Processing in OpenPipeline
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
- 4-min read
Dynatrace OpenPipeline can reshape incoming data for better understanding, processing, and analysis. OpenPipeline processing is based on rules that you create and offers a flexible way of extracting value from raw records.
Key terms
- Ingest sources
Source of ingestion for a configuration scope, collecting data from the provider into Dynatrace Platform, for example, API endpoints or OneAgent.
- Routing
Assignation of data to a pipeline, based either on matching conditions (dynamic) or direct assignation (static).
Pipeline
Once data is ingested and routed, OpenPipeline processing occurs in pipelines. Each pipeline contains a set of processing instructions (processors) that are executed in an ordered sequence of stages and define how Dynatrace should structure, separate, and store your data. After a record is processed, it's sent to storage and is available for further analysis.
Processing is based on available records and doesn't take into account record enrichment from external services.
Types
Pipelines can be of a custom or built-in type.
Custom pipeline
You can create new custom pipelines and modify them to group processing and extraction according to the relevant technology or team. By adding custom pipelines per team, you can manage them via owner-based access control.
Built-in pipeline
Built-in pipelines are provided out of the box. They are essential for OpenPipeline operation and generally cannot be modified within OpenPipeline. Access to these pipelines is intentionally restricted to preserve their configuration.
Default pipeline
The default pipeline is a built-in pipeline that processes unassigned incoming data for storage. It's unique to the configuration scope and ensures that records are assigned to the default bucket and not unintentionally dropped. It's available to all users in view-only mode. It's not available for log and business event configuration scopes where the Classic pipeline is available.
Route as much data as feasible to custom pipelines using explicit matching conditions; limit the use of the default pipeline to monitoring unassigned incoming data.
Classic pipeline
The Classic pipeline is a built-in pipeline specific to the log and business event configuration scopes. It represents and serves as an entry point to the rules you set in Settings Classic for log or business event processing via the classic pipeline.
If you use log processing via the classic pipeline, migrate your rules to OpenPipeline custom pipelines.
Processing via classic pipeline vs OpenPipeline
Processing via OpenPipeline offers higher limits and flexibility. The following table summarizes the key technical differences of processing logs via the log classic pipeline and OpenPipeline.
| Technical point | Log classic pipeline | OpenPipeline |
|---|---|---|
| Data type support | String | String, Number, and Boolean |
| Content field limit | 512 kB | 10 MB |
| Field name case sensitivity | Case-insensitive | Case-sensitive1 |
| Connect log data to traces | Built-in rules | Automatic2 |
| Technology parsers | Built-in rules | Preset bundles with broader technology support |
| Query language | LQL, DQL | DQL3 |
| Metric dimension naming | No | Yes |
Metric-key log prefix | Mandatory | Optional |
If logs are ingested via Log Monitoring API v2 - POST ingest logs, the field names are automatically lowercased after data is routed to the Classic pipeline.
The enrichment is done automatically, without requiring any user interaction.
See also Conversion to DQL for Logs.
Use cases
- Prepare, transform, and store data in Grail.
- Grant access to specific records.
Stage
A stage is a phase in a pipeline sequence that focuses on a task, such as masking, filtering, processing, or extraction. Stages contain a predefined list of configurable processors, which define the task of the stage.
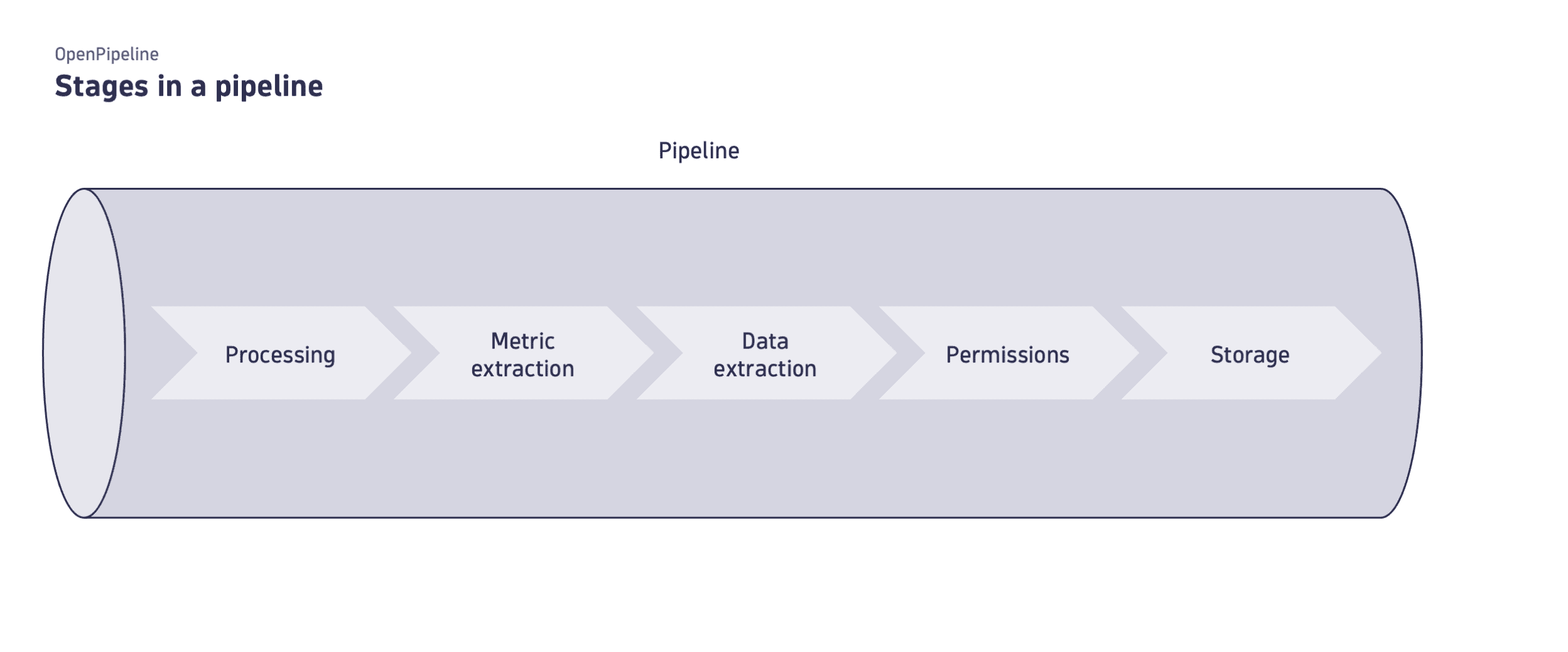
The following table is a comprehensive list of stages, ordered in the pipeline sequence of execution, specifying which processors are available and executed for each stage, for the supported configuration scopes.
Specific fields are excluded from matching and processing or restricted. To learn more, see Limits specific to fields.
The data remains in its original, structured form. This is important for detailed analysis and troubleshooting, as it ensures that no information is lost or altered.
Extracted metrics are sent to Grail only, except for the security events (new) and span configuration scopes.
Processor
A processor is a pre-formatted processing instruction that focuses either on modifying (for example, by renaming or adding a new field) or extracting data (for example, by creating an event from a log line or extracting metrics).
While the processor format is predefined, it contains a configurable matcher and processing definition.
- The matcher defines the target of a processor via a DQL query. It narrows down the available data to the specific set you want to process.
- The processing definition instructs Dynatrace on how to transform or modify the data filtered by the matcher.
The following table lists alphabetically all available processors in a pipeline.