Data flow in OpenPipeline
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
- 6-min read
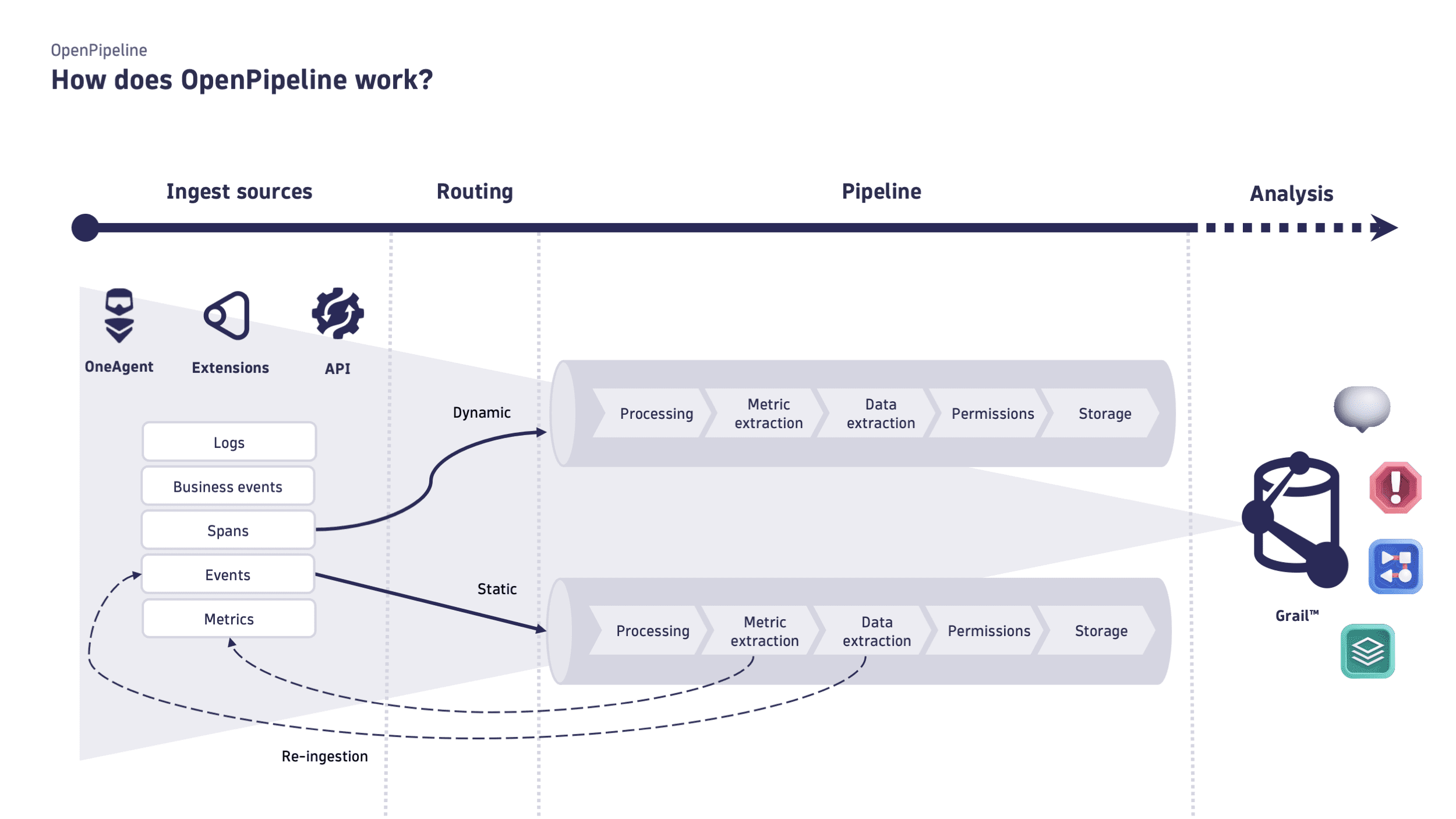
With OpenPipeline, you can ingest data in the Dynatrace platform from a wide variety of formats and providers, through ingest sources. Data is then routed to pipelines for processing, and stored in Grail buckets.
Key terms
- Pipeline
Collection of processing instructions to structure, separate, and store data.
Configuration scope
Configuration scopes, such as logs and events, provide observability insights into the health, performance, and behavior of your system enabling teams to detect, diagnose, and resolve problems. Each configuration scope offers a different perspective because of its unique characteristics.
OpenPipeline provides a unified solution to configure ingestion and processing while ensuring flexibility based on the configuration scope specifics.
Availability
The following table lists configuration scopes, summarizing availability in OpenPipeline.
| Configuration scope | Availability |
|---|---|
| Business events | |
| Events (generic events) | |
| Events - Davis events | |
| Events - Davis problems | |
| Events - SDLC events | |
| Events - Security events (legacy) | Will deprecate |
| Logs | |
| Metrics | |
| Security events (new) | |
| Spans | |
| System events | Limited support1 |
| Topology | Planned |
| User events | |
| User sessions |
System events supported by OpenPipeline are limited to: App Lifecycle Notifications (event.kind == "AUDIT_EVENT" AND event.provider == "APP_REGISTRY"), Workflow Execution events (event.kind == "WORKFLOW_EVENT" AND event.provider == "AUTOMATION_ENGINE"), and ECC self-monitoring events (event.kind == "EXTENSIONS_EVENT").
Ingest sources
Data reaches the Dynatrace platform via different ingestion sources, such as API endpoints, OneAgent, and extensions, which collect data from data providers. In OpenPipeline, they are defined by a name and a path (dt.openpipeline.source).
Once the records reach your Dynatrace SaaS environment via ingest sources, you can route it to a pipeline.
To learn the ingest sources available in OpenPipeline, see Ingest sources in OpenPipeline.
Types
Ingest sources can be of a built-in, ready-made, or custom type.
| Technical point | Built‑in ingest source | Ready‑made ingest source | Custom ingest source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | OpenPipeline | Extension | User or user group |
| Permissions | settings:read | settings:read | settings:read, settings:write |
| Access type | View‑only for all users | View‑only for all users | Owner‑based access control |
| Configuration scope availability | All | Events, Logs, Metrics | Events (excluding Davis problems and Davis events) |
| Routing option | Dynamic | Dynamic, static | Dynamic, static |
| Pre‑processing | Not configurable | Not configurable | Configurable |
Built-in ingest source
Built‑in ingest sources represent the primary data entry points provided by Dynatrace. They are owned by OpenPipeline, allowing all users with settings:read permissions to view them, but not modify or delete them. This type is always present in OpenPipeline tables, it's available for all configuration scopes, and only supports dynamic routing.
Ready-made ingest source
A ready‑made ingest source is automatically created when an extension is installed. In addition to the ingest source, the installation may also generate a pipeline and an active route. Ready‑made ingest sources are owned by the installing extension and are view‑only for all users with settings:read permissions. They remain unchanged through extension reactivations and are removed only when the extension is uninstalled. This type is available for the event, log, and metric configuration scopes. Typically, a ready-made ingest source routes records to the generated pipeline via static routing, however dynamic routing is supported as well.
Custom ingest source
Custom ingest sources are created by users, with ownership automatically assigned to them. Owners have view and edit access and can grant view access to other users or user groups, according to the user permissions. Custom ingest sources are available only within event configuration scopes, excluding Davis problems and Davis events. They support pre‑processing and allow both dynamic and static routing.
Use cases
- Configure multiple pipelines for the same configuration scope, adopting processing instructions specific to the ingest source.
Pre-processing
Optional data processing that occurs after ingestion and before routing. By setting pre-processing, you can transform raw data into structured formats as soon as it reaches your Dynatrace SaaS environment. Pre-processed data is then routed to a pipeline and is available for further processing before storage. Note that pre-processing is available only for custom ingest sources.
Use cases
- Apply a unified structure to different providers' data formats.
Best practices
Set up pre-processing to avoid creating complex matching conditions based on provider-specific data formats. This will help you streamline maintenance for routing and processing, for example, when you start ingesting data from a new provider.
Routing
After data is ingested (and optionally pre-processed), it's routed to pipelines. The route order is relevant—the position in the list establishes the order of execution. If no route matches the record, the record is routed via the Default route.
Routing is defined according to the following:
-
Configuration scope: Pipelines are specific to a configuration scope. Different configuration scopes are routed to different pipelines.
-
Ingest source: You can configure routing for each ingest source. Multiple ingest sources of the same configuration scope can be routed to the same pipeline.
-
Routing option
-
Dynamic routing: Data is routed based on a matching condition. The matching condition is a DQL query that defines the data set you want to route.
-
Static routing: Data is routed to a specific pipeline, which remains fixed unless manually updated. Static routing is available only for custom ingest sources.
If a record matches a different condition but you've already configured static routing for its custom ingest source, the match is skipped and data is routed directly to the pipeline you specified.
-
Use cases
- Route data of an ingest source to a dedicated pipeline.
Best practices
- Route as much data as feasible to custom pipelines using explicit matching conditions.
- When multiple routing options are available, choose according to the data set dimension. For example, large data sets benefit more from dynamic routing.
Processing
OpenPipeline processing occurs in pipelines containing instructions on how to structure, separate, and store your data. To learn more, see Processing in OpenPipeline.
Storage
Dynatrace Grail database provides a single unified storage solution for all your configuration scopes. OpenPipeline target storage are Grail buckets. You can leverage built-in buckets and, if available for the configuration scope, create new buckets with custom retention periods. Each bucket is assigned to a DQL database table. Assign permissions to user groups or single users to provide them with access to specific buckets and tables.
By default, OpenPipeline routes data into a built-in pipeline with target storage built-in Grail bucket of the configuration scope. You can configure storage assignment
- For a custom ingest source, by directly defining its targeted storage.
- For a pipeline, based on processing matching conditions.
Storage and retention for system events is not configurable.