Azure Logs
- Latest Dynatrace
- How-to guide
- 17-min read
DDU pricing applies to cloud Log Monitoring. See DDUs for Log Monitoring for details.
Azure log forwarding allows you to stream Azure logs from Azure Event Hubs into Dynatrace logs via an Azure Function App instance. It supports Azure resource logs, activity logs, and Entra ID sign-in logs.
Resources to be deployed
Azure log forwarding is performed directly through Cluster API. If you don't want to use direct ingest through the Cluster API, you have to use an existing ActiveGate for log ingestion.
Deployment of Azure log forwarder results in creating the following resources:
- Storage account (
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts) - Storage Account Blob Service (
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices) - Azure App Service plan (
Microsoft.Web/serverfarms) - Azure Function App (
Microsoft.Web/sites)
Azure log forwarder uses Linux based Azure function by default. Windows based function is not supported.
For details about the resources created, see the Azure Resource Manager file on GitHub
Limitations
Logs older than 24 hours are rejected (considered too old by the Dynatrace log ingest endpoint), so we recommend that you don't set a retention time of more than 24 hours for Azure Event Hubs.
The Azure log forwarder supports a maximum 70 MB per minute (~4 GB per hour) in the default configuration. The throughput is measured with Event Hubs metric Outgoing Bytes of the Event Hubs instance attached to the function. See Scaling guide for scaling instructions.
Prerequisites
See below the list of requirements for setting up Azure log forwarding. Some are needed before you start deployment, others during the deployment process.
Dynatrace
If you're using an earlier version of Dynatrace, see Alternative deployments for instructions.
- Dynatrace version 1.217+
- Create an API token and enable the Ingest logs permission. The API token applies to both versions.
Azure
-
In each Azure location from where you want to pull logs Create a resource group & Set up an Azure Event Hubs instance.
To be able to send logs,
- The Event Hubs instances and the resource group in which the deployment will run need to be in the same region.
- make sure that in Event Hubs Namespace > Public access > Public network access, the Disabled option button is NOT selected. Otherwise, the logs won't be sent to Dynatrace.
-
Create an authorization rule with the listen permission for the Event Hubs instance that is configured for receiving logs:
az eventhubs eventhub authorization-rule create --resource-group <your_resource_group> --namespace-name <your_event_hub_namespace> --eventhub-name <your_event_hub_instance> --name <authorization_rule_name> --rights Listen -
Get an Event Hubs connection string for the authorization rule created above:
az eventhubs eventhub authorization-rule keys list --resource-group <your_resource_group> --namespace-name <your_event_hub_namespace> --eventhub-name <your_event_hub_instance> --name <your_authorization_rule_name> -
Configure the diagnostic settings to stream both resource-related and Entra ID sign-in logs to the Azure Event Hub instances.
CLI
You can run Azure log forwarding deployment using Azure Portal Cloud Shell (Bash) or from any machine with Azure CLI and Bash shell (Linux or Windows WSL).
Deploy
-
Set the following environment variables, making sure to replace the placeholders (
<...>) with your own values.-
For
DEPLOYMENT_NAME, enter your deployment name between 3 and 20 characters long. You can use lowercase letters and numbers.Note: The name needs to be globally unique—it is appended to the created Azure resources.
-
- For
TARGET_URL, enter your environment URL:https://<your_environment_ID>.live.dynatrace.com. To learn how to determine your environment ID for the SaaS deployment, see environment ID.
- For
TARGET_API_TOKEN, enter your API token. See Dynatrace requirements for details. - For
RESOURCE_GROUP, enter the name of the Azure resource group in which deployment will run. See Azure requirements for details. - For
EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING, enter the connection string for the Azure Event Hubs instances configured for receiving logs. See Azure requirements for details.
Optional You can enable self-monitoring and/or log filtering during or after deployment.
DEPLOYMENT_NAME=<your_deployment_name>TARGET_URL=<your_environment_URL>TARGET_API_TOKEN=<your_API_token>RESOURCE_GROUP=<your_resource_group>EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING="<your_Event_Hub_connection_string>"
-
Download the
azure-log-forwarder-functionscript and deploy the infrastructure.wget -q https://github.com/dynatrace-oss/dynatrace-azure-log-forwarder/releases/latest/download/dynatrace-azure-logs.sh -O dynatrace-azure-logs.sh && chmod +x ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh \&& ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh --deployment-name $DEPLOYMENT_NAME --target-url $TARGET_URL --target-api-token $TARGET_API_TOKEN --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --event-hub-connection-string $EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING --require-valid-certificate true
View Azure logs
After deploying the script, you can view and analyze Azure logs in Dynatrace:
Go to  Logs & Events Classic and, in the attributes filter, search for Azure.
Logs & Events Classic and, in the attributes filter, search for Azure.
- If you see logs coming in, you managed to deploy Azure log forwarder successfully.
- If there are no logs within 10 minutes checkout the Verification guide section of the page.
You can use DQL to filter for Azure logs. As an example, you could add the following line to a DQL query:
fetch logs| filter matchesValue(dt.openpipeline.source, "/api/v2/logs/ingest") AND matchesValue(cloud.provider, "Azure")| sort timestamp desc
If you already have multiple integrations, you can additionally use the values cloud.log_forwarder and dt.auth.origin to further refine your filters.
Self-monitoring Optional
Self-monitoring allows a quick diagnosis to see if your function processes and sends logs to Dynatrace properly.
Enable self-monitoring
To enable self-monitoring, you have two options:
-
During deployment: Set the
--enable-self-monitoringparameter (or theSFM_ENABLEDenvironment variable) totrue. -
After deployment: In Azure Portal, go to the configuration of your deployed Function App instance and set
SELF_MONITORING_ENABLEDtotrue.
After enabling self-monitoring, you need to enable managed identity for your Function App instance created during deployment, and configure it to allow pushing metrics to the resource.
To set up managed identity
- In Azure Portal, go to the Settings of your Function App instance created during deployment, and select Identity.
- Select Yes to Enable system assigned managed identity.
- Go to your resource group where Function App is deployed and select Access control (IAM).
- Select Add to add a role assignment.
- Set the Monitoring Metrics Publisher role.
- Select Save to save your configuration.
Self-monitoring metrics
Once you enable self-monitoring, you can view the following metrics in your dynatrace_logs_self_monitoring namespace of the newly deployed Function App instance.
| Metric name | Description | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
all_requests | All requests sent to Dynatrace. | |
dynatrace_connectivity_failures | Reported when any Dynatrace connectivity issues occurred. | connectivity_status |
parsing_errors | Reported when any parsing errors occurred during log processing. | |
processing_time | Time needed to process all logs. | |
sending_time | Time needed to send all requests. | |
too_long_content_size | Reported when content of log is too long. The content will be trimmed. | |
too_old_records | Reported when logs received from Event Hubs are too old. |
Log filtering Optional
To reduce the number of logs that are sent to Dynatrace, you can apply filters.
To apply filters you have two options:
-
During deployment: Set the
FILTER_CONFIGenvironment variable in Azure Portal Cloud Shell (Bash) before running the deployment script.-
Add the
FILTER_CONFIGenvironment variable to the list of environment variables needed for the deployment script.Be sure to replace placeholders with your values. See Filter options for details.
FILTER_CONFIG="FILTER.GLOBAL.MIN_LOG_LEVEL=<log_level>;FILTER.GLOBAL.CONTAINS_PATTERN=<pattern>;FILTER.RESOURCE_TYPE.MIN_LOG_LEVEL.<resource_type>=<log_level>;FILTER.RESOURCE_TYPE.CONTAINS_PATTERN.<resource_type>=<pattern>;FILTER.RESOURCE_ID.MIN_LOG_LEVEL.<resource_id>=<log_level>;FILTER.RESOURCE_ID.CONTAINS_PATTERN.<resource_id>=<pattern>" -
Set the environment variables.
-
Download the
azure-log-forwarder-functionscript and deploy the infrastructure.
-
-
After deployment: Add
FILTER_CONFIGin Azure Portal.-
In Azure Portal, go to Environment variables of your deployed Function App instance.
-
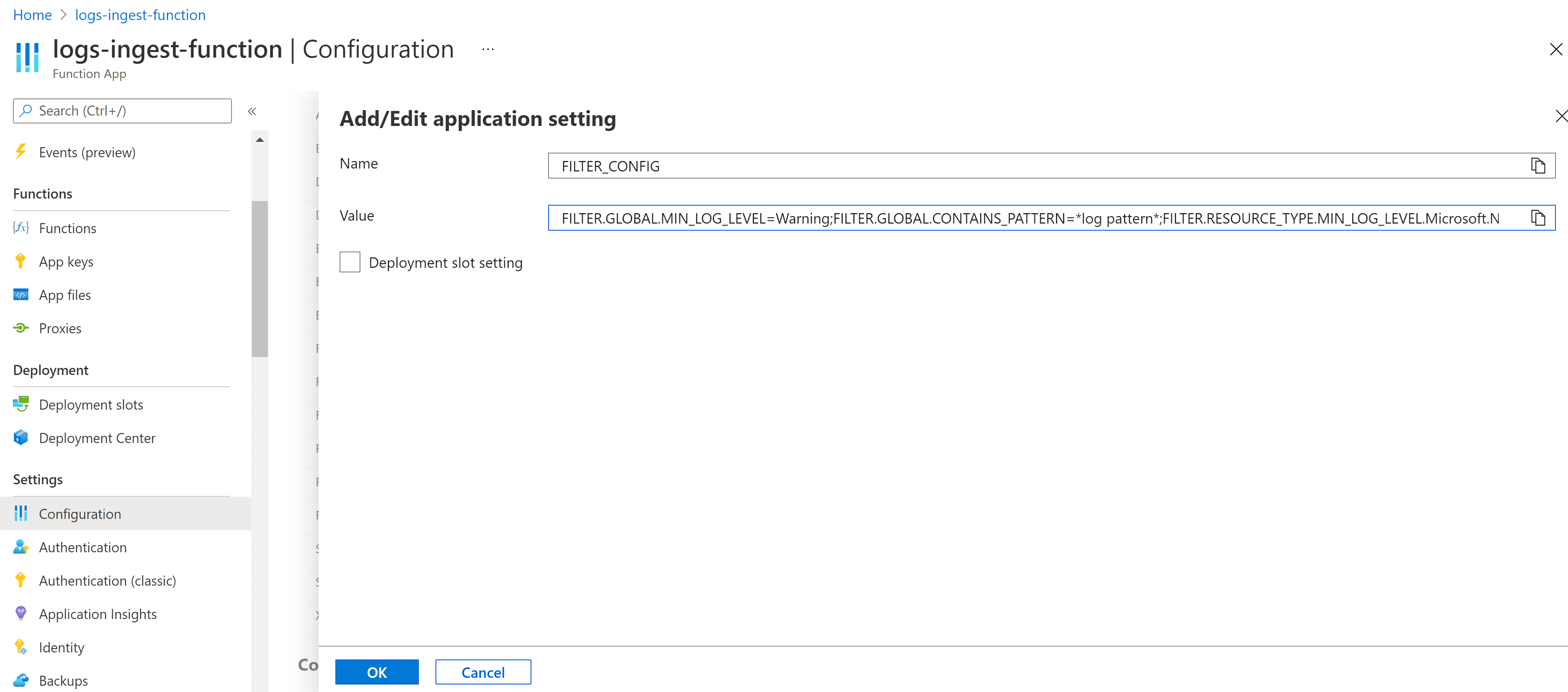
In App settings, search and select FILTER_CONFIG.
FILTER_CONFIG will appear in Azure after running the deployment script.
-
Select Edit to add a Value for your filter.
Example edit
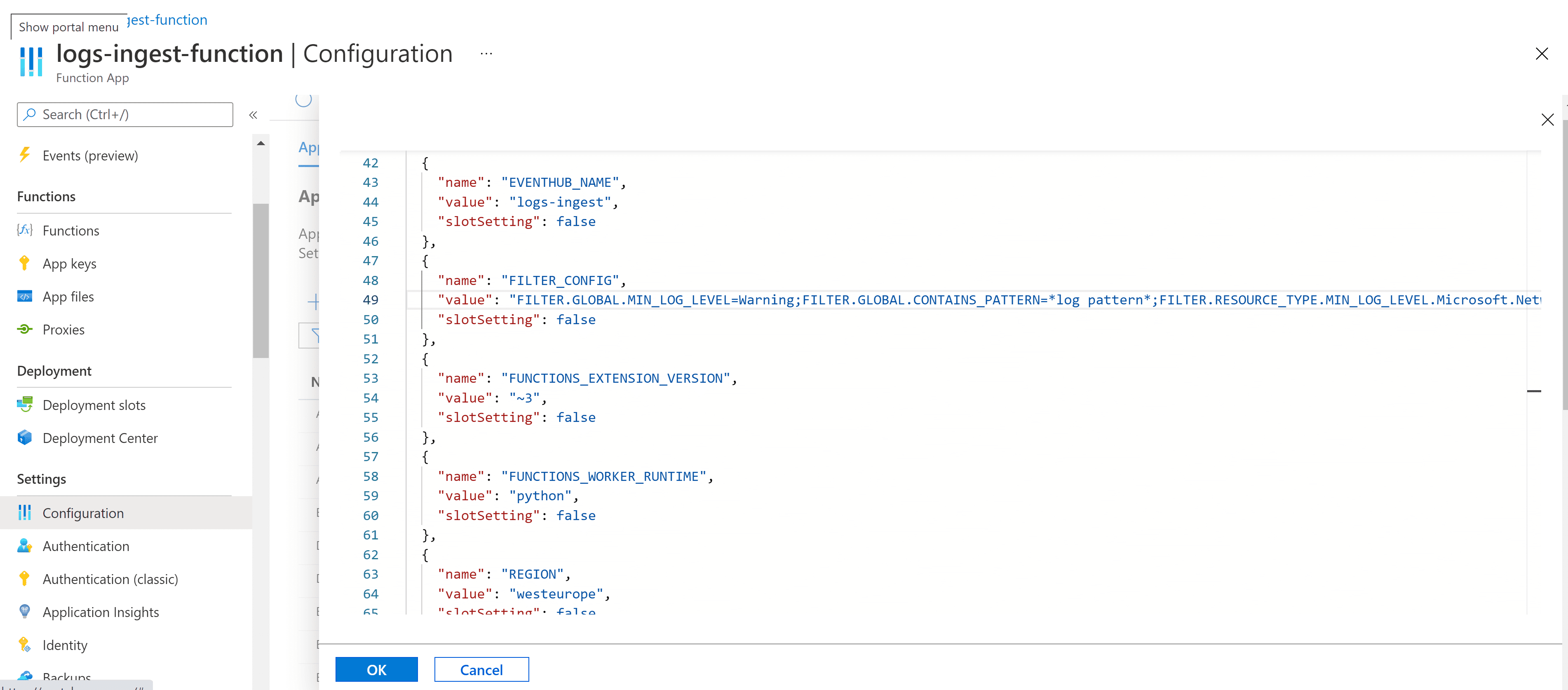
Alternatively, you can select Advanced edit to enter your value in the JSON.
Example advanced edit
-
Select OK.
-
Restart your Function App instance.
-
Filter options
FILTER_CONFIG is a key-value pair variable. You can set two types of filters (MIN_LOG_LEVEL and/or CONTAINS_PATTERN) for three filter groups (GLOBAL, RESOURCE_TYPE, and/or RESOURCE_ID).
Filter type: MIN_LOG_LEVEL
This filter type allows you to filter out logs with unwanted levels. Possible log levels are:
- Critical (or
1) - Error (or
2) - Warning (or
3) - Informational (or
4)
Example:
FILTER_CONFIG="FILTER.GLOBAL.MIN_LOG_LEVEL=Warning"
In the example above, Informational logs will be skipped, and only Warning, Error, and Critical logs will be sent to Dynatrace.
Syntax options are:
FILTER.GLOBAL.MIN_LOG_LEVEL=<log_level>FILTER.RESOURCE_TYPE.MIN_LOG_LEVEL.<resource_type>=<log_level>FILTER.RESOURCE_ID.MIN_LOG_LEVEL.<resource_id>=<log_level>
You can have one global-level filter and additional filters for a particular resource type/ID.
Example:
FILTER_CONFIG="FILTER.GLOBAL.MIN_LOG_LEVEL=Error;FILTER.RESOURCE_TYPE.MIN_LOG_LEVEL.MICROSOFT.WEB/SITES=Informational"
In the example above, all logs from instances with resource type MICROSOFT.WEB/SITES will be sent to Dynatrace, while for all other resources, Informational and Warning logs will be filtered out.
Filter type: CONTAINS_PATTERN
This filter type allows you to collect logs containing a particular text. We use fnmatch that provides support for Unix shell–style wildcards. See Unix filename pattern matching for details.
Syntax options are:
FILTER.GLOBAL.CONTAINS_PATTERN=<log_pattern>FILTER.RESOURCE_TYPE.CONTAINS_PATTERN.<resource_type>=<log_pattern>FILTER.RESOURCE_ID.CONTAINS_PATTERN.<resource_id>=<log_pattern>
Filter group: GLOBAL
This filter is set for all logs.
Filter group: RESOURCE_TYPE
This filter is used only for logs coming from resources of the given Azure resource type, such as Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines.
You can find the resource type in Azure Portal, in your resource's Properties.
If the Type field doesn't appear in Properties, you can extract it from the resource ID string.
Resource ID string syntax:
/subscriptions/<subscriptionId>/resourceGroups/<resourceGroupName>/providers/<resourceType>/<resourceName>
The resource type will be the part between /providers/ and /resourceName/.
Filter group: RESOURCE_ID
This filter is used only for logs coming from the given resource that is identified by the Azure resource ID.
You can look for the resource type in Azure Portal, in your resource's Properties.
Filter rules
-
If you set two filter types for the same group, both conditions need to be met, so the second filter will have to match the first filter.
For example, if you set
MIN_LOG_LEVELto Warning andCONTAINS_PATTERNto<some_important_message>, you will get only Warning logs containing<some_important_message>, and all other warning logs that don't contain that specific message will be filtered out. -
If you set one filter type for one group, and another filter type for another group, the two conditions do not overlap.
For example, if you set
MIN_LOG_LEVELto Warning forGLOBAL, andCONTAINS_PATTERNto<some_important_message>forRESOURCE_TYPE, you will get all Warning, Error, and Critical logs fromGLOBAL, and all logs containing<some_important_message>fromRESOURCE_TYPE. -
If you set more than one pair of filter types (
MIN_LOG_LEVELandCONTAINS_PATTERN) for the same group (global or resource type/ID), only the last pair of filter types will apply; all the others will be ignored.
Update Azure log forwarding
To update Azure log forwarding
-
You need a package that contains the source code of Azure log forwarder—download the latest Dynatrace version.
wget https://github.com/dynatrace-oss/dynatrace-azure-log-forwarder/releases/latest/download/dynatrace-azure-log-forwarder.zip -
Deploy the new version, making sure to replace the placeholders with the required values.
az webapp deployment source config-zip -g <your_resource_group_name> -n <application_name> --src <zip_file_path>
Some Azure log forwarder releases include changes that require full reinstallation. For more details, refer to the GitHub releases page.
Alternative deployments
Use existing ActiveGate
If you don't want to use direct ingest through the Cluster API, you have to use an existing ActiveGate for log ingestion.
See below for instructions.
Prerequisites
Dynatrace version 1.217+
- Dynatrace requirements listed above
- Azure requirements listed above
- CLI requirements listed above
Configuration
-
Set the following environment variables, making sure to replace the placeholders (
<...>) with your own values.- For
DEPLOYMENT_NAME, enter your deployment name (lowercase only). - For
TARGET_URL, enter the API URL of your ActiveGate endpoint:https://<your_activegate_IP_or_hostname>:9999/e/<your_environment_ID>. To learn how to determine your environment ID, see environment ID. - For
TARGET_API_TOKEN, enter your API token. For details, see the prerequisites above. - For
RESOURCE_GROUP, enter the name of the Azure resource group in which deployment will run. See Azure requirements for details. - For
EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING, enter the connection string for the Azure Event Hubs instances configured for receiving logs. See Azure requirements for details. - For
USE_EXISTING_ACTIVE_GATE, entertrue. - Optional For
REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE, entertrueorfalse. This parameter tells the log forwarder to verify the SSL certificate of your ActiveGate. By default, certificates are validated.
Optional You can enable self-monitoring and/or log filtering during or after deployment.
DEPLOYMENT_NAME=<your_deployment_name>TARGET_URL=<your_environment_URL>TARGET_API_TOKEN=<your_API_token>RESOURCE_GROUP=<your_resource_group>EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING="<your_Event_Hub_connection_string>"USE_EXISTING_ACTIVE_GATE=trueREQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE=true - For
-
Download the
azure-log-forwarder-functionscript and deploy the infrastructure.Be sure to check whether you want to set other optional parameters as well. All parameters between brackets (
[...]) are optional. For details, see Deploy table.wget -q https://github.com/dynatrace-oss/dynatrace-azure-log-forwarder/releases/latest/download/dynatrace-azure-logs.sh -O dynatrace-azure-logs.sh && chmod +x ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh \&& ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh --deployment-name $DEPLOYMENT_NAME --target-url $TARGET_URL --target-api-token $TARGET_API_TOKEN --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --event-hub-connection-string $EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING --require-valid-certificate $REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE
Use a user-assigned managed identity
There are two managed identity types: system-assigned and user-assigned. By default, a system-assigned managed identity is used. If you prefer to use a user-assigned managed identity, see below for instructions.
Prerequisites
Dynatrace version 1.217+
- Dynatrace requirements listed above
- Azure requirements listed above
- CLI requirements listed above
In addition to the Azure requirements listed above, you should also create a user-assigned managed identity in Azure Portal.
Add Event Hubs roles in the user-assigned managed identity. For the event hub trigger binding, you need to assign corresponding built-in roles. The built-in roles are Azure Event Hubs Data Receiver and Azure Event Hubs Data Owner.
Configuration
-
Set the following environment variables, making sure to replace the placeholders (
<...>) with your own values.DEPLOYMENT_NAME=<your_deployment_name>TARGET_URL=<your_environment_URL>TARGET_API_TOKEN=<your_API_token>RESOURCE_GROUP=<your_resource_group>EVENT_HUB_NAME=<your_Event_Hub_name>REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE=trueENABLE_USER_ASSIGNED_MANAGED_IDENTITY=trueEVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_CLIENT_ID=<your_user_assigned_MI_client_id>MANAGED_IDENTITY_RESOURCE_NAME=<your_user_assigned_MI_resource_name>EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAMESPACE="<your_eventhub_namespace_host_name>"CONSUMER_GROUP ="<Your_custom_default_consumer_group_name>"- For
DEPLOYMENT_NAME, enter your deployment name (lowercase only).
- For
- For
TARGET_URL, enter your environment URL:https://<your_environment_ID>.live.dynatrace.com. To learn how to determine your environment ID for a SaaS deployment, see environment ID.
- For
TARGET_API_TOKEN, enter your API token. For details, see the prerequisites above. - For
RESOURCE_GROUP, enter the name of the Azure resource group in which deployment will run. See Azure requirements for details. - For
EVENT_HUB_NAME, enter the name of the Azure Event Hubs instances configured for receiving logs. See Azure requirements for details. - Optional For
REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE, entertrueorfalse. This parameter tells the log forwarder to verify the SSL certificate of your ActiveGate. By default, certificates are validated. - For
ENABLE_USER_ASSIGNED_MANAGED_IDENTITY, entertrue. This parameter is used to determine if a user-assigned managed identity is used instead of system assigned. - For
EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_CLIENT_ID, enter theClient IDof the created managed identity. - For
MANAGED_IDENTITY_RESOURCE_NAME, enter the resource name of the created managed identity. - For
EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAMESPACE, enter:- The
Host nameof the Event Hubs namespace. - The custom name of the default consumer group.
- The
Optional You can enable self-monitoring and/or log filtering during or after deployment.
-
Download the
azure-log-forwarder-functionscript and deploy the infrastructure.Be sure to check whether you want to set other optional parameters as well. All parameters between brackets (
[...]) are optional. For details, see Deploy table.wget -q https://github.com/dynatrace-oss/dynatrace-azure-log-forwarder/releases/latest/download/dynatrace-azure-logs.sh -O dynatrace-azure-logs.sh && chmod +x ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh \&& ./dynatrace-azure-logs.sh --deployment-name $DEPLOYMENT_NAME --target-url $TARGET_URL --target-api-token $TARGET_API_TOKEN --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --event-hub-name $EVENT_HUB_NAME --require-valid-certificate $REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE --enable-user-assigned-managed-identity $ENABLE_USER_ASSIGNED_MANAGED_IDENTITY --eventhub-connection-client-id $EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_CLIENT_ID --managed-identity-resource-name $MANAGED_IDENTITY_RESOURCE_NAME --eventhub-connection-fully-qualified-namespace $EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAMESPACE --custom-consumer-group $CONSUMER_GROUP
Deploy table
For a complete list of parameters, see the deploy table below.
| Command-line parameter | Environment variable | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
--deployment-name | DEPLOYMENT_NAME | Required Your deployment name. Lowercase only. | |
--target-url | TARGET_URL | Required Your Dynatrace environment where you want to set up generic log ingestion. | |
--target-api-token | TARGET_API_TOKEN | Required Your API token. | |
--resource-group | RESOURCE_GROUP | Required Name of the Azure resource group in which the deployment will run. | |
--event-hub-connection-string | EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING | Required The connection string for the Azure Event Hubs instance configured for receiving logs. (Azure Event Hubs name that is configured for receiving logs.) | |
--event-hub-name | EVENT_HUB_NAME | Optional Optional by default. If a user-assigned managed identity is your method of authentication, then Required. | |
--require-valid-certificate | REQUIRE_VALID_CERTIFICATE | Optional If set to true, the log forwarder verifies the SSL certificate of your ActiveGate. By default, certificates are validated. | |
--enable-self-monitoring | SFM_ENABLED | Optional If set to true, Dynatrace sends custom metrics to Azure. See Enable self-monitoring for details. By default, custom metrics aren't sent to Azure. | |
--filter-config | FILTER_CONFIG | Optional Apply filters to reduce the number of logs sent to Dynatrace. See Log filtering for details. | |
--tags | TAGS | Optional Apply Azure tags to newly created resources in comma-separated key:value pair format (for example, "tag:value,tag2:value2"). The following characters are not supported in a tag key: ,:<>%&\?/ | |
--enable-user-assigned-managed-identity | ENABLE_USER_ASSIGNED_MANAGED_IDENTITY | Optional If set to true, options --eventhub-connection-client-id, --managed-identity-resource-name, --eventhub-connection-fully-qualified-namespace, --event-hub-name are Required. Enables usage of a user-assigned managed identity instead of a system-assigned managed identity. | |
--custom-consumer-group | CONSUMER_GROUP | Optional If provided, this value will be used as the name of a default consumer group. Leave empty to apply the default Azure value. | |
--eventhub-connection-client-id | EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_CLIENT_ID | Optional Client ID of the created managed identity. Example value: d8916c27-4c4r-482o-895b-doe0b48c76f7 | |
--managed-identity-resource-name | MANAGED_IDENTITY_RESOURCE_NAME | Optional Resource name of the created managed identity. Example value: test-managed-identity | |
--eventhub-connection-fully-qualified-namespace | EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAMESPACE | Optional Host name of the Azure Event Hubs namespace. Example value: sample-eventhub-namespace.servicebus.windows.net |
Verification
To verify if the deployment was successful, in Dynatrace, go to  Logs & Events Classic and confirm that the following log line is present:
Logs & Events Classic and confirm that the following log line is present:

In around 10 minutes, further logs should start coming in. If no logs are coming in, make sure that:
- The Event Hubs instances and the resource group in which the deployment will run are in the same region
- You carefully followed the steps to Configure diagnostic settings
Furthermore, you can read Azure Function logs in which the Azure-log-forwarder is running. Enable streaming execution logs in Azure Functions
SNAT port exhaustion: Azure Functions have a limited number of ports that can be opened at a time (128). The number of instances, the number of worker processes, and the number of concurrent calls are the factors that contribute to the open connections. If the limit is reached, see the scaling guide below.
Check your version
To check the version of the currently deployed Azure log forwarder
- Open Azure Portal and go to Subscriptions.
- Select your subscription.
- Go to Resource groups.
- Choose the resource group that contains the function.
- Choose your deployed function app.
- Select log_ingest on the Functions tab.
- Select Code + Test from the Developer menu on the left.
- Select the dropdown file selector (
main.pyis selected by default). - Choose
version.txt. - Open the file to check your currently deployed version.
Scaling guide
The recommended way of scaling up the default throughput of 70 MB/min is to upgrade the App Service plan, increase the number of App Service instances respectively, increase FUNCTIONS_WORKER_PROCESS_COUNT (default is 1), increase NUMBER_OF_CONCURRENT_SEND_CALLS (default is 2). You can add FUNCTIONS_WORKER_PROCESS_COUNT and NUMBER_OF_CONCURRENT_SEND_CALLS as New application setting in Azure Portal (Azure function > Configuration > New application setting).
Please note that the performance of the log forwarder may vary depending on the log content (size/ processing complexity).
| Maximum throughput | App Service Plan | Number of instances | Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
up to 70 MB/minute (up to 4 GB/hour) | S1 | 1 | no configuration |
up to 580 MB/minute (up to 32 GB/hour) | P1V3 | 1 | FUNCTIONS_WORKER_PROCESS_COUNT: 4, NUMBER_OF_CONCURRENT_SEND_CALLS: 5 |
up to 1 GB/minute (up to 60 GB/hour) | P2V3 | 1 | FUNCTIONS_WORKER_PROCESS_COUNT: 8, NUMBER_OF_CONCURRENT_SEND_CALLS: 5 |
up to 2.3 GB/minute (up to 138 GB/hour) | P2V3 | 3 | FUNCTIONS_WORKER_PROCESS_COUNT: 8, NUMBER_OF_CONCURRENT_SEND_CALLS: 5 |
As a last resort, scale horizontally: deploy more integrations and distribute the logs' load into different Event Hubs instances.
Uninstall Azure log forwarding
To uninstall the Dynatrace Azure log forwarder
-
In Azure Portal, go to the resource group used for installation.
-
Filter resources by tag.
The deployment script tags all created resources with
LogsForwarderDeployment = <your_deployment_name>. -
Delete the resources.