Automate vulnerability remediation with GitHub Copilot and Dynatrace
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
- Preview
Overview
Not every code issue needs to be fixed. Dynatrace helps development teams focus on what matters by verifying vulnerabilities with runtime context and streamlining remediation through GitHub Copilot. This use case demonstrates how to prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities that impact production applications. It supports two implementation paths, depending on where you want to triage and trigger fixes—both powered by Dynatrace and GitHub integrations.
Challenge
In complex codebases, the number of detected vulnerabilities can be overwhelming. While AI agents like GitHub Copilot can assist with automated remediation, human review and approval are still essential. Code changes may also introduce breaking changes, adding to development overhead. This makes effective prioritization and triaging of vulnerabilities—supported by rich context—critical to maintaining velocity and stability.
Solution
Dynatrace integrates with GitHub by enriching Dependabot alerts with runtime context and Runtime Vulnerability Analytics (RVA) validation. This enables GitHub Copilot to take targeted action:
-
Confirmed vulnerabilities are automatically fixed: GitHub Copilot opens a pull request with a secure fix for each vulnerability validated and confirmed by Dynatrace.
Example
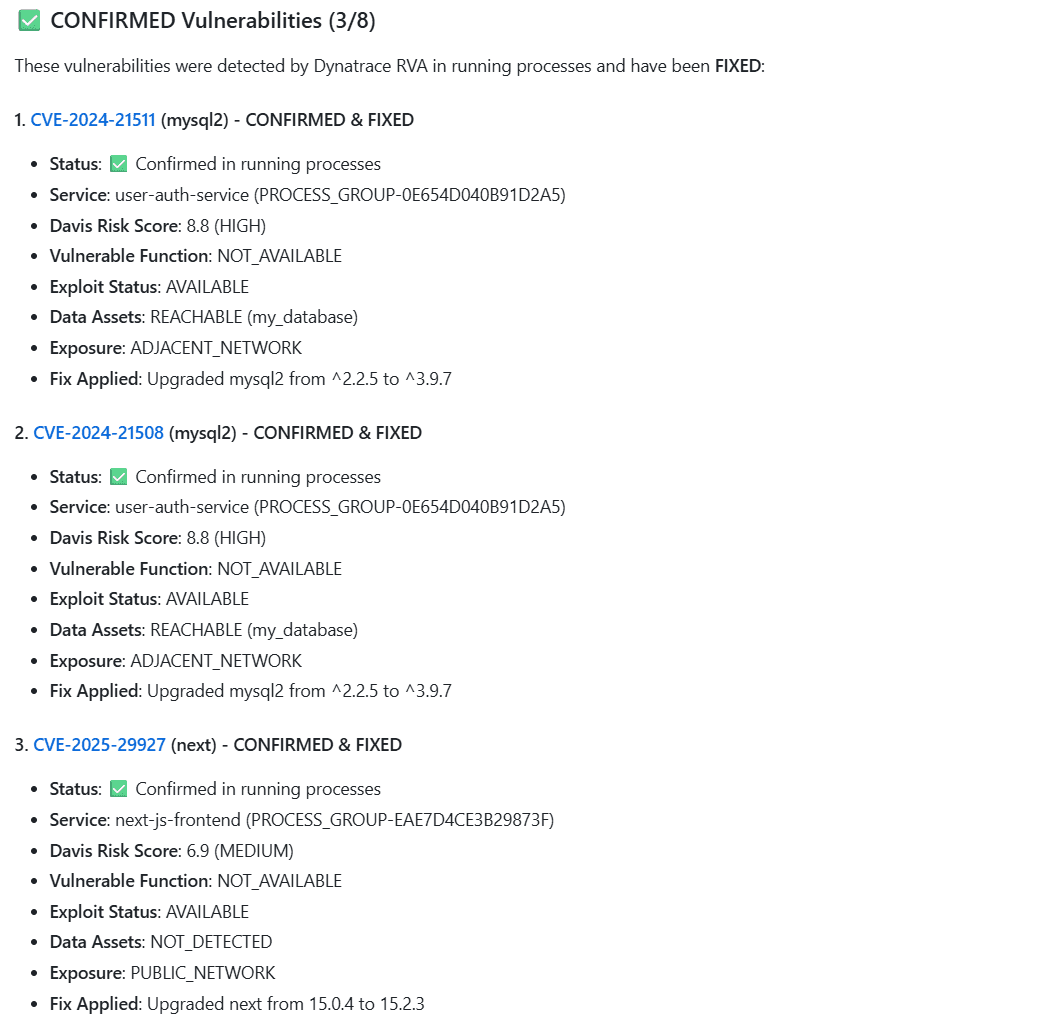
-
Unconfirmed vulnerabilities are dismissed with a reason: If Dynatrace validated a vulnerability at runtime and the vulnerable library isn't loaded or the vulnerable function isn't in use, the vulnerability is not confirmed, and GitHub Copilot dismisses the alert and explains why.
Example

This reduces noise and developer effort by ensuring only relevant vulnerabilities are remediated.
You can implement this solution in two ways, depending on where you want to triage vulnerabilities and trigger remediation:
-
GitHub-based workflow: Uses the Dynatrace MCP Server integrated with the GitHub Copilot coding agent or as a Dynatrace Security custom agent, triggered by a GitHub Actions workflows.
-
Dynatrace-driven workflow: Uses Dynatrace
 Workflows as the trigger and processing engine, with generative AI as the AI-driven analysis tool.
Workflows as the trigger and processing engine, with generative AI as the AI-driven analysis tool.
GitHub-based workflow
This scenario uses GitHub Actions workflow to detect new critical vulnerabilities and trigger GitHub Copilot to fix only those verified by Dynatrace.
How it works (GitHub-based workflow)
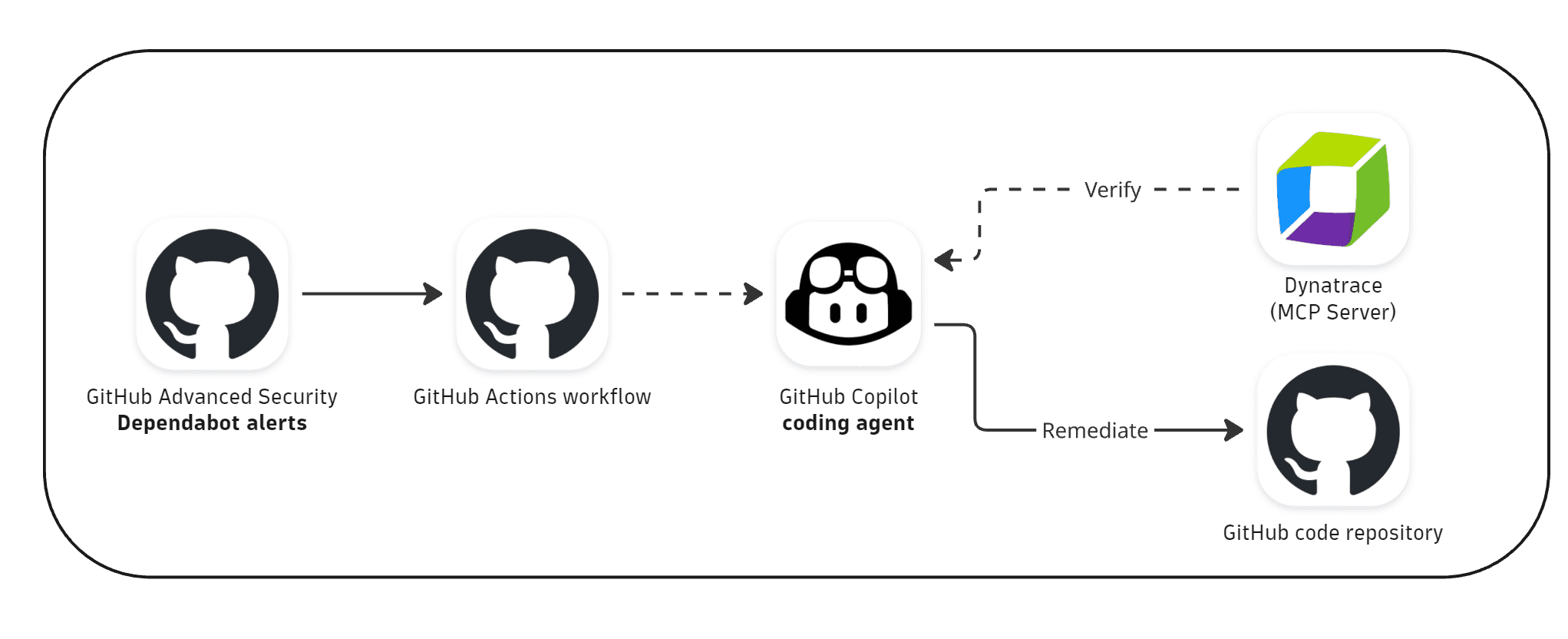
-
GitHub Dependabot detects vulnerabilities in code dependencies.
-
A GitHub workflow runs on a configured period to check for new critical vulnerabilities.
-
If new vulnerabilities are found, a GitHub issue is created and assigned to GitHub Copilot.
-
GitHub Copilot verifies each vulnerability by querying Dynatrace MCP for runtime context and RVA confirmation.
-
Confirmed vulnerabilities are remediated in a pull request; unconfirmed ones are dismissed in Dependabot with a reason.
-
Developers review and merge the pull request.
Get started (GitHub-based workflow)
To get started, follow the steps below.
1. Set up Dynatrace
-
Set up monitoring with Dynatrace OneAgent for the production services.
-
Create a Dynatrace platform token with the proper permissions to both access the MCP server and to query various event types.
1. List permissions
mcp-gateway:servers:invokemcp-gateway:servers:readdavis-copilot:conversations:executedavis-copilot:nl2dql:executedavis-copilot:dql2nl:executedavis-copilot:document-search:executestorage:entities:readstorage:smartscape:readstorage:buckets:readstorage:bucket-definitions:readstorage:security.events:read
2. Prepare your GitHub repository
-
Enable Dependabot. This ensures GitHub can detect vulnerabilities in dependencies and raise alerts.
-
Generate a fine-grained personal access token (PAT) with the proper permissions.
1. List permissions
- Read:
VariablesAdministrationDependabot secretsEnvironmentsMetadataWebhooksSecrets
- Read and write:
Dependabot alertsActionsCode scanning alertsCustom propertiesIssuesPull requestsWorkflowsContents
- Read:
-
Store the PAT created in step 2 as a GitHub secret for Copilot environment named
COPILOT_SPONSOR_PAT. This secret is exposed to the GitHub Copilot coding agent as an environment variable, allowing it to authenticate and perform actions in your repository on your behalf.
3. Connect GitHub Copilot to Dynatrace
To connect GitHub Copilot with Dynatrace MCP Server:
-
Configure Dynatrace MCP Server in your GitHub code repository.
-
Store your Dynatrace platform token as a GitHub secret for the Copilot environment named
COPILOT_MCP_DT_API_TOKEN. -
In your GitHub repo, go to Settings > Copilot > Agents.
-
Add an MCP server configuration like this:
{"mcpServers":{"dynatrace": {"type": "http","url": "https://pia1134d.dev.apps.dynatracelabs.com/platform-reserved/mcp-gateway/v0.1/servers/dynatrace-mcp/mcp","headers": {"Authorization": "Bearer $COPILOT_MCP_DT_API_TOKEN"},"tools": ["*"]}}}Make sure to replace
your-tenant-idwith the ID of your Dynatrace environment.
For reference, see Extending GitHub Copilot coding agent with the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
4. Add instructions for GitHub Copilot
To guide the GitHub Copilot coding agent on the verification procedure with Dynatrace, as well as required DQL knowledge for a successful Dynatrace MCP interaction, you have two options:
- Guide GitHub Copilot coding agent through a global instructions file: Download the
copilot-instructions.md file and add it in.github/. For instructions, see Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot. - Define a Dynatrace custom agent that GitHub Copilot will use to perform the use case: Download the
dynatrace-security-agent.md file and add it in.github/agents.
5. Set up the GitHub workflow
Download dependabot-alerts-processing.yml and add it in .github/workflows/. This checks for new critical vulnerabilities and triggers GitHub Copilot to remediate only those confirmed by Dynatrace.
For details, see Creating your first workflow.
Once configured, GitHub Copilot will begin triaging and remediating vulnerabilities as new alerts are detected.
You can test the workflow to ensure that everything is working as expected.
Dynatrace-driven workflow
This scenario uses Dynatrace to ingest and triage GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) alerts, then trigger GitHub Copilot to apply fixes only for vulnerabilities confirmed with runtime evidence.
How it works (Dynatrace-driven workflow)
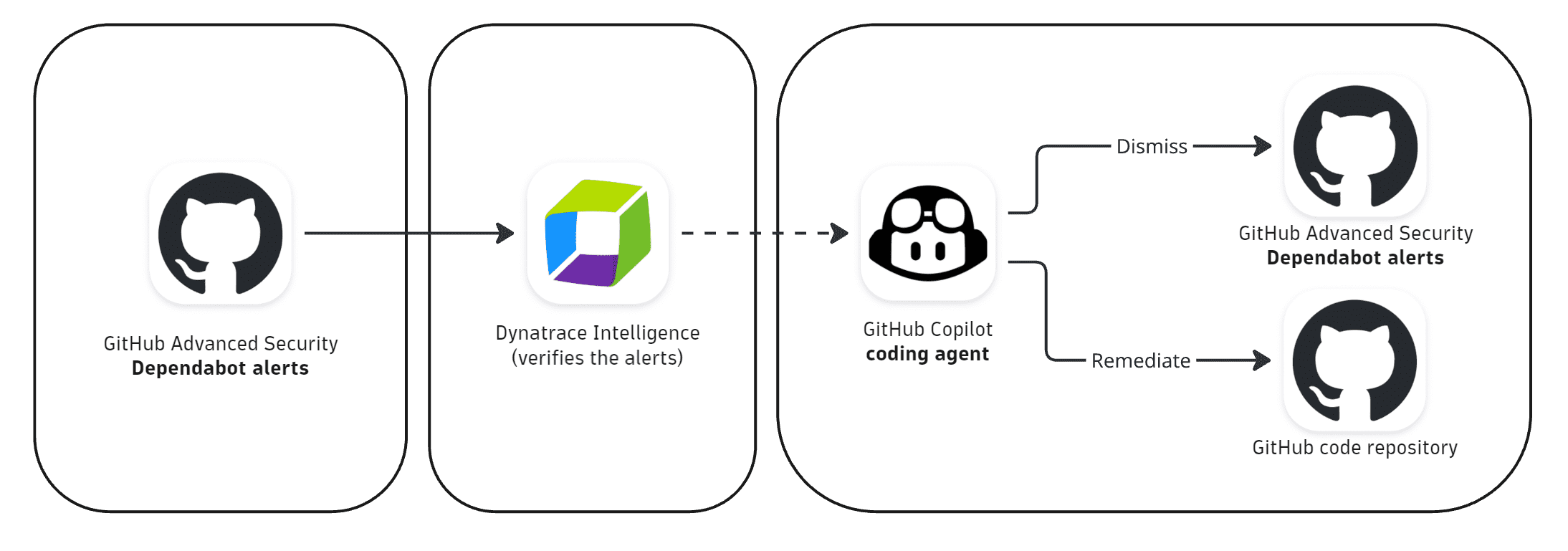
-
GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) detects vulnerabilities via Dependabot.
-
The Dynatrace integration with GHAS ingests these alerts using the GitHub Advanced Security extension and stores them in Grail for analysis.
-
A Dynatrace workflow triages alerts using runtime context and Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI workflow action for validation. For more information, see Dynatrace Intelligence (Preview) app.
-
A GitHub issue is created and assigned to GitHub Copilot, including both confirmed and unconfirmed vulnerabilities.
-
GitHub Copilot coding agent automatically picks up the issue, remediates confirmed vulnerabilities, and dismisses unconfirmed ones.
-
Developers review and merge the pull request with the fixes applied.
Get started (Dynatrace-driven workflow)
To get started, follow the steps below.
1. Set up Dynatrace
-
Create a Dynatrace platform token with the proper permissions to both access the MCP server and to query various event types.
-
Install and configure the GitHub Advanced Security integration in Dynatrace.
2. Prepare your GitHub repository
-
Enable Dependabot to detect vulnerabilities in dependencies.
-
Generate a fine-grained personal access token (PAT) with the proper permissions.
1. List permissions
- Read:
VariablesAdministrationDependabot secretsEnvironmentsMetadataWebhooksSecrets
- Read and write:
Dependabot alertsActionsCode scanning alertsCustom propertiesIssuesPull requestsWorkflowsContents
- Read:
-
Store the PAT created in step 2 as a GitHub secret for Copilot environment named
COPILOT_SPONSOR_PAT. This secret is exposed to the GitHub Copilot coding agent as an environment variable, allowing it to authenticate and perform actions in your repository on your behalf.
3. Connect GitHub Copilot to Dynatrace
To connect GitHub Copilot with Dynatrace MCP Server
-
Store your Dynatrace platform token as a GitHub secret named
COPILOT_MCP_DT_API_TOKEN. -
In your GitHub repo, go to Settings > Copilot > Agents.
-
Add an MCP server configuration like this:
{"mcpServers":{"dynatrace": {"type": "http","url": "https://pia1134d.dev.apps.dynatracelabs.com/platform-reserved/mcp-gateway/v0.1/servers/dynatrace-mcp/mcp","headers": {"Authorization": "Bearer $COPILOT_MCP_DT_API_TOKEN"},"tools": ["*"]}}}Make sure to replace
<your-dynatrace-mcp-endpoint>with your Dynatrace MCP URL.
For reference, see Extending GitHub Copilot coding agent with the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
4. Add instructions for GitHub Copilot
To help tailor suggestions from the GitHub Copilot coding agent to your coding standards and security policies, you have two options:
- Guide GitHub Copilot coding agent through a global instructions file: Download the
copilot-instructions.md file and add it in.github/. For instructions, see Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot. - Define a Dynatrace custom agent that GitHub Copilot will use to perform the use case: Download the
dynatrace-security-agent.md file and add it in.github/agents.
Once configured, GitHub Copilot will begin triaging and remediating vulnerabilities as new alerts are detected.
5. Deploy and schedule the Dynatrace triaging workflow
To automate vulnerability triage and issue creation, download the following two Dynatrace workflows for Dependabot alerts and upload them in  Workflows:
Workflows:
-
GitHub Dependabot alert verification.yml: This is the parent workflow, which performs the following actions:
- Queries new GitHub Dependabot critical findings.
- Verifies them using runtime context.
- Prepares the issue content and calls the sub-workflow.
-
GitHub issue creation and Copilot assignment.yml: This is the sub-workflow, called by the parent workflow to:
- Create a GitHub issue with the verification results.
- Assign the issue to GitHub Copilot for remediation.
Before running the workflow:
-
Store the GitHub personal access token (PAT) created in step 2 (Prepare your GitHub repository) in the Dynatrace vault so it can be securely accessed by the workflow.
-
Update the default input configuration of the sub-workflow to specify the owner and repository where the GitHub issue should be created.
-
In the HTTP actions of the sub-workflow, reference the vault-stored credentials to authenticate GitHub API requests.
Once configured, GitHub Copilot will assist with remediating vulnerabilities by suggesting code changes based on new alerts.