Version detection strategies for deep-monitored processes
- Classic
- How-to guide
- 3-min read
Dynatrace supports multiple strategies to detect and ingest release version information. These strategies help enrich observability data with release context, enabling better traceability, filtering, and analysis. Version detection can be influenced by environment variables, Kubernetes labels, event ingestion, and resource attributes from OpenTelemetry.
Environment variables
Use environment variables to provide release metadata directly to Dynatrace OneAgent.
DT_RELEASE_VERSIONfor VersionDT_RELEASE_STAGEfor StageDT_RELEASE_PRODUCTfor ProductDT_RELEASE_BUILD_VERSIONfor Build version
Example
- Set an environment variable, making sure to replace
<YOUR_VERSION>with your version information.
$env:DT_RELEASE_VERSION='<YOUR_VERSION>'
- Start the process. After a short time, the version of this process appears in Dynatrace.
Kubernetes labels
We recommend that you propagate Kubernetes labels to environment variables in the deployment configuration.
Example
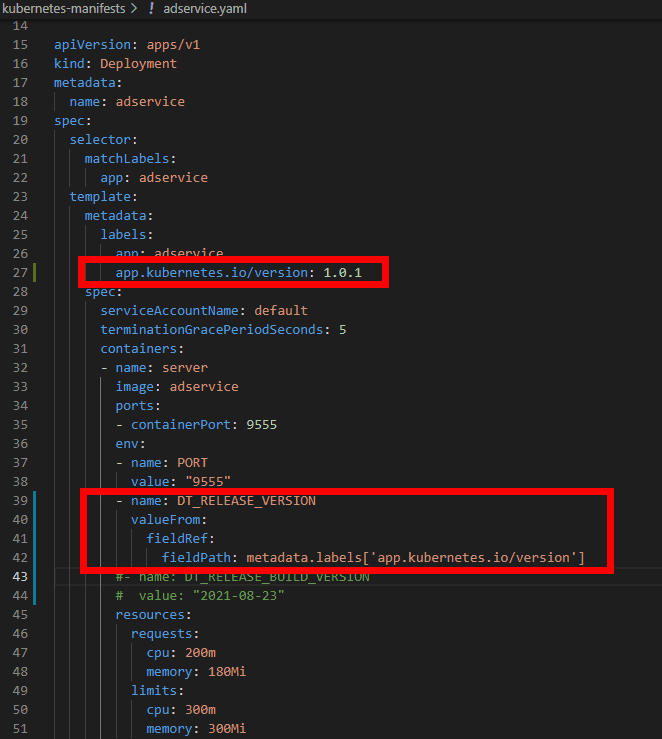
Starting with Dynatrace Operator version 0.10.0+, you can configure release label propagation by setting the feature.dynatrace.com/label-version-detection=true feature flag in the DynaKube custom resource. For details, see Configure build label propagation.
You can use:
- Kubernetes pod labels to provide metadata for:
- Stage information (label:
dynatrace-release-stage)
- Stage information (label:
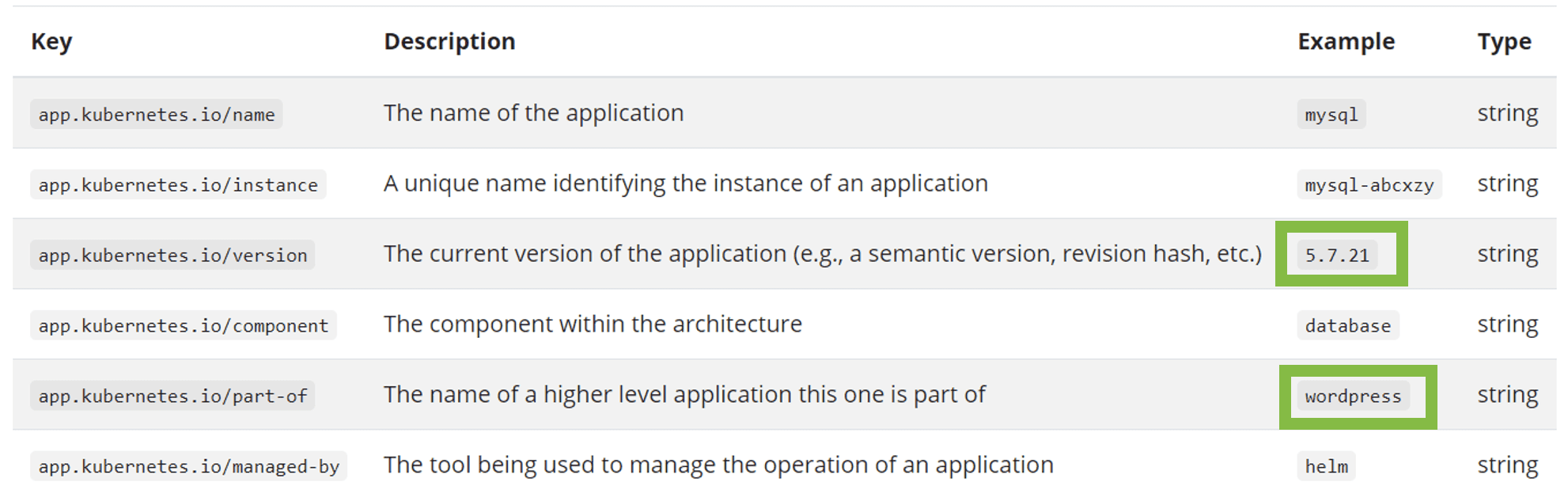
- Kubernetes recommended labels for deployed pods to provide metadata for:
- Versions information (label:
app.kubernetes.io/version) - A related product (label:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of) Optional
- Versions information (label:
Be sure to use only pod labels, not the Kubernetes workload labels.
Kubernetes recommended labels mapped to release metadata:
Dynatrace OneAgent with viewer permissions on the namespace can automatically detect labels attached to the Kubernetes pods.
- Version and Product show up in the release inventory.
- Kubernetes namespaces or configured Dynatrace host-group names show up as Stages in the release inventory.
If you need to update version information, update the deployment configuration to include the updated label and redeploy the pods. This ensures that DT_RELEASE_VERSION environment variable is correctly set when the pod starts. For more information, see Configure build label propagation.
The command below will not propagate the updated label to the DT_RELEASE_VERSION environment variable used by OneAgent.
kubectl label --overwrite pod yourPodId -n yourNamespace app.kubernetes.io/version=42
Events ingestion
Use the Dynatrace Events API to send custom deployment events with release metadata.
- Version information sent via events can't be used to filter traces or metrics.
Always set environment variables to reflect the currently deployed version to ensure accurate filtering and analysis.
Ensure that environment variables always indicate the currently deployed version.
- Because processes are matched using tags, a separate event is emitted for each process. As a result, any workflow subscribed to these events may be triggered multiple times. To avoid redundant executions, we recommend sending a dedicated event to the workflow instead.
The example JSON below shows how to send custom deployment events to the event ingestion API.
For a release to be discovered, the following requirements must be fulfilled:
eventTypeis set toCUSTOM_DEPLOYMENTentitySelectoris mandatory and should point to a process group instance or a list of process group instancesdt.event.deployment.versionis mandatory
Example
{"eventType": "CUSTOM_DEPLOYMENT","title": "Easytravel 1.1","entitySelector": "type(PROCESS_GROUP_INSTANCE),tag(easytravel)","properties": {"dt.event.deployment.name":"Easytravel 1.1","dt.event.deployment.version": "1.1","dt.event.deployment.release_stage": "production" ,"dt.event.deployment.release_product": "frontend","dt.event.deployment.release_build_version": "123","approver": "Jason Miller","dt.event.deployment.ci_back_link": "https://pipelines/easytravel/123","gitcommit": "e5a6baac7eb","change-request": "CR-42","dt.event.deployment.remediation_action_link": "https://url.com","dt.event.is_rootcause_relevant": true}}
OpenTelemetry Resource Attributes
Dynatrace supports ingesting release metadata via OpenTelemetry resource attributes, allowing you to propagate version information through telemetry data.
To use this method, define the OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES environment variable in your application and set key-value pairs that represent release metadata.
Refer to the Semantic Dictionary for the complete list of supported attributes, called deployment attributes.
While Dynatrace enriches telemetry data with these attributes, they're not propagated to process group instance entities.
As a result, releases defined via OpenTelemetry resource attributes won't appear in the release inventory.
Example
-
Create or extend the
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTESenvironment variable with release metadata.$env:OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=deployment.release_version='<YOUR_VERSION>',deployment.release_stage='<YOUR_STAGE_NAME>' -
Once the environment variable is set, Dynatrace automatically detects the resource attributes and enriches traces and logs with the provided release metadata.
 Releases
Releases