Containerized ActiveGate configuration
- Latest Dynatrace
- 6-min read
- Published Sep 01, 2023
An ActiveGate container can be configured to some degree using container-specific methods via variables or secrets. More advanced settings require providing an ActiveGate custom.properties file. See Advanced configuration to learn how to use Kubernetes mechanisms such as ConfigMap to map it into the custom.properties.
To ensure security, you must pass the sensitive information to an ActiveGate container in a file containing a secret.
Environment configuration
An ActiveGate container image does not hold any configuration related to your environment.
See below for the mandatory configuration settings to make your ActiveGate container work.
Communication endpoints
This is a comma-separated list of the communication endpoints to be used by ActiveGate to send data to your Dynatrace environment.
To determine the endpoints, use GET connectivity information for ActiveGate in the Dynatrace API.
Environment ID
The Dynatrace environment ID.
Token
The tenant token is used by OneAgents and ActiveGates to report data to Dynatrace. Dynatrace automatically generates the tenant token for your ActiveGate.
To determine the token, use GET connectivity information for ActiveGate in the Dynatrace API.
ActiveGate token
ActiveGate requires a unique ActiveGate token to authorize in the Dynatrace Cluster.
For instructions, see Generate ActiveGate token.
Deployment settings
Activation group
Defines the ActiveGate group to which the ActiveGate belongs. An ActiveGate can belong to only one group. The name of an ActiveGate group is a string of alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and dots (.). Dots are used as separators, so you must not use a dot as the first character of a group name. The length of the string is limited to 256 characters. You can use ActiveGate groups to perform bulk actions on your ActiveGates, such as managing Extensions running on ActiveGates. If you want to assign your ActiveGate to a group, see ActiveGate group.
Network zone
Defines the network zone to which the ActiveGate belongs. An ActiveGate can belong to only one network zone. The name of a network zone is a string of alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and dots (.). Dots are used as separators, so you must not use a dot as the first character of a network zone name. The length of the string is limited to 256 characters.
Enabled modules
Containerized ActiveGate does not enable any functionalities by default. Enabled modules need to be specified using the DT_CAPABILITIES environment variable. Add a comma-separated list of module names as the variable value.
See ActiveGate modules for a complete list. Generally, you should refer to the custom.properties section names as the module names, for example, cloudfoundry_monitoring.
The exceptions to this rule are the following modules that are stored in the [collector] section.
MSGrouter—Enables message routingrestInterface—Enables REST API modulejava-script-agent-servlet—Enables JavaScript agent
Not all modules are supported in containerized deployments yet. For more information, see ActiveGate purposes and functionality.
Network settings
Proxy
The proxy used for communication with the Dynatrace Cluster to which ActiveGate sends data.
Advanced scenarios
For more advanced scenarios where one or more proxies are used for means other than communication with the Dynatrace Cluster, see Proxy for ActiveGate. Once you have crafted the required configuration, you can provide it to the ActiveGate container as a custom.properties file.
Rules for the proxy password
The proxy password needs to meet the following requirements.
| Requirements | Corresponding characters |
|---|---|
| Characters allowed | [A-Za-z0-9] ! " # $ ( ) * - . / : ; < > ? @ [ ] ^ _ { | } |
| Characters not allowed | blank space ' ` , & = + % \ |
Load balancer between ActiveGate and OneAgents
Dynatrace OneAgent accesses the ActiveGate via an auto-detected endpoint list. If a load balancer is placed on the path from OneAgent to the ActiveGate, such as Kubernetes Service, you need to explicitly set the endpoint to be used by OneAgents.
Load balancer between ActiveGate and the Dynatrace Cluster
A reverse proxy or a load balancer can be placed on the path from an ActiveGate to the Dynatrace Cluster. This allows your ActiveGate to connect to any available node of the Cluster, spreading the load between the nodes.
To do this, you need to:
- Provide the address of the reverse proxy/load balancer.
- Ensure that ActiveGate will ignore any further target address information sent from the Dynatrace Cluster, and will thus connect only to the address you have specified.
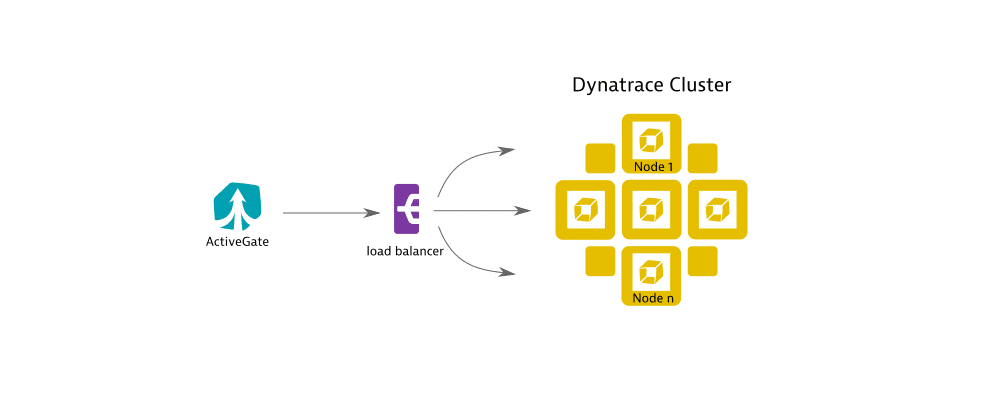
In this scenario, you need to set the following environment variables.
SSL settings
Custom SSL certificate
ActiveGate will serve a custom certificate instead of the default one. To configure this, you need a file in PKCS#12 format that contains a private key and its corresponding certificate chain. For more information, see Custom SSL certificate for ActiveGate.
Trusted root certificates
Additional trusted root certificates can be used by ActiveGate. To configure this, you need a file in the PEM format that contains a list of certificates to be included in the trust store. For more information, see Trusted root certificates for ActiveGate.
HTTP port
An ActiveGate container by default opens HTTPS port 9999. If you require your ActiveGate to communicate over plain HTTP, you need to explicitly specify the HTTP port.
Advanced configuration
In addition to the configuration settings passed via environment variables or files, you can configure all other configuration settings by providing the contents of the custom.properties file.
-
Define
ConfigMap.kind: ConfigMapapiVersion: v1data:custom.properties: |-[vmware_monitoring]vmware_monitoring_enabled = truemetadata:name: vmware-confignamespace: dynatrace -
Reference
ConfigMapin your deployment file.[...]volumeMounts:[...]- name: ag-confmountPath: /var/lib/dynatrace/gateway/config_template/custom.propertiessubPath: custom.properties[...]volumes:- name: ag-confconfigMap:name: vmware-configitems:- key: custom.propertiespath: custom.properties