Automate cloud misconfiguration triaging and remediation with Kiro CLI and Dynatrace
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
- Preview
Overview
Not every cloud misconfiguration needs to be fixed. Dynatrace helps SREs focus on what matters by verifying cloud misconfigurations with runtime context and streamlining remediation with Kiro CLI. This use case demonstrates how to prioritize and remediate cloud misconfigurations that impact production applications. It supports two implementation paths, depending on where and how you want to triage the issues—both powered by Dynatrace and Kiro CLI integrations.
Challenge
In complex cloud environments, the number of high and critical findings that need to be handled is very high. SREs cannot handle all of them, and they need an effective way to remediate those misconfigurations that risk their environments and introduce compliance issues. Cloud misconfiguration might not have a direct impact on production applications. An additional validation and context is needed for more effective triage and remediation efforts.
Solution
Dynatrace integrates with AWS products, such as AWS Security Hub, to enrich their findings with additional runtime context and verify them for production impact.
-
Confirmed findings require an immediate fix, which can be automated with the Kiro CLI.
-
Unconfirmed findings can be suppressed to remove them from the list of active issues.
This reduces noise and SRE effort by ensuring only relevant misconfigurations are remediated.
You can implement this solution in two ways, depending on where you want to triage cloud misconfigurations:
-
Kiro CLI-based triaging: Uses Kiro CLI as the main engagement point, connected to Dynatrace and (natively) AWS MCP servers. Users interact with Kiro CLI to first get the top cloud misconfigurations, contextualize and prioritize with Dynatrace context, and finally, remediate them.
-
Dynatrace-driven triaging: Uses
 Workflows as the main triaging engine with Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI workflow action to summarize the outcomes into a Jira ticket. The rest of the flow takes place in the Kiro CLI as in the first scenario.
Workflows as the main triaging engine with Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI workflow action to summarize the outcomes into a Jira ticket. The rest of the flow takes place in the Kiro CLI as in the first scenario.
Prerequisites
See below for the AWS and Dynatrace requirements.
AWS
-
Enable AWS Security Hub to monitor your AWS environment.
-
Install Kiro CLI and authenticate it with AWS.
Dynatrace
- Set up Dynatrace AWS monitoring for the desired AWS environment.
-
Create a Dynatrace platform token with the proper permissions to both access the MCP server and to query various event types.
Kiro CLI-based triaging
In this scenario, an SRE interacts with Kiro CLI to perform validation and remediation actions with the help of Dynatrace MCP.
How it works (Kiro CLI-based triaging)
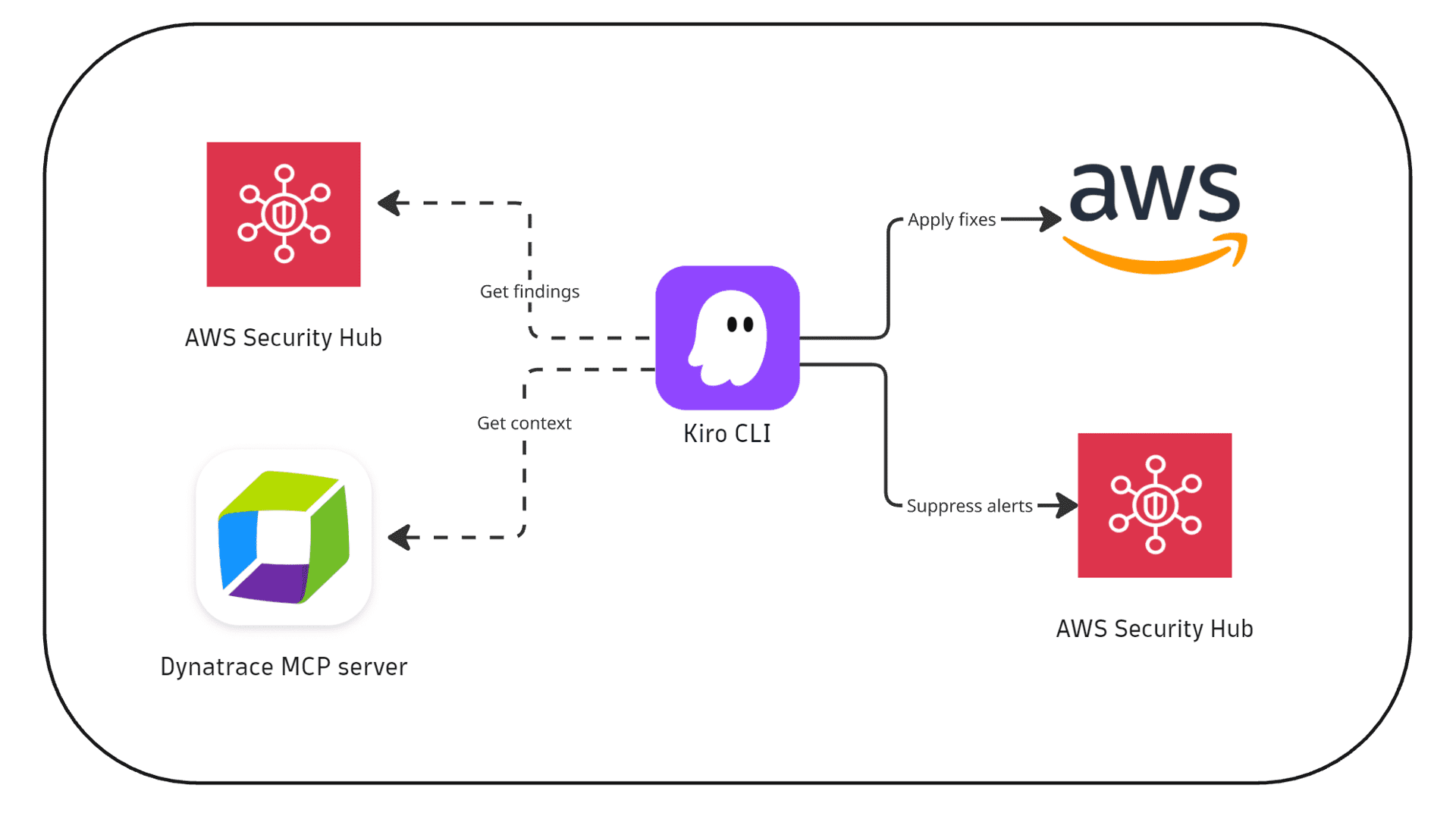
1. Detection
AWS Security Hub identifies cloud misconfigurations.
2. Verification
-
An SRE interacts with the Kiro CLI to extract top findings.
-
The Dynatrace agent, invoked by the Kiro CLI, utilizes the Dynatrace MCP server to verify whether these findings impact production applications.
3. Remediation
-
SRE remediates confirmed findings via Kiro CLI; others are suppressed.
-
Findings are resolved and verified in AWS Security Hub.
Get started (Kiro CLI-based triaging)
To get started, follow the steps below.
- Download the
dynatrace-security-agent.jsonfile and place it in.kiro/agents/. It contains the Dynatrace MCP configuration with the proper Dynatrace API Platform Token, and the reference to an instructions file. Make sure to replace:<DYNATRACE_TENANT>with your environment, for examplemytenant.apps.dynatrace.com.<DYNATRACE_PLATFORM_TOKEN>with the Dynatrace token generated in prerequisites.
- Download the
instructions.mdfile and place it in the same.kiro/agents/directory, next to the agent configuration file.
Dynatrace-driven triaging
In this scenario, initial validation and triage are automated in Dynatrace Workflows, and the SRE then acts on the Jira tickets to perform assisted remediation using the Kiro CLI.
How it works (Dynatrace-driven triaging)
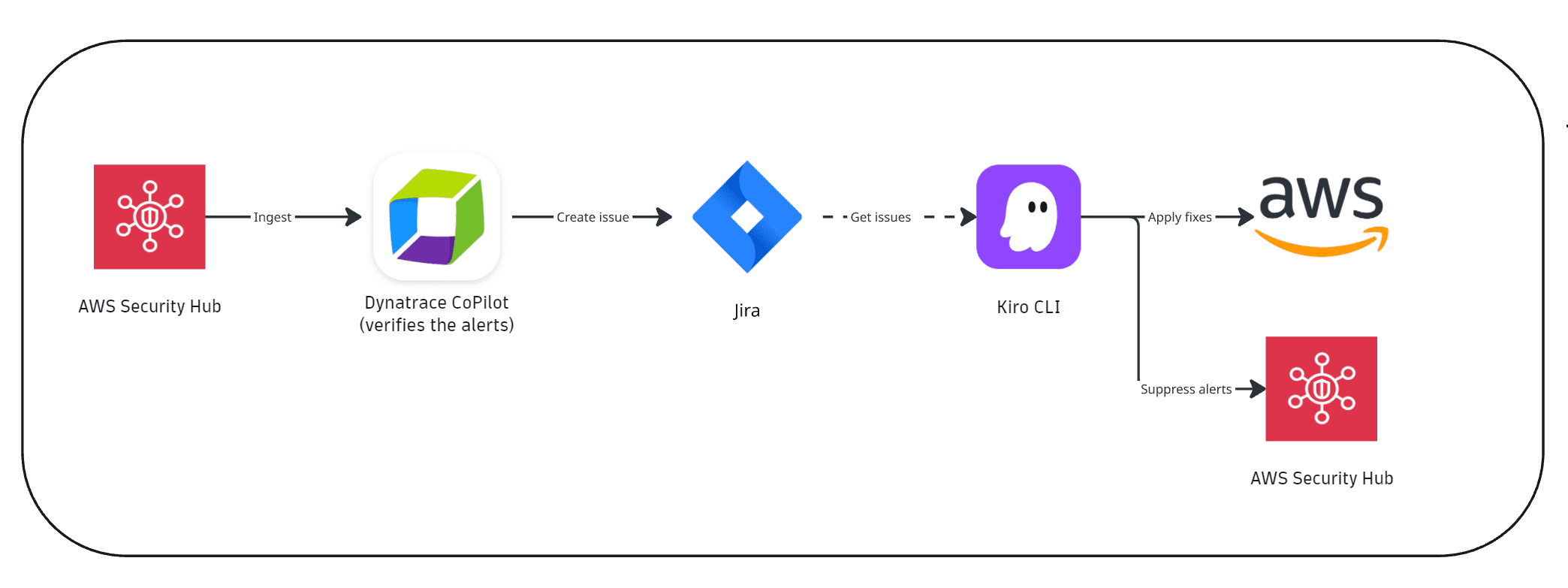
1. Detection
AWS Security Hub identifies cloud misconfigurations.
2. Verification
-
AWS Security Hub integration ingests findings into Dynatrace.
-
A Dynatrace workflow analyzes new critical/high-risk findings and performs the automated verification using the Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI workflow action.
3. Remediation
-
A Jira ticket is created automatically with the summary of the verification results.
-
An SRE uses Kiro CLI to act on the Jira findings. Confirmed findings are remediated, while the unconfirmed findings can be suppressed.
-
Findings are resolved in AWS Security Hub and are no longer in the top findings dashboard in Dynatrace.
Get started (Dynatrace-driven triaging)
To get started, follow the steps below.
-
Download the
dynatrace-security-agent.jsonfile and place it in.kiro/agents/. It contains the Dynatrace MCP configuration with the proper Dynatrace API Platform Token, and the reference to an instructions file. Make sure to replace:<DYNATRACE_TENANT>with your environment, for examplemytenant.apps.dynatrace.com.<DYNATRACE_PLATFORM_TOKEN>with the Dynatrace token generated in prerequisites.
-
Download the
instructions.mdfile and place it in the same.kiro/agents/directory, next to the agent configuration file. -
Optional Configure the Jira remote MCP as part of the Dynatrace agent or as a global Kiro setting (
.kiro/settings/mcp.json). For details, see Model context protocol (MCP). -
Deploy the Dynatrace triaging workflow for AWS Security Hub findings.
- Edit the configuration to set the desired values for Jira parameters (such as project key, issue type, assignee, reporter, and labels), which will be used by the Jira ticket creation action.
- Schedule the workflow to run periodically.