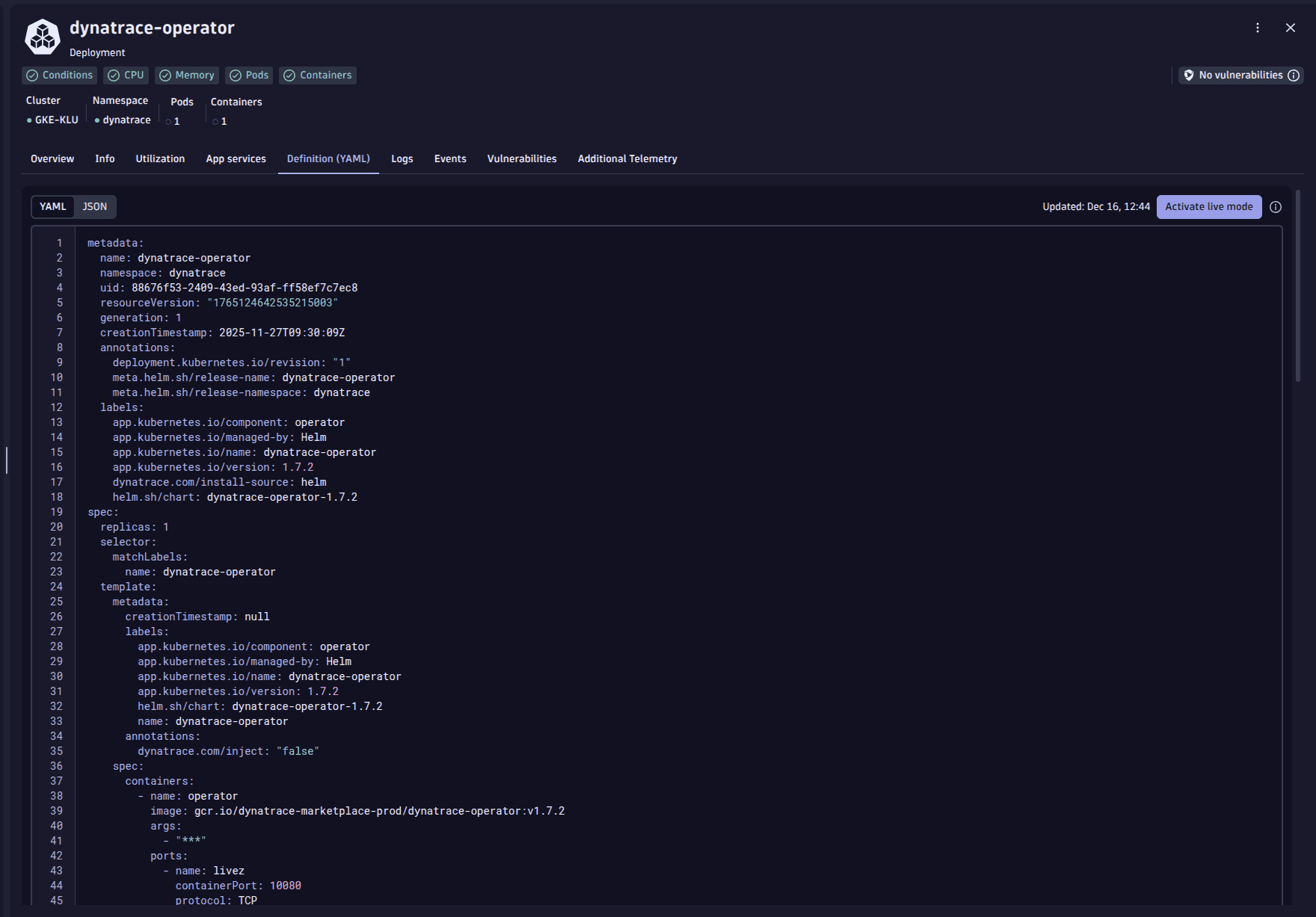
What do I see in the Definition (YAML) view?
ActiveGate version 1.327+
When you first open this view you see a reduced version of the original YAML code as available from the Kubernetes API. When you activate the live mode, you get the full YAML code directly streamed from the Kubernetes API. The reduced version of the YAML code is also available in .json format via DQL in the k8s.object field of the respective Smartscape node.
Labels and annotation are not part of this field, but are stored as tags.
The YAML code is limited to a size of 32 kB. Dynatrace automatically strips less important fields, for example, /metadata/managedFields and kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration annotation.
How can I unlock ConfigMaps and Secrets?
To gain visibility into ConfigMaps and Secrets, you need to grant additional permissions to ActiveGate, allowing it to access these objects. By default, this functionality is disabled because these objects might contain sensitive data. For Secrets, ActiveGate automatically applies data masking.
-
For new clusters, deployed with Dynatrace Operator version 1.8.0+, these permissions are automatically set when checking Monitor potentially sensitive data on the Add cluster page.
-
For existing cluster, deployed with Dynatrace Operator version 1.7.0 and earlier, you need to manually grant these permissions by applying the following YAML with
kubectl.Apply the following YAML with
kubectlto enable these objects:apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata:name: dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoring-sensitiveroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: ClusterRolename: dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoring-sensitivesubjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoringnamespace: dynatrace---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:name: dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoring-sensitivelabels:rbac.dynatrace.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"rules:- apiGroups:- ""resources:- configmaps- secretsverbs:- list- watch- get
How can I add permissions to ClusterRoles?
Starting with Dynatrace Operator version 1.8.0+ a label based aggregationRule is used to extend default ClusterRole permissions for Kubernetes monitoring. If you want to add new permissions, create a new ClusterRole (for example, dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoring-custom) with the correct label:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:labels:rbac.dynatrace.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"name: dynatrace-kubernetes-monitoring-customrules:- apiGroups:- example.api.groupresources:- custom-resource-exampleverbs:- list- watch- get
How is data masked on the ActiveGate?
No sensitive data is forwarded to the Dynatrace Cluster, as masking happens directly on the ActiveGate side.
The ActiveGate masks:
- Secret values (keys remain visible).
- Environment variable values (names remain visible).
- Container
commandandargsvalues.
Starting with ActiveGate version 1.335, only sensitive values are masked for environment variable values and container command and args values.
Sensitive data is detected based on heuristics, for example, if the name of the environment variable contains password.
Secret values are still fully masked.
Why do I see two Explorer tabs inside the  Kubernetes?
Kubernetes?
Some environments might have two Explorer tabs inside  Kubernetes. This happens for environments which were created before the transition to Dynatrace's new storage layer, Smartscape on Grail. The second Explorer (Classic) is deprecated and will be shown during the transition phase until June, 2026.
Kubernetes. This happens for environments which were created before the transition to Dynatrace's new storage layer, Smartscape on Grail. The second Explorer (Classic) is deprecated and will be shown during the transition phase until June, 2026.