Upgrade guide – Alert Notification
- Latest Dynatrace
- 60-min read
Almost all Dynatrace classic customers use problem notification integrations and alerting profile filters.
This is a guide for upgrading from Dynatrace classic to the latest Dynatrace, ensuring that the use-case of sending out problem notifications is upgraded. The solutions introduced in this guide require an active Dynatrace Platform Subscription (DPS) license.
Why upgrade
The purpose of alerting notifications in Dynatrace is to send out a filtered subset of newly detected problems to external systems, such as Slack or ServiceNow.
In the previous Dynatrace:
- Such configurations were always global to the Dynatrace environment, which means that no individual (email) notification could be set up by users without granting them admin permissions.
- Existing integrations were hardcoded and limited in terms of their flexibility.
In the latest Dynatrace:
- Email notifications via Problems addresses personalized user notification.
- Integration with external systems via Workflows Connectors offers improved, flexible integration with third-party systems.
New concepts
Before you start with performing this upgrade, please familiarize yourself with core concepts of the latest Dynatrace, including:
- Using Workflows (and Simple workflows) to automate tasks in Dynatrace
- Integrate external systems into your workflows using connectors
- Use the Jinja template engine to dynamically configure Workflows
- Securely connect your workflow to your (on premise) system using EdgeConnect
- Configure your individual problem notifications
- How to filter data stored in Grail using DQL
Problem notifications and alerting profiles in the previous Dynatrace
The main use case for setting up alerting profiles and problem notifications is to receive active notifications whenever Dynatrace Intelligence detects a new Problem.
While the problem notification configuration defines the channel those notifications can be sent to, the alerting profiles represent a reusable Problem filter to reduce the total number of problems to a subset the user wants to receive a notification for.
Dynatrace classic supports the following out-of-the-box problem notification channels:
- Ansible
- Custom Integration, which represents a generic HTTP webhook
- Jira
- OpsGenie
- PagerDuty
- ServiceNow
- Slack
- Trello
- VictorOps
- xMatters
Example problem notifications setup page:
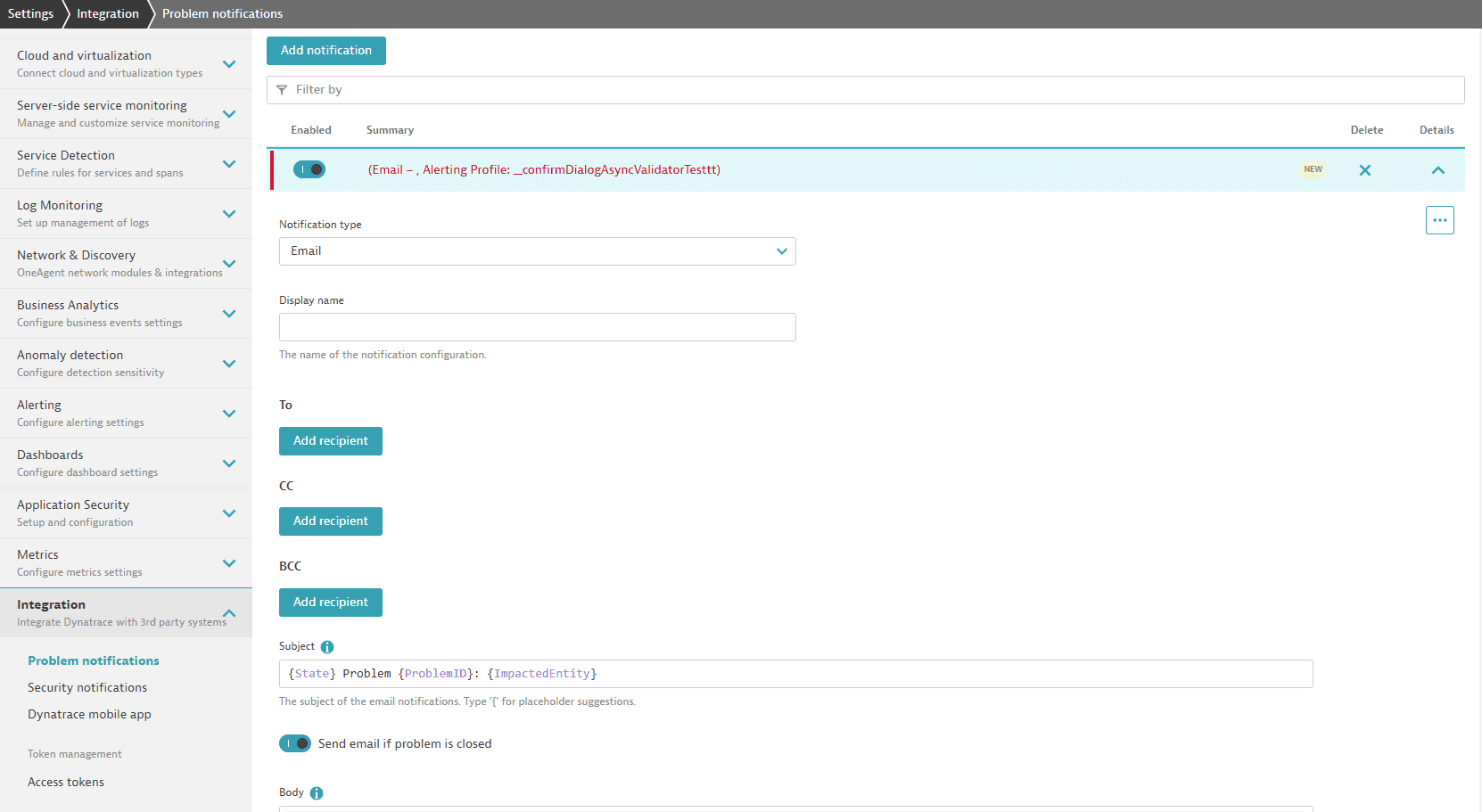
Along with configuring the problem notification channel, a configured alerting profile setting is used to reduce the total number of problems to a subset.
Alerting profiles primarily use the following filter options:
- Management zones
- Problem categories (Availability, Error, Slowdown, Resource, Custom, and Monitoring unavailable alert)
- Problem included event type and text filter
- Problem duration filter
Example alerting profile setup page:
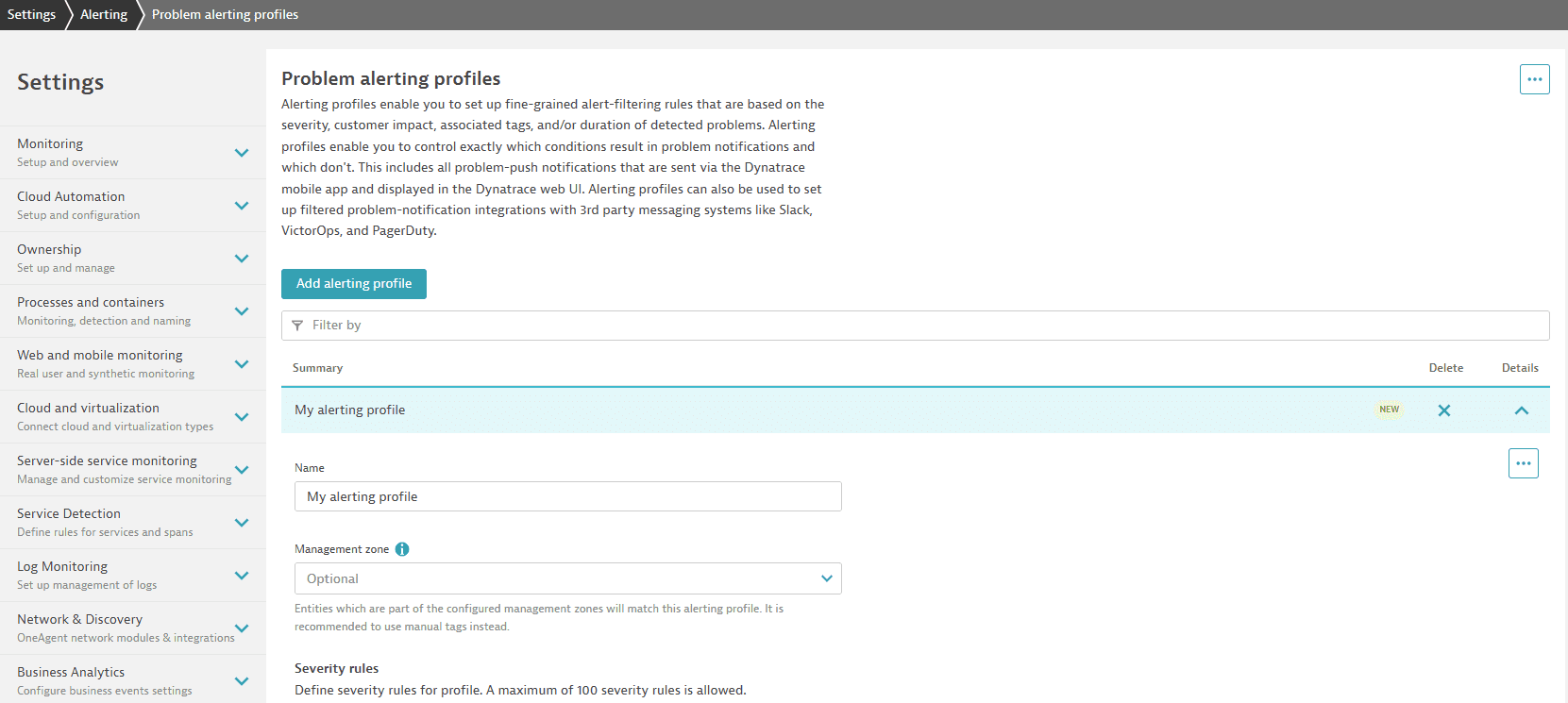
How to upgrade
To upgrade alerting profiles and notifications:
- Use the notification setting in the
 Problems app to receive email notifications.
Problems app to receive email notifications. - Use Workflows Connectors to integrate with external systems.
Email notifications via Problems
Suppose you want to receive an email for a detected problem without having to change global environment settings.
-
In the previous Dynatrace, you can’t subscribe to receive email notifications for a detected problem without having admin rights. A new entry for an alerting profile as well as a dedicated email Problem integration has to be created.
-
In the latest Dynatrace, a dedicated user flow lets you easily subscribe to newly reported problems directly within the
 Problems app. Turn on email notification for filters applied in
Problems app. Turn on email notification for filters applied in  Problems.
Problems.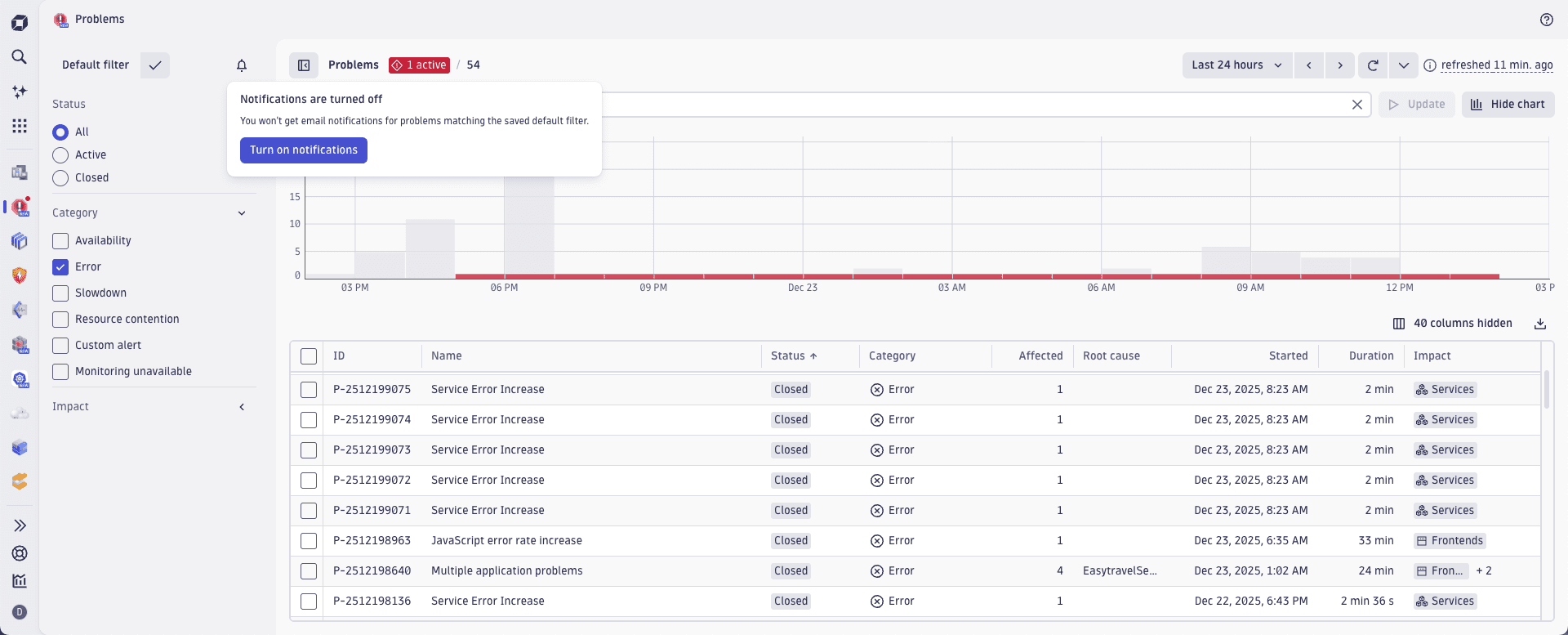
This user flow sends a predefined email template to your account email address. The email text is in Markdown format and is also available under the problem Grail record field (event.description).
- It doesn't interfere with any other user in the same environment.
- It doesn't require any admin permissions.
- It doesn't add any additional license costs.
Integration with external systems via Workflows Connectors
Most of the time, sending out individual problem notifications won't cover all of your requirements. You want to integrate with standard third-party tools (such as Service Now, Jira, Pager Duty, or Slack) or use a generic HTTP webhook to support your individual needs. Workflows Connectors is the answer.
Mapping of classic integrations and connectors
The following table will help you to find the right workflow action.
These connectors are not limited to sending a notification. They also offer more advanced actions, such as this example for Jira:
Furthermore, we are currently offering connectors for Microsoft Teams, plus several connectors to actually remediate problems in, for example, Kubernetes, AWS, Azure, GitHub, GitLab, and Jenkins.
Upgrade to simple workflow configurations
For simple notifications, we recommend using simple workflows. While those are limited to a single action—similar to the classic integration-they come without any additional license cost and offer a lot of functional advances:
- Using a workflow trigger eliminates the need for adding and managing a separate alerting profile to filter incoming problems. The filter for problems can be directly applied within the workflow trigger.
- The problem filter can use DQL matchers on the incoming problem record, which is much more flexible and powerful than alerting profiles.
- A convenient preview of the most recent filtered problems helps to define the filter, and a possibility to try the flow with the previewed records helps to test your integration.
- Unlike the classic problem integrations, workflow triggers are not limited to problems, but can also be time-triggered (similar to a cron job) or by a Davis event (such as process restart, deployment, info events, and many more).
- All workflows and their actions are transparently logged in Dynatrace system events in Grail.
Example: Upgrade of a classic webhook notification
This example shows how to upgrade from an existing classic webhook problem integration to a simple workflow.
Set up the trigger
Within the classic notification configuration, an AlertingProfile filter is responsible for selecting the subset of problems that should trigger the notification. The following is a mapping of AlertingProfile filter conditions to a simple workflow trigger:
-
Management Zone filter: No longer supported. Use Grail record-based field filters instead. See the below examples on event, category, and text filters.
-
Duration filter: No longer supported. Currently there is no alternative to deliver problems that are active longer than X minutes.
-
Category filter (Availability, Error, Slowdown, and so on): Directly supported by the workflow problem trigger. For example:
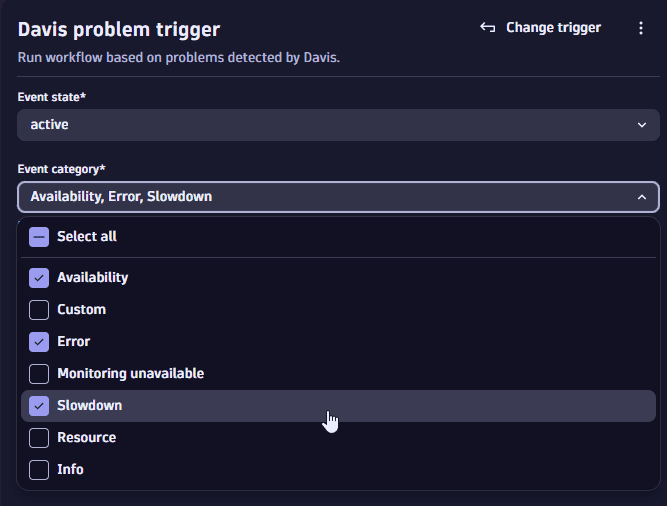
-
Entity tag filter: Directly supported by the workflow problem trigger. For example:
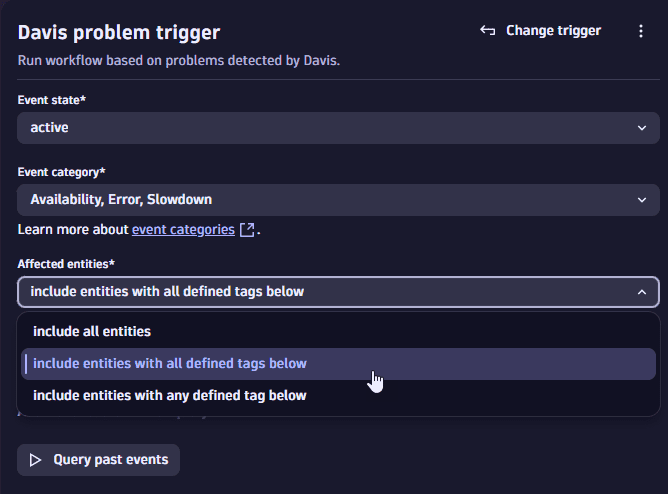
-
Event name and description text filters (for example, event type, event name, and event description): Using the Davis event trigger instead of the Davis problem trigger, these are supported through the workflow custom DQL filters. For example:
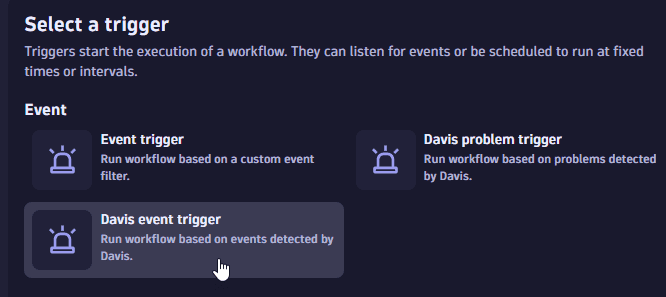
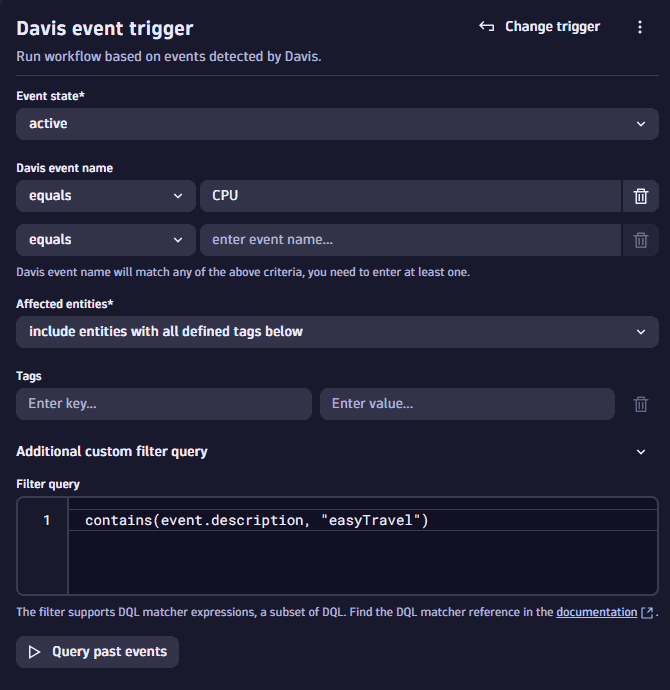
Configure the workflow action
After selecting the workflow trigger, you need to configure the HTTP Request action. It allows sending GET and POST HTTP requests and configuring HTTP headers along with the payload.
The payload field lets you either send the full event (problem) record that triggered the workflow, or select individual event record fields by using the Jinja template approach.
The following example shows where the complete problem record JSON is sent with a HTTP POST request:
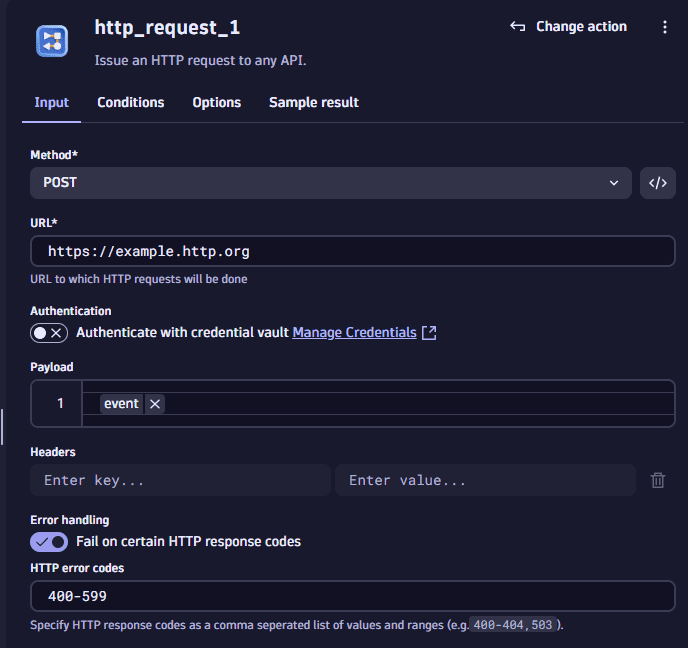
 Workflows conveniently allows you to run a test with a given problem record or event record example with the given HTTP Request configuration so that the workflow can be tested before activation.
Workflows conveniently allows you to run a test with a given problem record or event record example with the given HTTP Request configuration so that the workflow can be tested before activation.
Additional examples
Dynatrace Managed: Trigger workflows from classic notifications
If you're migrating from Dynatrace Managed to Dynatrace SaaS, you might face challenges with upgrading away classic notifications.
- Firewall policy blocks incoming problem notifications from Dynatrace SaaS that were previously triggered from Dynatrace Managed inside your data center.
- Dependency on the complex classic problem notification JSON DTO structure (
ProblemDetailsJSONandProblemDetailsJSONv2). - Dependency on an existing
AlertingProfilefilter setup.
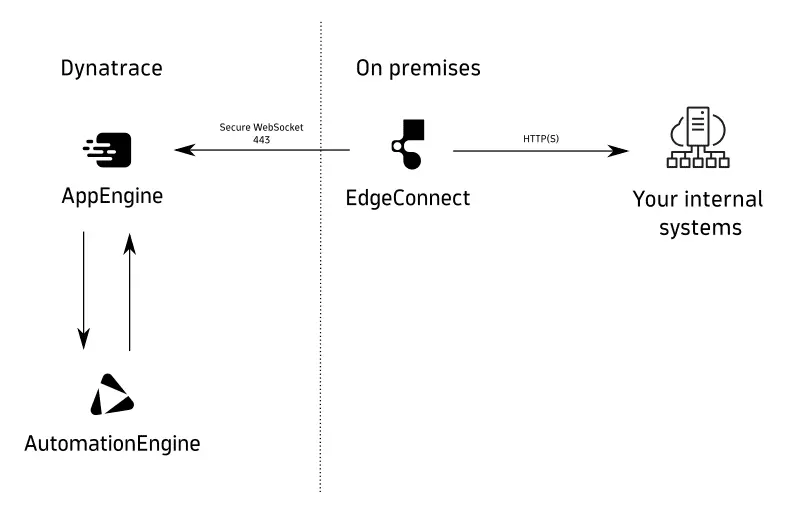
You need a way to securely connect Dynatrace Managed with the SaaS environment.
To bridge the upgrade gap between Dynatrace Managed and notifications in the latest Dynatrace, we recommend the following approach.
-
Set up EdgeConnect to push an HTTP Request to your data center.
-
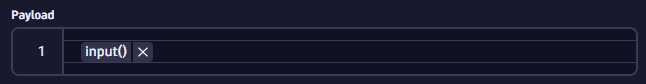
Configure a simple workflow with an On demand trigger along with an HTTP Request action.
Use the
inputplaceholder within the HTTP Request action payload field to pass on the payload that is given by the API trigger request.See the workflow HTTP Request payload below:
-
In your existing classic custom webhook notification, enter the on-demand workflow REST API endpoint, along with using the webhook's input JSON format together with the classic
ProblemDetailsJSONplaceholder: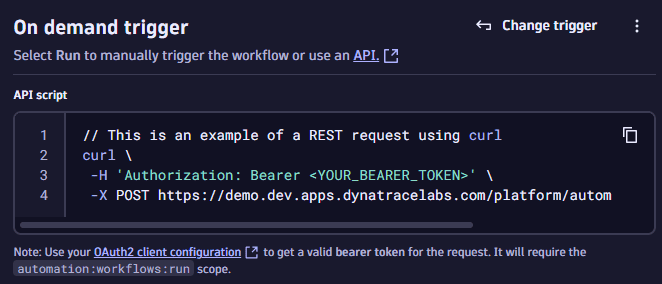
Enter it in the classic webhook setting:
Settings > Integration > Problem notifications

-
Use the on-demand trigger's API endpoint within your classic problem custom webhook integrations to trigger the workflow whenever the classic problem notification triggers. Either use the static platform API tokens or a configured OAuth client to authenticate the classic webhook request against the AutomationEngine API.
Once step 3 is finished, the classic webhook integration is triggered on every problem that matches the alerting profile. The classic webhook integration will then call the on-demand workflow trigger, pass the given classic webhook payload and run the configured Dynatrace workflow action. As workflows support the use of EdgeConnect to call into on premises servers, the webhook action can be used to call the previously configured server endpoint.
FAQ
How can I check past workflow executions
With classic notifications, you didn't have a detailed history of all the sent-out notifications. This led to a lot of support tickets that were hard to debug.
With the new workflow approach, if you have read access to dt.system.events you can query for all workflow executions to check if a notification was triggered. The following DQL query allows you to check the trigger history of workflow executions:
fetch dt.system.events| filter event.kind == "WORKFLOW_EVENT" and event.provider == "AUTOMATION_ENGINE" and event.type == "WORKFLOW_EXECUTION"| summarize count = count(), by:{dt.automation_engine.workflow.title}| sort count desc
How can I map my problem notification placeholders?
Classic notifications offer a list of predefined placeholders that allowed the integrator to send selected problem information to the receiving system.
Because the structure of problems in Grail changed, not all of those placeholders are directly supported in "Simple workflow" payloads. See below for a list of classic placeholders and their replacement with problem record fields available in the latest Dynatrace.
Don’t forget that the record fields in Grail along with the newly introduced ‘Custom problem fields’ and JINJA templates offer a lot more flexibility compared to the hardcoded classic placeholders.
Can I also send event details of a given Problem?
The classic ProblemDetailsJSON and ProblemDetailsJSONv2 contained problem record information along with potentially huge single individual event details. For large problems with hundreds of contained single events, this led to JSON payload sizes that were hard to process by receiving systems (for example, 10 MB or more per problem).
In a workflow, single event details can only be sent out with a Davis event trigger. You decide whether to trigger on a problem or on a single event or both.
- In a problem trigger, only problem record information can be used in the payload.
- In an event trigger, only event record information can be used.
As a positive side-effect, workflow notifications can now also be configured on events and event types that do not raise problems in Dynatrace. This means that you can set up and run automations on informational purpose events, such as deployment or software lifecycle events, without annoying your operations team with a red problem.
Can I send out the classic JSON payload?
No, it is not supported to directly use the classic problem JSON payloads (ProblemDetailsJSON and ProblemDetailsJSONv2) within a workflow.
Nevertheless, there is a workaround that allows Dynatrace Managed customers to easily switch from their classic notifications to SaaS workflows.
What are the workflow limits?
Workflow limit:
- 10’000 workflows per customer environment
- 100 workflows per trial environment
Execution limits:
- 1’000 executions per workflow per hour
If a workflow exceeds this limit, no further triggers run for up to one hour. If the limit is exceeded three times within a seven-day period, the event trigger is automatically deactivated.
You can request higher limits by submitting your use case for review by creating a support ticket.
How can I prevent sending notifications during a maintenance window?
In the problem trigger, use maintenance.is_under_maintenance==false as a filter query to only trigger the workflow when the problem didn’t occur during a maintenance window.