Davis Security Score calculations
- Classic
- Explanation
This page refers to the classic  Third-Party Vulnerabilities app, which is deprecated. If you're currently using this app, we recommend transitioning to the corresponding
Third-Party Vulnerabilities app, which is deprecated. If you're currently using this app, we recommend transitioning to the corresponding  Vulnerabilities in the latest Dynatrace experience, which offers enhanced functionality and ongoing support. For details, see Vulnerabilities upgrade guide.
Vulnerabilities in the latest Dynatrace experience, which offers enhanced functionality and ongoing support. For details, see Vulnerabilities upgrade guide.
Davis Security Score (DSS) is an enhanced risk-calculation score based on the industry-standard Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). Davis AI is designed to provide a more precise risk-assessment score by considering additional parameters such as public internet exposure and whether or not data assets are reachable from an affected entity.
How DSS is better than CVSS
Virtually all security products use the CVSS Base Score to set the severity of security vulnerabilities. CVSS was designed to be risk-averse, which means that, for any given vulnerability, the assigned score assumes the worst-case scenario. The CVSS specification does allow for some modifications based on environmental influences, but this is usually not factored into the risk score calculation, which leads to many high or critical vulnerability scores that the user needs to handle.
DSS is more accurate: Davis doesn't assume the worst-case scenario. Instead, Davis adapts the characteristics of the vulnerability to your particular environment, taking into consideration its structure and topology, and advises you as to which elements are at risk and how to handle security issues. With Davis AI, you can find out if the affected entity is reachable from the internet and if there is any data storage in reach of an affected entity.
DSS makes you more efficient: By including additional parameters in its analysis, Davis is designed to leverage data to more precisely calculate the security score and predict the potential risk of a vulnerability to your environment. By reducing the score of vulnerabilities that are considered less relevant for your environment, you gain time to focus on the most critical issues and fix them faster.
Davis Security Score scale
The DSS scale ranges between 0.1 (lowest risk) and 10.0 (most critical risk):
- Low risk: Vulnerabilities are indicated with blue and range between 0.1 and 3.9
- Medium risk: Vulnerabilities are indicated with yellow and range between 4.0 and 6.9
- High risk: Vulnerabilities are indicated with red and range between 7.0 and 8.9
- Critical risk: Vulnerabilities are indicated with red and range between 9.0 and 10.0
Calculation process

CVSS Base

Davis adds context to public internet exposure

Davis adds context to reachable data assets

Final score
 CVSS Base
CVSS Base
Davis calculation starts from the base CVSS Score1, and takes into consideration metrics pertaining to
- Public internet exposure: Attack vector (AV)
- Reachable data assets: Confidentiality (C) and Integrity (I)
CVSS v2 is deprecated. For vulnerabilities relying on this data, Davis Security Score can't be assessed.
 Davis adds context to public internet exposure
Davis adds context to public internet exposure
To influence the security score of a third-party vulnerability based on the public internet exposure, Davis uses the Modified Attack Vector (MAV) metric. This metric reflects the context by which vulnerability exploitation is possible.
Result
- If the original AV value shows exploitation is possible via network access, but, based on the topology information extracted from your environment, the service isn't actually exposed, Davis lowers the MAV value.
- In all other cases, the MAV value doesn't differ from the original AV value.
 Davis adds context to reachable data assets
Davis adds context to reachable data assets
To influence the security score of a third-party vulnerability based on reachable data assets, Davis uses the Modified Confidentiality (MC) and Modified Integrity (MI) metrics. These metrics reflect the actual accessibility of a reachable data asset to an affected service.
Result
- If the original C and I values show that data exposure or manipulation are possible, but, based on Davis' evaluation, there aren't any reachable data assets accessible by the affected service, Davis lowers the corresponding MC and MI values.
- In all other cases, the MC and MI values don't differ from the original C and I values.
 Final score
Final score
The final score is calculated based on the previous two results.
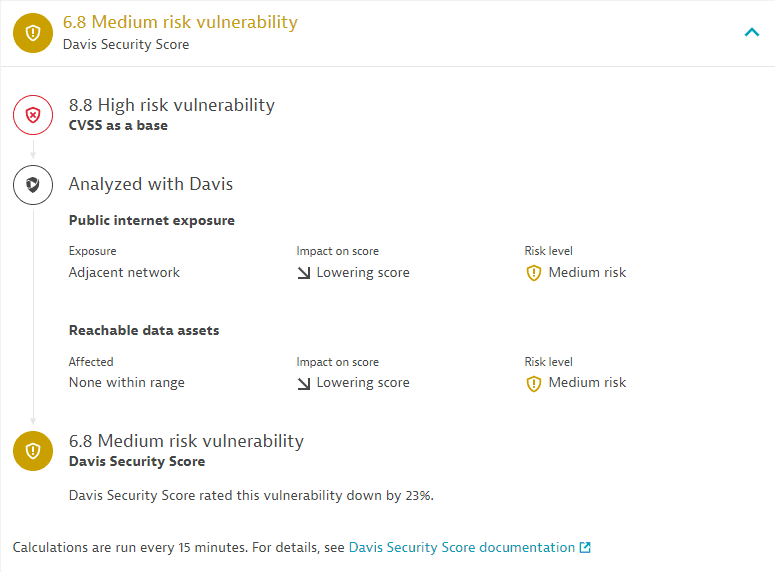
Example:
In this example, the evaluation of public internet exposure and reachable data assets lowers the score by 23 percent, from high to medium.
FAQ
-
How is the score calculated if a third-party vulnerability has more affected services?
- Davis modifies the scores on the service level. If a vulnerability has more than one affected service, Davis uses the highest score.
-
In which cases does Davis raise the final score?
- Davis never raises DSS higher than the base CVSS. The values for public internet exposure and reachable data assets can only lower the score or leave it unchanged.
Limitations
The DSS calculation currently differs in Grail-powered apps (such as  Dashboards,
Dashboards,  Notebooks,
Notebooks,  Workflows) from third-party vulnerabilities pages:
Workflows) from third-party vulnerabilities pages:
- On third-party vulnerabilities pages, DSS is assessed based on the remediable entities within the selected scope.
- In Grail-powered apps, DSS is assessed based on the DSS of the remediable entities within the selected scope.
Thus, the DSS (score and risk level) for vulnerabilities on Grail-powered apps can be lower than on the vulnerabilities pages.
 Third-Party VulnerabilitiesApplication Security
Third-Party VulnerabilitiesApplication Security