Query and filter logs
- Latest Dynatrace
- How-to guide
- 4-min read
- Published Jul 02, 2025
In  Logs, you can build queries, use filters, search for particular log lines, and more.
Logs, you can build queries, use filters, search for particular log lines, and more.
Build a query in  Logs
Logs
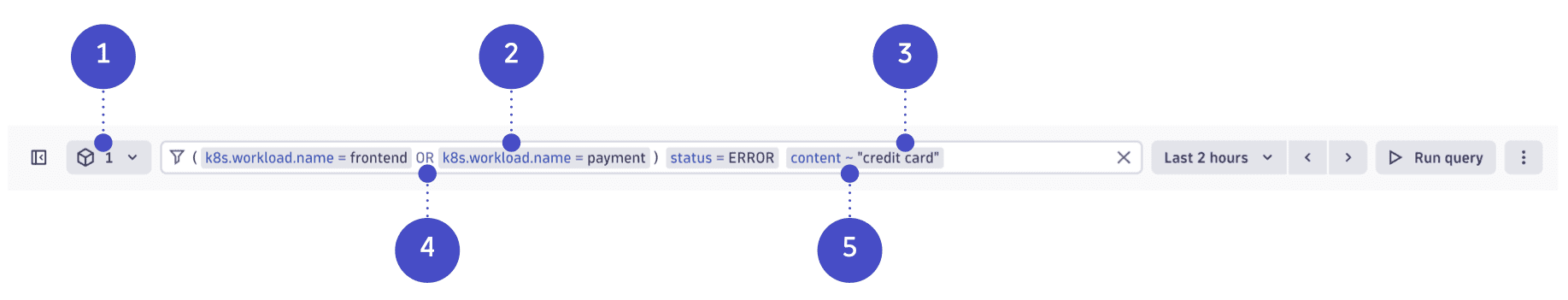
Query logs by specifying a segment and filter statement with keys and values with your search terms, comparators, and logical operators.
-
Segment: A common filter for observability data across apps on the Dynatrace platform.
-
Key: The field or attribute you want to filter on.
-
Value: The specific value that you're looking for.
-
Logical operator: Connects multiple filter statements.
By default, all filter statements are
ANDconnected. -
Comparator: Determines the type of comparison.
Filter with facets to add keys and and values to your filter automatically.
Use the date picker to apply the correct timeframe for your query.
Select Run query to execute the query.
After your query has returned records in the result table, you can search for keywords in this data. Use the Search in results field to filter the table using your keyword. This filtering does not execute a new query but only shows the already returned and loaded results in your browser.
Use  Segments
Segments
Apply a segment filter to your query whenever possible.
-
Segments let you filter on logs and other observability data with a consistent filter.
-
Segments are convenient to limit your queries to only specific Grail buckets, which reduces the amount of data that you need to scan to get the relevant results.
For additional details, see Segment logs by bucket and the best practices for logs.
-
Segments let you save and reuse commonly used filters, which are applicable in
 Logs and across other Dynatrace apps.
Logs and across other Dynatrace apps.
Explore recent filters and pin filters
 Logs saves your recently used filters so that you can re-apply them with just a click. You can also persist filters by pinning them.
Logs saves your recently used filters so that you can re-apply them with just a click. You can also persist filters by pinning them.
Select the filter field and check the Recently used filters section. The section displays filters you have recently applied, with the most recent on top. As you type a new filter statement, this list is reduced to match similar statements from your recently used filters.
Select (Pin filter) to pin any filter that you've created. When the filter field is empty, select it and scroll down to the Pinned filters section to view your previously pinned filters. Unpin a filter by selecting (Pin filter) again.
Search for a phrase in logs
If you need to find logs that contain a specific phrase, you have multiple options, which range from broadest to more narrow filtering.
Search from all fields
Use * instead of a keyname and ~ as the comparator to search for your phrase from all the fields of the log record that match your filters.
For example, the * ~ "failed to charge card" filter matches logs that contain this phrase in any field.
This is equivalent to using the search DQL command.
Search from content
Typically, original log payload is preserved in the content field of the log record. Restrict your search to this field to increase query performance.
For example, the content ~ "failed to charge card" filter matches logs that contain this phrase in the content field.
This is equivalent to using the matchesPhrase DQL string function.
Wildcard in value
You can also specify just a part of the value with a wildcard by using * in your search term.
For example, the content = "*card*" filter matches logs that contain the card phrase in the content field.
This is equivalent to using the matchesValue DQL string function.
For the full reference, see Filter field.
Filter on a field with multiple values
By default, all filter statements are connected with the AND logical operator. For example, status = ERROR status = WARN returns no results, as one a log record cannot have two statuses.
To query by a field with different values, use the in operator. For example, status in (ERROR, WARN) returns logs that have either the ERROR or WARN status. Alternatively, you can use OR to combine multiple filter statements.
Leverage automatic suggestions for log filters
 Logs provides autocomplete suggestions for keys, comparators, and values.
Logs provides autocomplete suggestions for keys, comparators, and values.
- Select the filter field to get a list of suggestions for most common or relevant fields for filtering.
- After choosing a field, you get a list of suggestions for comparators.
- After choosing a comparator, you get a list of suggestions for values for this field. This is not supported for the
contentfield.
Note that suggestions are presented based on actual values queried in the background from your log data, but there is no query cost for contextually relevant suggestions.
 LogsLog Analytics
LogsLog Analytics