Automate vulnerability remediation with Atlassian Rovo Dev and Dynatrace
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
- Published Jan 29, 2026
- Preview
Overview
Dynatrace helps development teams focus on what matters by verifying vulnerabilities with runtime context and streamlining remediation through Atlassian Rovo Dev. This use case demonstrates how to prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities that impact production applications, with seamless integration to Jira for ticket management and Bitbucket for pull request creation. It supports two implementation paths, depending on where you want to triage and trigger fixes—both powered by Dynatrace MCP and Atlassian integrations.
Challenge
Vulnerability scanners detect hundreds of high and critical CVEs in application dependencies, but they lack runtime context. Without knowing which libraries are actually loaded or which code paths are executed in production, developers face a difficult choice: attempt to fix every vulnerability—wasting valuable time on issues that don't impact production—or prioritize based on guesswork and risk missing the vulnerabilities that actually affect business-critical services.
This lack of context creates alert fatigue and slows down remediation. Teams need a way to focus on vulnerabilities that are confirmed to impact production, while confidently deprioritizing those that pose no real risk.
Solution
Dynatrace integrates with Atlassian Rovo Dev via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enriching the developer experience with runtime context and Runtime Vulnerability Analytics (RVA) validation. This enables Rovo Dev to take targeted action directly from the IDE:
-
Confirmed vulnerabilities are prioritized for remediation: Rovo Dev queries Dynatrace for runtime-validated vulnerabilities, ensuring developers focus on issues that actually impact production.
-
Intelligent ticket management: Rovo Dev creates Jira tickets for confirmed findings, automatically checking for duplicates before creation, and updates tickets as remediation progresses.
-
End-to-end remediation workflow: From vulnerability detection to code fix, pull request creation, and ticket updates—all without leaving the IDE.
This reduces noise and developer effort by ensuring only relevant vulnerabilities are remediated, while maintaining full traceability in Jira.
You can implement this solution in two ways, depending on where you want to triage vulnerabilities and trigger remediation:
-
IDE/CLI-based workflow: Uses Rovo Dev in the IDE or Rovo Dev CLI as the main engagement point, connected to Dynatrace MCP server. Developers interact with Rovo Dev to query vulnerabilities, apply fixes, create Bitbucket pull requests, and manage Jira tickets.
-
Dynatrace-driven workflow: Uses
 Workflows as the trigger and processing engine, with Jira tickets created automatically. Developers then use Rovo Dev to pick up tickets, apply fixes, and complete the remediation cycle.
Workflows as the trigger and processing engine, with Jira tickets created automatically. Developers then use Rovo Dev to pick up tickets, apply fixes, and complete the remediation cycle.
Prerequisites
See below for the Atlassian and Dynatrace requirements.
Atlassian
-
Have access to your organization's Jira Cloud instance.
-
Install an Atlassian extension (VS Code, JetBrains IDEs) in your IDE.
-
Install Atlassian Rovo Dev in your IDE.
-
Create an Atlassian API token for authenticating with the following project permissions:
-
Browse projects -
Create issues -
Edit issues -
Transition issues -
Add comments -
Link issues
-
-
Configure Bitbucket or any other Git repository with write access in your IDE (required for Rovo Dev to commit code changes and create pull requests on your behalf). Ensure the AI agent has permissions to push to branches and open PRs.
-
Configure Rovo Dev with the Jira and Bitbucket integrations.
Dynatrace
-
Set up monitoring with Dynatrace OneAgent for the production services.
-
Create a Dynatrace platform token with the following permissions:
-
mcp-gateway:servers:invoke -
mcp-gateway:servers:read -
davis-copilot:conversations:execute -
davis-copilot:nl2dql:execute -
davis-copilot:dql2nl:execute -
storage:entities:read -
storage:smartscape:read -
storage:buckets:read -
storage:bucket-definitions:read -
storage:security.events:read
-
IDE/CLI-based workflow
In this scenario, a developer interacts with Rovo Dev in their IDE to query Dynatrace for vulnerabilities, apply fixes, and manage the entire remediation lifecycle through Jira and Bitbucket.
How it works (IDE-based workflow)
-
Dynatrace detects vulnerabilities in production applications via Runtime Vulnerability Analytics.
-
A developer opens their IDE with the affected repository and invokes Rovo Dev.
-
The developer prompts Rovo Dev to query vulnerabilities for the relevant service (for example, "List critical vulnerabilities for the frontend service"). RovoDev uses the Dynatrace MCP server to retrieve runtime-validated vulnerabilities.
-
The developer selects a vulnerability and requests detailed information from Dynatrace.
-
Rovo Dev checks Jira for existing tickets; if none exist, it creates a new ticket with vulnerability details.
-
The developer instructs Rovo Dev to apply the fix based on the Jira ticket context.
-
Rovo Dev analyzes the codebase, applies the necessary changes, and runs tests.
-
Rovo Dev creates a Bitbucket pull request with the fix and links it to the Jira ticket.
-
The Jira ticket is updated with the PR link and transitioned to "In Review".
-
Developers review and merge the pull request.
Get started (IDE-based workflow)
To get started, follow the steps below.
1. Configure Dynatrace MCP server
-
Configure the MCP server in your IDE's Rovo Dev settings as shown below, making sure to replace
<DYNATRACE_TENANT>with your environment, for examplemytenant.apps.dynatrace.com<DYNATRACE_PLATFORM_TOKEN>with the Dynatrace token generated in prerequisites
{"mcpServers": {"dynatrace": {"transport": "sse","url": "https://<DYNATRACE_TENANT>/platform/mcp-gateway/sse","headers": {"Authorization": "Api-Token <DYNATRACE_PLATFORM_TOKEN>"}}}}
2. Add custom instructions for the Dynatrace agent
You can provide custom instructions to guide Rovo Dev when interacting with Dynatrace. Download the instructions.md file and configure it using one of the following methods:
-
Option 1: Global Memory file
-
In Rovo Dev, click the menu (three dots) and select Open Global Memory file.
-
Add the contents of the instructions.md file to provide Dynatrace-specific guidance across all your projects.
-
-
Option 2: Repository-level instructions
-
Create an
AGENTS.mdfile in the root of your repository (or the folder in context). -
Add the contents of the
instructions.mdfile to provide project-specific Dynatrace agent instructions.
-
The instructions file contains guidance for querying vulnerabilities, interpreting Dynatrace security events, and following remediation best practices.
3. Configure Atlassian integrations
-
Ensure Rovo Dev is connected to your Jira Cloud instance. Follow the Rovo Dev setup guide to authenticate.
-
Connect Rovo Dev to your Bitbucket repository for pull request creation. You can use the Atlassian VSC extension to authenticate.
-
Clone the affected repository locally and open it in your IDE.
4. Interact with Rovo Dev
Use natural language prompts to drive the workflow:
- Query vulnerabilities:
List all critical vulnerabilities from Dynatrace
- Get vulnerability details:
Get details for [this] vulnerability from Dynatrace
- Create a Jira ticket (with duplicate check):
Create a Jira ticket for this vulnerability, but only if there isn't an existing ticket already
- Apply fixes based on ticket context:
Based on the Jira ticket context, analyze my codebase and apply the necessary fixes for this vulnerability
- Create a pull request:
Create a pull request for this fix to the main branch
- Update the Jira ticket:
Update the Jira ticket with the PR link and move it to "In Review"
Dynatrace-driven workflow
This scenario uses  Workflows to automatically triage vulnerabilities and create Jira tickets, with Rovo Dev handling the remediation phase.
Workflows to automatically triage vulnerabilities and create Jira tickets, with Rovo Dev handling the remediation phase.
How it works (Dynatrace-driven triaging)
-
Dynatrace detects vulnerabilities via Runtime Vulnerability Analytics.
-
A Dynatrace workflow runs on a configured schedule to identify new critical, runtime-confirmed vulnerabilities.
-
The workflow uses Davis CoPilot to summarize findings and automatically creates Jira tickets for confirmed vulnerabilities.
-
A developer receives the Jira ticket notification and opens the affected repository in their IDE.
-
The developer loads the Jira ticket as context by selecting it in the Atlassian extension, providing full vulnerability details.
-
If necessary, the developer can get additional observability context using the configured Dynatrace MCP server.
-
The developer instructs Rovo Dev to apply the fix, create a Bitbucket pull request, and update the ticket.
-
Developers review and merge the pull request.
Get started (Dynatrace-driven workflow)
To get started, follow the steps below.
1. Deploy Dynatrace workflow
Download and deploy the Dynatrace workflow.
2. Configure Rovo Dev
-
Ensure Rovo Dev is connected to your Jira Cloud instance. Follow the Rovo Dev setup guide to authenticate.
-
Connect Rovo Dev to your Bitbucket repository for pull request creation. You can use the Atlassian VSC extension to authenticate.
-
Clone the affected repository locally and open it in your IDE.
3. Remediate from Jira context
When a Jira ticket is assigned:
-
Open the affected repository in your IDE.
-
Load the Jira ticket as context in Rovo Dev.
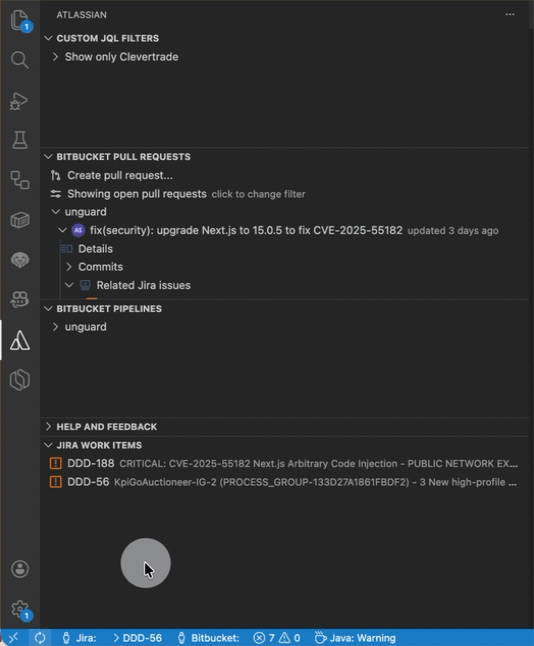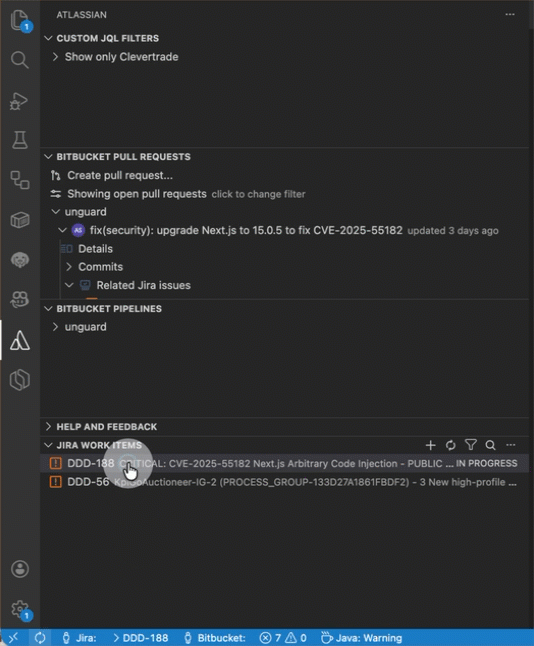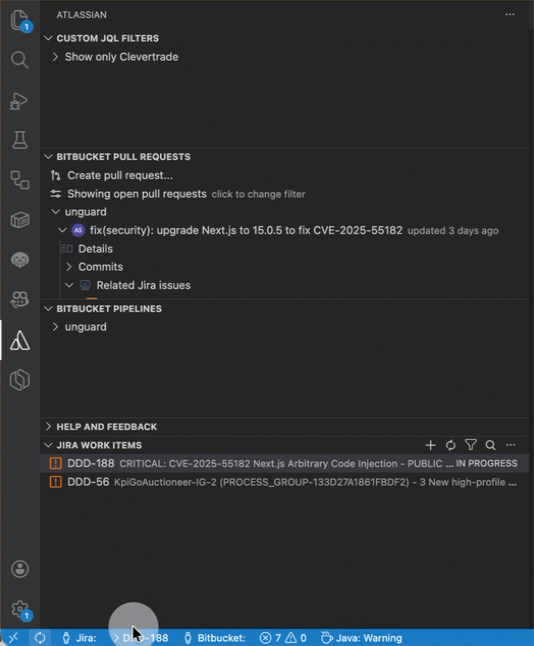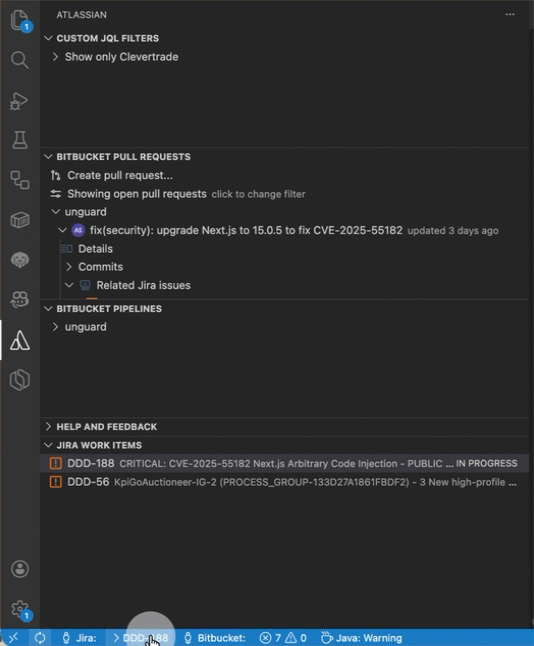
-
Use natural language to drive remediation:
Based on the Jira ticket context, apply the fix for this vulnerability, create a PR, and update the ticket
Additional use cases
The Dynatrace MCP server provides additional tools that Rovo Dev can use, enabling additional use cases, such as:
-
Incident response: Query active problems from Dynatrace, get root cause analysis, and create incident tickets in Jira with full observability context.
-
Performance optimization: Retrieve slow transaction data, database query insights, and service dependencies to inform optimization efforts.
-
Capacity planning: Use timeseries forecasting to predict resource utilization and create proactive capacity tickets.
-
Observability context for existing tickets: For any Jira ticket, query Dynatrace for related logs, traces, metrics, and entity relationships to accelerate troubleshooting.