Create a private Synthetic location
- Classic
- How-to guide
- 24-min read
You can run your Dynatrace synthetic monitors from a private Synthetic location, which is a location in your private network infrastructure where you install one or more Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate instances.
With monitors executed from a private location, you can bring the testing capabilities available in public locations right into your own environment. With private locations you can:
- Measure internal webpage performance and availability.
- Measure complex internal applications with browser clickpaths.
- Measure external resources with synthetic monitors run from internal locations.
- Monitor APIs, both internal and external.
Private Synthetic locations support all types of Dynatrace synthetic monitors.
System and hardware requirements for private locations
Make sure the target host you plan to use for running synthetic monitors complies with system and hardware requirements for private Synthetic locations. Note that Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates have more demanding hardware and system requirements than a regular Environment or Cluster ActiveGate.
- There are no new versions of Chromium for Red Hat/Oracle Linux/Rocky Linux 8 beyond version 133. For important security and stability reasons, we've decided to discontinue our support for installing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate on Red Hat/Oracle Linux/Rocky Linux 8 after ActiveGate version 1.325. ActiveGate version 1.325 is the last Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate supported on Red Hat/Oracle Linux/Rocky Linux 8. Additionally, with Dynatrace version 1.326, we plan to introduce mechanisms preventing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates on Red Hat/Oracle Linux/Rocky Linux 8 from being updated beyond version 1.325.
- Chromium development for Amazon Linux 2 stopped at version 126. For important security and stability reasons, we've decided to discontinue our support for installing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate on Amazon Linux 2 after ActiveGate version 1.307. ActiveGate version 1.307 is the last Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate to support Amazon Linux 2. Additionally, with Dynatrace version 1.308, we have introduced mechanisms preventing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates on Amazon Linux 2 from being updated beyond version 1.307.
- Chromium development for Red Hat/CentOS 7 stopped at version 126.
For important security and stability reasons, we've decided to discontinue our support for installing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate on Red Hat/CentOS 7 after ActiveGate version 1.305.
ActiveGate version 1.305 is the last Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate to support Red Hat/CentOS 7.
Additionally, with Dynatrace version 1.306, we have introduced mechanisms preventing Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates on Red Hat/CentOS 7 from being updated beyond version 1.305.
- Since Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 reached End of Maintenance support on June 30, 2024, all of its packages have been archived. This means that it may not be possible to find the required dependencies for update. For more details, see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 status
- Until version 1.329 Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates on Ubuntu 20 and Ubuntu 22 use Chromium snap. When customizing the default temporary directory for private Synthetic files—
/var/tmp/dynatrace/synthetic, the path must begin with/var/tmp, for example,TEMP=/var/tmp/syn. Dynatrace requires write access to/var/tmpfor the installation of Chromium snap packages. Since version 1.331, these restrictions no longer apply. The latest ActiveGate version on Ubuntu 20 and Ubuntu 22 uses Chrome for Testing, just like Ubuntu 24.
Before you begin
-
You cannot execute synthetic monitors using an Environment ActiveGate configured for multi-environment support.
-
You can create a private location using a clean-installed Synthetic-enabled Environment ActiveGate version 1.169+ or Cluster ActiveGate with Dynatrace Managed version 1.176+. If you want to use an existing ActiveGate host, uninstall ActiveGate first.
-
Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate is used exclusively to run synthetic monitors. A clean ActiveGate installation for the purpose of synthetic monitoring disables all other ActiveGate features, including communication with OneAgents.
-
Make sure that the ActiveGate can connect to other Dynatrace components as well as the resource you want to test. See Set up a proxy for private synthetic monitoring.
-
Only IPv4 and DNS UDP are supported for network configuration.
-
Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate needs access to the Amazon S3 service to upload and access browser monitor screenshots from private locations. Ensure that your firewall configuration allows connections to
*.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.comon port443. You can also set up your proxy to connect to the Amazon S3 service. (Screenshots are stored in a different folder for each monitoring environment, but the S3 Bucket is the same (ruxit-synth-screencap). Data is encrypted by Amazon S3-managed key.) -
Both manual and automatic browser updates require access to
https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com. For security reasons, public access to the S3 bucket is enabled only for specific files; trying anything else will result in a 403 error.
Install a Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate
The instructions below describe how to install an ActiveGate in the previous Dynatrace. To learn how to install an ActiveGate in the latest Dynatrace, see Private synthetic locations on Grail.
Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate is used exclusively to run synthetic monitors. A clean ActiveGate installation for the purpose of synthetic monitoring disables all other ActiveGate features, including communication with OneAgents. Make sure the host on which you install the ActiveGate has access to the internet.
If this web UI-guided installation fails, or you prefer to prepare the host for the Synthetic engine yourself, you can manually install the browser and other dependencies via S3. You can also install the browser from a custom, local repository.
-
For Environment ActiveGate, in Dynatrace Hub, select ActiveGate > Set up.
For Cluster ActiveGate, go to the Dynatrace Cluster Management Console and select More
> Add new Cluster ActiveGate.
-
Select the operating system to view instructions.
-
Create a PaaS Token or enter an existing token. This token has the Download OneAgent and ActiveGate installers
InstallerDownloadtoken scope, which allows you to download the ActiveGate installer. Once provided, the token is automatically appended to download and installation commands, which are then displayed in the UI.You can find existing tokens listed on the Access tokens page. Note that a PaaS token is only displayed once upon creation, after which it's stored encrypted and cannot be revealed. We recommend that you store a PaaS token after creation in a password manager so that you can reuse it as needed.
-
Linux only For Choose installer type, keep the default selection:
x86/64. -
For What's the purpose of this ActiveGate, select Run synthetic monitors from a private location.
-
Optional Assign the ActiveGate to a private Synthetic location—select a location from the dropdown list. You can also assign the ActiveGate to a location after installation.
-
Optional You can turn off support for browser monitors. If you do so, the Synthetic ActiveGate will be treated as browserless.
-
Optional Set customized options to assign the ActiveGate to a Network zone and ActiveGate group.
-
Download the installer to the target host.
-
Linux only Recommended Verify signature—run the displayed command on the target host to download a certificate file and verify the installer.
-
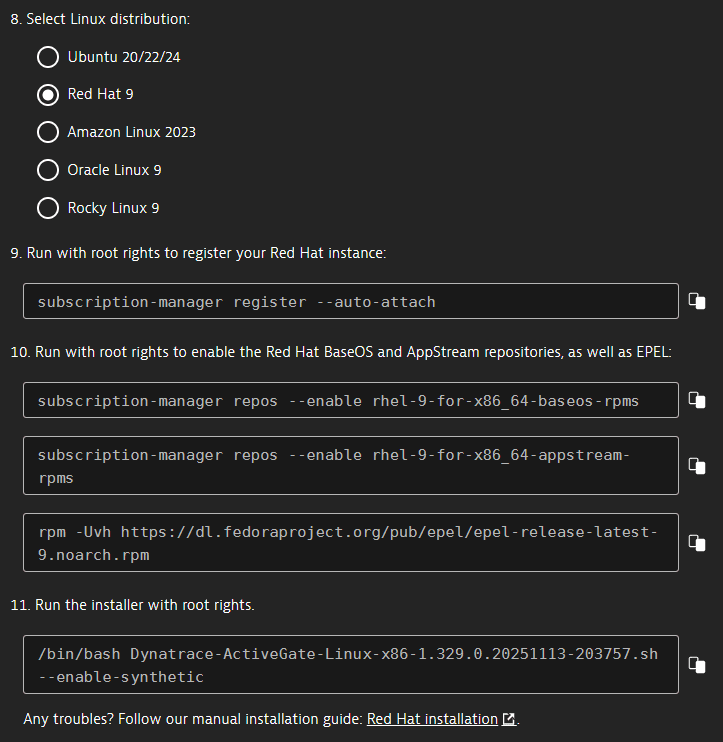
Linux only Select a Linux distribution.
-
Run the installer and any other commands—make sure you use the exact commands displayed in the UI.
Linux only The installer automatically downloads the browser and dependencies required by the Synthetic engine. On Red Hat, Oracle Linux, and Rocky Linux you also need to enable repositories from which the installer downloads the dependencies. As a prerequisite for enabling proprietary repositories on Red Hat, you need to register your Red Hat instance. The web UI provides you with all the required commands for doing so, as shown in the example below.
-
Verify the ActiveGate installation (Show deployment status).
Add a private location
The instructions below describe how to add a private location in previous Dynatrace. To learn how to add a private location in latest Dynatrace, see Private synthetic locations on Grail.
-
Search for and select Settings. Then select Web & mobile monitoring > Private synthetic locations.
-
Select Create location.
-
Give your location a custom Name, for example
Boston office, 3rd floor. -
Map it from an existing geographic location or add a custom geographic location defined by Country, Region, City, and Geographic coordinates.
-
Add a Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate to the location. Note that an ActiveGate can only be assigned to a single location.
You can also leave the location temporarily unassigned and assign it during the ActiveGate installation process.
-
Select Add.
-
Select Save.
Create a synthetic monitor
Now, when you create your HTTP or browser monitor, select the location you've just created from the list of all available locations. For more information, see Create an HTTP monitor, Create a single-URL browser monitor, or Record a browser clickpath.
Linux only Install the browser and dependencies manually from S3
This section is not relevant for browserless locations.
Amazon Linux 2023, Ubuntu and Oracle Linux 9 use Chrome for Testing instead of Chromium. For manual installation of Chrome for Testing on these operating systems, see Amazon Linux 2023, Ubuntu and Oracle Linux 9 (Chrome for Testing).
If the web UI-guided installation fails or you prefer to prepare the host for the Synthetic engine yourself, you can install the browser and other dependencies using the procedure below. Ensure that you can connect to https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com to access the browser and dependencies. For security reasons, public access to the S3 bucket is enabled only for specific files; trying anything else will result in a 403 error.
Also see Install the browser from a custom repository below.
See how to update the browser manually in Manage private Synthetic locations. We strongly recommend that you keep your Linux-based Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates and browser versions updated—Dynatrace supports browser versions that are no more than two versions behind the latest Dynatrace-supported version for a specific ActiveGate release.
Ubuntu Server 20.04 and 22.04
This section is only relevant for releases 1.329 and earlier.
-
Install Synthetic engine dependencies:
Synthetic engine dependencies:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install xvfb x11-xkb-utils xfonts-100dpi xfonts-75dpi xfonts-scalable libnss3-tools auditdChromium dependencies:
sudo apt-get -y install fonts-dejavu-coresudo snap install gnome-3-38-2004 gtk-common-themes -
Download and install Chromium.
-
Download the snap (Ubuntu Server 20.04 and 22.04) package archive. This is a safe and verified archive hosted by Dynatrace.
ActiveGate version 1.329
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-142.0.7444.175-3313.tgzActiveGate version 1.327
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-141.0.7390.122-3285.tgzActiveGate version 1.325
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-140.0.7339.185-3251.tgzActiveGate version 1.323
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-139.0.7258.138-3235.tgzActiveGate version 1.321
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-138.0.7204.157-3203.tgzActiveGate version 1.319
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-138.0.7204.100-3199.tgzActiveGate version 1.317
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-137.0.7151.103-3169.tgzActiveGate version 1.315
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-136.0.7103.59-3121.tgzActiveGate version 1.313
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-135.0.7049.95-3110.tgzActiveGate version 1.311
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-134.0.6998.35-3060.tgzActiveGate version 1.309
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-132.0.6834.159-3036.tgzActiveGate version 1.307
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/snap/chromium-131.0.6778.85-3002.tgzYou can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
-
Extract the installation packages. Go to the directory where you saved the archive and run the following command:
mkdir /tmp/chromium ; tar xzf chromium.tgz -C /tmp/chromiumThis creates a
/tmp/chromiumdirectory and extracts the packages into it. -
Install the extracted packages.
sudo chown -R root:root /tmp/snap-private-tmpsudo snap ack /tmp/chromium/chromium.assertsudo snap install --devmode /tmp/chromium/chromium.snapSubstitute
dtuseragwith the names of the ActiveGate service user and group if they differ from the default values.sudo chown -R dtuserag:dtuserag /tmp/snap-private-tmpThis installs all the packages extracted to the
/tmp/chromium/directory. You can delete the/tmp/chromium/directory and the downloadedchromium.tgzarchive after successful Chromium installation.
-
-
After you satisfy the dependencies, run the ActiveGate installer with root rights with the
--enable-syntheticparameter set tomanual. For example:/bin/bash ./Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux.sh --enable-synthetic=manual
You can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux 8, and Rocky Linux
- Chromium development for Red Hat/CentOS 7 and Amazon Linux 2 stopped at version 126.
- Since Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 reached End of Maintenance support on June 30, 2024, all of its packages have been archived. This means that it may not be possible to find the required dependencies for update. For more details, see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 status
- Chromium installation when a proxy is required for internet access.
- If you need to download and install Chromium, and your system requires a proxy for internet access, you should configure
curlto use the correct proxy. Specify your proxy and port details by running the commands as in this example:vi /root/.curlrcproxy=http://proxy.example.com:8080
- If you need to download and install Chromium, and your system requires a proxy for internet access, you should configure
-
Set up repositories and install dependencies.
Deprecated operating systemActiveGate version 1.305 is the last Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate to support Red Hat 7.
- Register the Red Hat instance.
sudo subscription-manager register --auto-attach
- Enable the Red Hat
ExtrasandOptionalrepositories as well asEPEL(Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux).sudo subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpmssudo subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-optional-rpmssudo rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm - Install Synthetic engine dependencies.
sudo yum install -y xorg-x11-server-Xvfb xorg-x11-xkb-utils xorg-x11-server-utils xorg-x11-fonts-100dpi xorg-x11-fonts-75dpi xorg-x11-fonts-Type1 libwayland-server mesa-libgbm curl nss-tools
- Register the Red Hat instance.
-
Download and install Chromium.
-
Download the rpm package archive. This is a safe and verified archive hosted by Dynatrace.
ActiveGate version 1.331
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-143.0.7499.192-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.329
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-142.0.7444.175-2.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.327
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-141.0.7390.122-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.325
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-140.0.7339.185-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.323
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-139.0.7258.138-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.321
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-138.0.7204.157-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.319
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-138.0.7204.100-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.317
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-137.0.7151.103-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.315
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-136.0.7103.59-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.313
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-135.0.7049.95-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.311
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-133.0.6943.141-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-134.0.6998.35-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.309
Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-132.0.6834.159-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-132.0.6834.159-1.el9.tgzActiveGate version 1.307
Amazon Linux 2
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-126.0.6478.114-1.el7.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Oracle/Rocky Linux 8
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-131.0.6778.204-1.el8.tgzRed Hat Enterprise Linux/Rocky Linux 9
curl --output chromium.tgz https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-131.0.6778.204-1.el9.tgzYou can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
-
Extract the installation packages. Go to the directory where you saved the archive and run the following command:
mkdir /tmp/chromium ; tar xzf chromium.tgz -C /tmp/chromiumThis creates a
/tmp/chromiumdirectory and extracts the packages into it. -
Install extracted packages.
sudo yum install -y /tmp/chromium/*.rpmThis installs all the packages extracted to the
/tmp/chromium/directory. You can delete the/tmp/chromium/directory and the downloadedchromium.tgzarchive after successful Chromium installation.
-
-
Disable automatic update of Chromium packages:
sudo yum -y install yum-plugin-versionlocksudo yum versionlock chromiumsudo yum versionlock chromium-common -
Optional Install non-Latin TrueType fonts:
sudo yum install dejavu-fonts-common.noarch dejavu-sans-fonts.noarch -
After you satisfy the dependencies, run the ActiveGate installer with root rights with the
--enable-syntheticparameter set tomanual. For example:/bin/bash ./Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux.sh --enable-synthetic=manual
You can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
Amazon Linux 2023, Ubuntu, and Oracle Linux 9 (Chrome for Testing)
See how to update Chrome for Testing manually in Manage private Synthetic locations. We strongly recommend that you keep your Linux-based Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates and Chrome for Testing versions updated—Dynatrace supports Chrome for Testing versions that are no more than two versions behind the latest Dynatrace-supported version for a specific ActiveGate release.
Unlike Chromium on other distributions, Chrome for Testing updates do not use package managers. You manually manage the Chrome binaries while dependencies are managed by the system package manager.
On Ubuntu Server 20.04 and 22.04 Chrome for Testing is supported since 1.331
-
Set up repositories and install dependencies.
-
Install Synthetic engine dependencies:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install xvfb x11-xkb-utils xfonts-100dpi xfonts-75dpi xfonts-scalable libnss3-tools auditd unzip -
Install Chrome for Testing dependencies:
sudo apt-get -y install libasound2t64 libatk-bridge2.0-0t64 libatk1.0-0t64 libcairo2 libcups2t64 libgbm1 libnspr4 libnss3 libpango-1.0-0 libxcomposite1 libxdamage1 libxfixes3 libxkbcommon0 libxrandr2
-
-
Download and set up Chrome for Testing.
-
Create the Chrome for Testing directory:
sudo mkdir -p /usr/lib/chrome_for_testing -
Download the Chrome for Testing package archive to a temporary location. This is a safe and verified archive hosted by Dynatrace.
ActiveGate version 1.331
curl --output /tmp/chrome.zip https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zipActiveGate version 1.329
curl --output /tmp/chrome.zip https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-142.0.7444.175.zipActiveGate version 1.327
curl --output /tmp/chrome.zip https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-141.0.7390.122.zipYou can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
-
Extract the installation package and clean up:
sudo unzip /tmp/chrome.zip -d /usr/lib/chrome_for_testingrm /tmp/chrome.zipThis creates a
chrome-linux64directory inside/usr/lib/chrome_for_testingand extracts the Chrome binary and supporting files into it. -
Verify Chrome for Testing by checking the version:
/usr/lib/chrome_for_testing/chrome-linux64/chrome --versionCommand output should show the Chrome version you downloaded.
-
-
After you satisfy the dependencies, run the ActiveGate installer with root rights. The installer will automatically detect and validate Chrome for Testing. For example:
/bin/bash ./Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux.sh --enable-synthetic=manual
-
Custom Chrome for Testing directory: If you want to use a different directory than the default
/usr/lib/chrome_for_testing, specify it by setting thesynthetic_chrome_for_testing_pathproperty in thecustom.propertiesfile after installation. The new directory will be used after the upgrade of Synthetic module. -
Chrome for Testing files are preserved during ActiveGate uninstallation. If you uninstall the ActiveGate, the Chrome for Testing directory and its contents will remain on the system and can be reused during reinstallation.
-
You can verify the authenticity of the packages using the signature files stored together with the package archives.
Linux only Install the browser from a custom repository
ActiveGate version 1.243+ In addition to web UI-guided ActiveGate installation and manual installation of the browser and dependencies, you can also install ActiveGate by pointing to a custom, local repository for browser components. As this repository is an HTTP server that you set up within your network, the advantage of this method is that it can be used in environments with intranet-only or limited network access.
This method of installing the browser broadly consists of:
- Downloading the required Dynatrace-hosted deb, snap, or rpm package archives and their corresponding signature files.
- Installing and running a locally hosted web server where the downloaded browser components reside.
- Downloading and running the ActiveGate installer on the target host with an environment variable pointing to the location of the custom repository on the HTTP server.
- A custom browser repository can be used only for the browser components, not their dependencies. Installing the browser from a custom repository will only work if all dependencies have been resolved before installation.
- Custom repositories can only be used for Browser installation and autoupdate—see Browser autoupdate from a custom repository in Manage private Synthetic locations for details.
-
Download the browser components—the package archive and signature file—from the safe and verified archive hosted by Dynatrace. See Requirements for private Synthetic locations for links to the latest supported and provided browser versions.
We recommend keeping your Linux-based Synthetic-enabled ActiveGates and browser versions up to date; choose the latest provided browser version for ActiveGate.
For example, for ActiveGate version 1.331 on Ubuntu 24 the required files are:
- Package archive—
https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zip - Signature file—
https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zip.sig
The corresponding download commands are:
curl -o chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zip https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zipcurl -o chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zip.sig https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chrome/chrome-for-testing-linux64/chrome-for-testing-linux64-143.0.7499.192.zip.sig - Package archive—
-
Install a web server of your choice and create a directory, for example,
chromium-repo, to serve the browser components to the ActiveGate host. Copy the downloaded browser components to this directory. -
Download the ActiveGate installer from Dynatrace Hub.
-
Resolve all dependencies and enable repositories as required as shown in Install the browser and dependencies manually from S3 above. The custom repository can be used only for browser packages, not their dependencies.
-
Install the ActiveGate with the Synthetic module enabled (
--enable-synthetic) and theDYNATRACE_SYNTHETIC_CUSTOM_CHROMIUM_REPOenvironment variable pointing to the location of the custom repository (https://172.18.0.100/chromium-repoin this example).sudo DYNATRACE_SYNTHETIC_CUSTOM_CHROMIUM_REPO=http://172.18.0.100:8000/chromium-repo /bin/bash Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux-x86-*.sh --enable-syntheticYou can use the hostname of the HTTP server instead of the IP address so long as the ActiveGate host can resolve the hostname.
Once you've installed the browser in this way from a custom repository, it can only be autoupdated. See Browser autoupdate from a custom repository in Manage private Synthetic locations for details and update alternatives.
Custom browser version
You can install a custom browser version, that is, override the browser version that the ActiveGate installer looks for. This is applicable for manual ActiveGate installation, as described in Browser installation via S3 or via a custom repository.
In this command for manual ActiveGate installation via S3, an environment variable points to an explicit browser version number 143.0.7499.192, which is part of the Chrome for Testing package archive.
sudo /bin/bash -c "export DYNATRACE_SYNTHETIC_EXPLICIT_CHROMIUM_VERSION=143.0.7499.192; /bin/bash Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux-x86-*.sh --enable-synthetic"
This command searches for the browser version 143.0.7499.192 in the custom repository https://172.18.0.100/chromium-repo.
sudo DYNATRACE_SYNTHETIC_EXPLICIT_CHROMIUM_VERSION=143.0.7499.192 DYNATRACE_SYNTHETIC_CUSTOM_CHROMIUM_REPO=http://172.18.0.100:8000/chromium-repo /bin/bash Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux-x86-*.sh --enable-synthetic
Browserless Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate
In general, we recommend the deployment of a Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate to support the execution of all types of synthetic monitors (HTTP, browser, NAM).
If you don’t need to run browser monitors, consider deploying your node in browserless mode. This mode deploys the node without a browser, reducing hardware requirements. However, browser monitors can’t run on a browserless node.
Consider browserless nodes as an alternative to nodes with browser monitor support when you're focused purely on:
- Network and infrastructure use cases (using NAM monitors)
- API monitoring (using HTTP monitors)
Kerberos client setup
If you want to run browser monitors using Kerberos authentication, the private location should be configured to be able to get a ticket from the Kerberos Key Distribution Center.
- Each Windows machine using Kerberos has to be properly configured with Active Directory.
- If you are unable to authenticate with Kerberos on Windows, use the following command to register the machine.
ksetup /addkdc DOMAIN.TO.ADD address.of.kerberos.server
The DOMAIN.TO.ADD is your domain name and address.of.kerberos.server is the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (Active Directory Controller if you're using a Microsoft solution). Note that in the credentials used, the domain name must be in uppercase (for example, user@EXAMPLE.COM).
Synthetic FIPS compliance
ActiveGate version 1.315+
Installation
To install Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate in FIPS compliant mode you need to add --fips-mode flag, see also customize ActiveGate installation for FIPS compliance.
/bin/bash ./Dynatrace-ActiveGate-Linux.sh --enable-synthetic --fips-mode
Please note that FIPS-compliant mode cannot be changed after installation. To change the mode, you need to uninstall ActiveGate and reinstall it with the desired settings. Additionally, if you intend to execute browser monitors, additional setup will be required as described in Proxy configuration for FIPS mode and Proxy configuration for FIPS mode with corporate proxy
Requirements and limitations
- We require operating system with FIPS-compliant mode enabled, see also ActiveGate FIPS compliance.
- Following operating systems are currently supported:
- Ubuntu Pro 22.04
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9
- Private Synthetic locations on Kubernetes are not supported at the moment.
Ensuring compliance
To ensure the browser monitor traffic is FIPS compliant, it must be routed through a local intercepting proxy that encrypts traffic with a FIPS-certified crypto library. See Proxy configuration for FIPS mode for details.
For HTTP monitors, we use the Amazon Corretto Crypto Provider FIPS-certified cryptographic library that uses AWS-LC-FIPS 2.x as its cryptographic module. See Certificate #4816.
Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate in FIPS compliant mode supports the same set of cipher suites as regular ActiveGate.
FAQ
How can I verify the authenticity of downloaded Chrome(-ium) packages?
Each tgz package archive is stored in the S3 bucket together with the *.tgz.sig signature file. To verify if the packages on your drive are authentic Dynatrace-provided archives:
-
Download the signature file. The filename is identical to the package archive but has the
sigfilename extension. For example, for Chromium 140, the command is:curl --output chromium.tgz.sig https://synthetic-packages.s3.amazonaws.com/Chromium/rpm/chromium-140.0.7339.185-1.el9.tgz.sig -
Verify the package:
wget https://ca.dynatrace.com/dt-root.cert.pem ; openssl cms-verify-in chromium.tgz.sig-inform PEM-content chromium.tgz-binary-CAfile dt-root.cert.pem > /dev/null -
Verify the signature timestamp.
You can also get the exact timestamp of a signature. Download the
*.tgz.sig.tsrfile from the same location as installation packages and signature and run the following command:openssl ts -reply -in chromium.tgz.sig.tsr -text
Can I use a proxy with the Synthetic-enabled ActiveGate?
With ActiveGate version 1.175+, an ActiveGate executing synthetic monitors can connect through the proxy to both the Dynatrace Cluster and the tested resource. For more information, see Setting up proxy for private synthetic monitoring.
Can I update an earlier ActiveGate to version 1.169+ and configure it to use with private synthetic monitors?
No, you need to run a clean installation specifically for the purpose of synthetic monitoring to enable your ActiveGate to execute monitors from private locations.
Can I turn on Synthetic on an existing ActiveGate installation?
Private Synthetic locations require a clean installation of ActiveGate specifically for the purpose of synthetic monitoring.
Manually editing the custom.properties file is not enough to enable the ActiveGate to execute synthetic monitors.
Troubleshooting
Can't see screenshots in browser monitor results
Visit the Troubleshooting forum in the Dynatrace Community for more troubleshooting information.
Related topics
 Synthetic Classic
Synthetic Classic