Leverage enhanced endpoints for SDv1
- Latest Dynatrace
- How-to guide
- 7-min read
- Published Jan 19, 2026
With the Enhanced endpoints for Service Detection v1 (SDv1) feature, you can get full endpoint visibility for SDv1 services. When this feature is turned on, all endpoints are shown in  Services without requiring you to configure key requests. This is consistent with the behavior already in place for SDv2 services.
Services without requiring you to configure key requests. This is consistent with the behavior already in place for SDv2 services.
The Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature is turned on by default for the environments created in Dynatrace version 1.330+. For existing environments, the feature is available in Dynatrace version 1.333+.
No endpoints are created for external services and for the following SDv1 service types: Background activity services, Queue listener services, and Key value store.
Benefits
- Complete endpoint visibility in
 Services: Gain a complete list of endpoints for SDv1 services in
Services: Gain a complete list of endpoints for SDv1 services in  Services.
Services.
If you don't enable the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature, the Endpoints section in
 Services either remains empty or only shows key requests.
Services either remains empty or only shows key requests. - Improved service insights: The list of endpoints enhances visibility into the service's behavior, enabling quick identification and resolution of issues.
- Dedicated metrics for endpoints: Detected endpoints feature dedicated metrics, which you can add to dashboards and analyze for long-term endpoint history.
Endpoint metrics
When the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature is turned on, Dynatrace starts collecting metrics for all detected endpoints of an SDv1 service in Grail.
The following metrics are collected for each endpoint:
- Failure rate
- Response time
- Throughput
These endpoint metrics are available not only in  Services but also in other Dynatrace apps, such as
Services but also in other Dynatrace apps, such as  Notebooks or
Notebooks or  Dashboards.
Dashboards.
Enable enhanced endpoints for SDv1
You can activate the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature for the entire environment or for a specific host group, Kubernetes namespace, and cluster.
Environment
- Go to
 Settings > Process and contextualize > Services.
Settings > Process and contextualize > Services. - Under Service detection v1, select Enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
- Turn on Enable enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
Host group
-
Go to
 Deployment Status > OneAgents.
Deployment Status > OneAgents. -
On the OneAgent deployment page, turn off Show new OneAgent deployments.
-
In the Filter by field, enter Host group, and then select the host group you want to configure from the dropdown list.
The host list is now filtered by the selected host group. Each listed host has a Host group:
<group name>link, where<group name>is the name of the host group that you want to configure.The Host group property is not displayed when the selected host doesn't belong to any host group.
-
Select the host group name in any row.
As you have filtered by host group, all displayed hosts go to the same host group.
- Close the overlay with the host group settings.
- Go to Process and contextualize > Services > Enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
- Turn on Enable enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
Kubernetes namespace or cluster
- Go to
 Kubernetes.
Kubernetes. - Select the required namespace or cluster.
- In the upper-right corner of the namespace or cluster details pane, select (Actions menu) > Service detection settings.
- Go to Process and contextualize > Services > Enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
- Turn on Enable enhanced endpoints for SDv1.
Enabling the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature changes some request names and their associated endpoint names. For this reason, your existing API metric queries, dashboards, and configured alerts for the changed endpoints might be impacted, so you should reconfigure them. See Changes to endpoint names for the details.
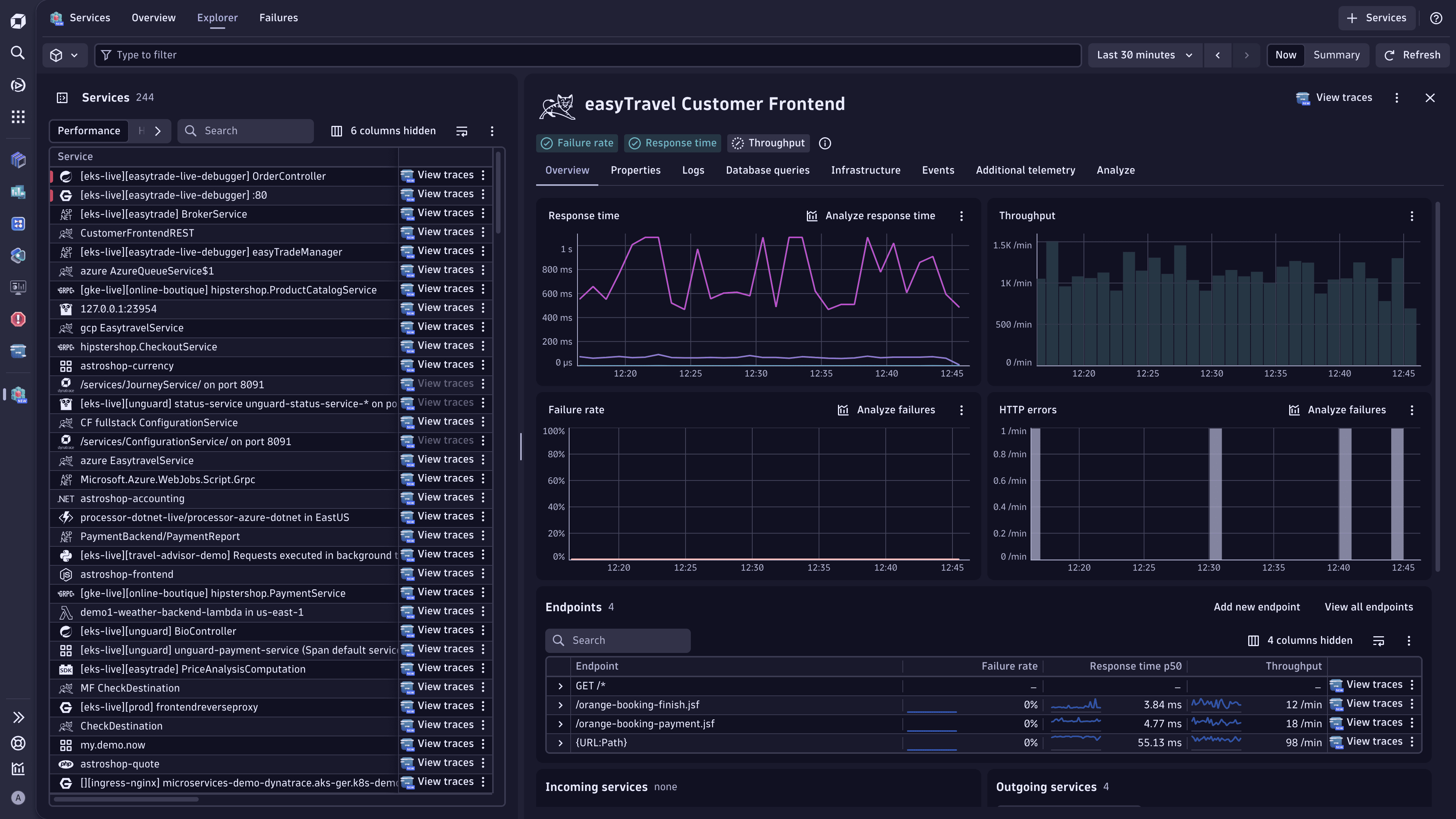
View service endpoints
Service endpoints as well as the related metrics are displayed in  Services, in the Endpoints section.
Services, in the Endpoints section.
- Go to
 Services > Explorer.
Services > Explorer. - Find and select the service for which you want to explore the endpoints.
- On the Overview tab, scroll down to the Endpoints section.
From there, you can view the service endpoints, check the related endpoint metrics, view traces for each endpoint, and more. Select (Actions menu) for the endpoint to view the available options.
Changes to endpoint names
Enabling the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature changes some request names and their associated endpoint names. Check the flowchart and textual description below for the details.
For all service types, the already existing key requests and request naming rules continue to apply.
If you have set up key requests, the associated endpoints have the same names as their key requests. If you have configured request naming rules, they are also applied to the related endpoint names.
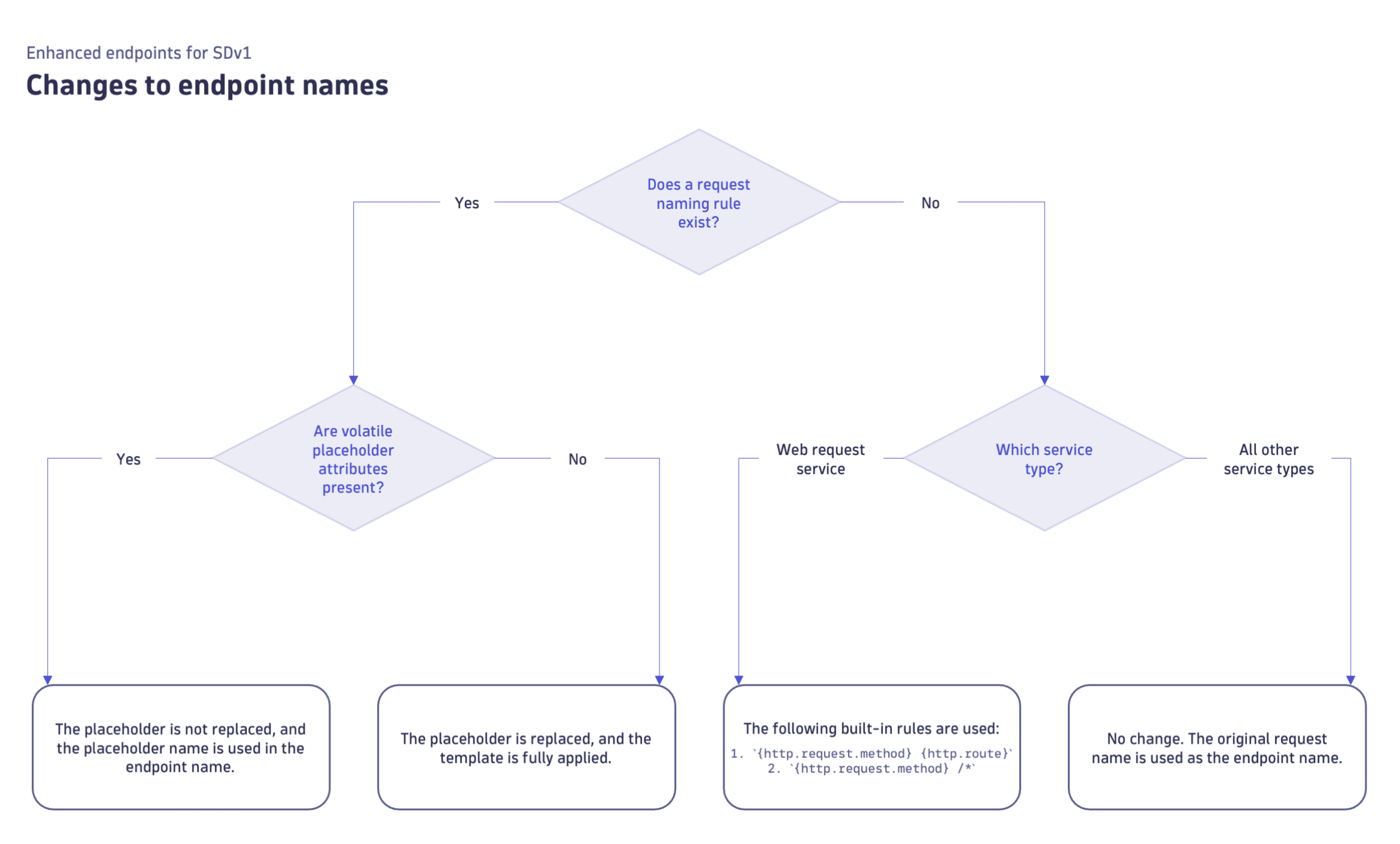
When the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature is on, some endpoint names for web request services and other service types are changed. This depends on whether there's an associated request naming rule and whether volatile placeholder attributes are used in these rules.
Endpoint names for web request services
Endpoint names for all other service types
No request naming rule
The following built-in rules are used for the endpoint names:1
{http.request.method} {http.route}{http.request.method} /*
No change. The original request name is kept as the endpoint name.
For example, if the spans have no {http.route}, the endpoint name is GET /*.
For example, the {HTTP-Method} - {Request:IsKeyRequest} - user authentication endpoint template results in the GET - yes - user authentication endpoint endpoint name. Note that both {HTTP-Method} and {Request:IsKeyRequest} are replaced with their corresponding values (that is, GET and yes), as these are non-volatile placeholder attributes.
For example, the {HTTP-Method} - {URL} - user authentication endpoint template results in the GET - {URL} - user authentication endpoint endpoint name. Note that {HTTP-Method} (non-volatile placeholder attribute) is replaced with GET , while {URL} (volatile placeholder attribute) is not replaced and is used as is.
You can modify endpoint names by creating custom naming rules.
Volatile placeholder attributes
The volatile placeholder attributes are as follows:
{OneAgentAttribute:}excepthttp.route{Relative-URL}{URL:Path}{URL:Query}{URL}- Customer-defined patterns based on one of the above-stated patterns
Required actions
As some request names and their associated endpoint names change after you enable the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature, your existing API metric queries, dashboards, and configured alerts for the changed endpoints might be impacted. For this reason, you should reconfigure the affected entities.
Static resource requests
Static resource requests include Image, Binary, CSS, and JavaScript.
When the Enhanced endpoints for SDv1 feature is turned on, all static resource requests are unmuted and grouped into a single Static resources endpoint that has the same metrics as other regular endpoints.
However, you can mute your static resource requests.
Whether the Static resources endpoint is muted or not, you can always go to 
Mute static resource requests
To mute static resource requests, follow the steps described in Mute monitoring of service requests.
After you mute your static resource requests, the Static resources endpoint is not displayed in the endpoint list in  Services, and these requests don't count toward the overall service metrics.
Services, and these requests don't count toward the overall service metrics.
Manage resource request detection
You can add or edit filename extensions that count towards the Static resources endpoint. For details, see Configure resource request detection.
Your existing configuration for resource request detection is still applicable, so if you have already added additional filename extensions, the corresponding requests should also become a part of the Static resources endpoint.
 Services
Services