Data retention periods
- 8-min read
Dynatrace stores and retains different types of monitored data from your environments. The monitoring data is stored on the Dynatrace cluster. The following table shows the general retention periods for service data (distributed traces), Real User Monitoring (user actions and user sessions), synthetic monitors, and metric time series data.
Trial accounts
After a 15-day trial account expires, Dynatrace continues to store the monitoring data from the account for 30 days to ensure that no data is lost.
Purchased accounts
For active Dynatrace accounts, the following retention rates are set by default:
Distributed traces Classic
Dynatrace stores the complete details of every transaction for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration. This enables you to analyze individual transactions and get all the details available with your instrumentation.
For trial users, an additional storage-size limit applies, which might lead to shorter retention times.
Data is stored in Transaction store at DATASTORE_PATH/server/tenantData. Data is not replicated across cluster nodes.
Code-level insights
Code-level insights are available with OneAgent instrumentation for 10 days.
After 10 days, session data is optimized for aggregated views. Non-aggregated and aggregated code-level data produce comparable results for longer timeframes, while differences may be expected for shorter timeframes.
Services Classic: Requests and request attributes
Short-term storage of the data related to service metrics used in multidimensional analysis and request charting. This data is available for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration with the following interval granularity levels:
| Timeframe | Interval granularity |
|---|---|
| Less than 20 minutes | 10 seconds |
| 20–40 minutes | 20 seconds |
| 40–60 minutes | 30 seconds |
| More than 1 hour | 1 minute |
A short-timeframe analysis accesses code-level data that is available for 10 days.
After 10 days, session data is optimized for aggregated views. Non-aggregated and aggregated code-level data produce comparable results for longer timeframes, while differences may be expected for shorter timeframes.
Data is stored in Transaction store at DATASTORE_PATH/server/tenantData. Data is not replicated across cluster nodes.
RUM: User action data
Aggregated user action metrics, which are used in tables like Top user actions and Top JavaScript errors, are available for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration. After 10 days, user actions data is optimized for aggregated views, and some individual user actions become unavailable for individual analysis. However, the sample set is large enough for statistically correct aggregations.
For key user actions, raw user action data is also kept for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration. The retention for timeseries data of key user actions is the same as for timeseries metrics.
Data is stored in Transaction store at DATASTORE_PATH/tenantData. Data is not replicated across cluster nodes.
RUM: User sessions
Includes Session Replay data. All user session data is stored for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration. Note that waterfall analysis and JavaScript error data is stored with distributed trace code-level insights and errors.
Data is stored in Elasticsearch store at DATASTORE_PATH/elasticsearch. Data is replicated across cluster nodes. Replication factor is set to three.
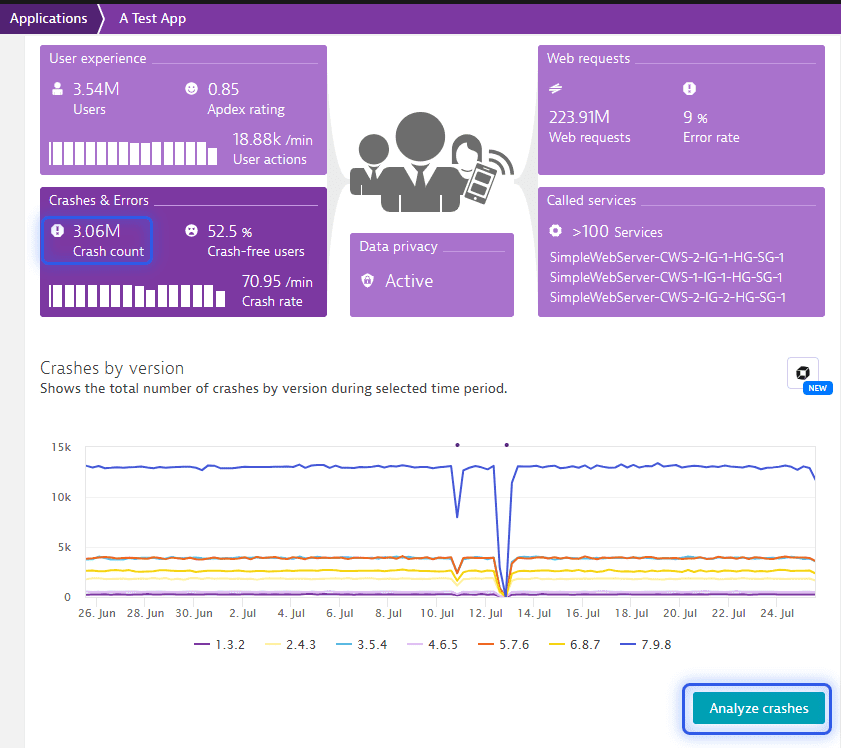
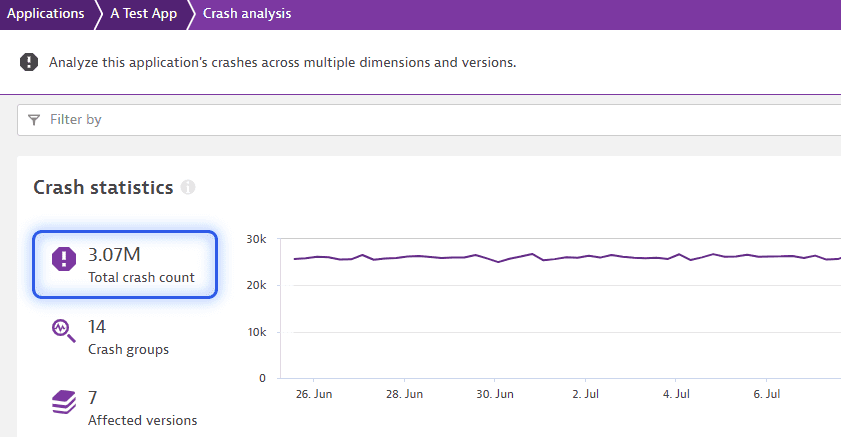
RUM: Mobile crashes
Includes all crash data and stack traces of mobile and custom applications. The data is stored for a maximum of 365 days, depending on your configuration.
The crash reporting data displayed in the application detailed page may differ from such data in the statistics page. For these pages, it is pulled from different storage, and has a different retention period.
Data is stored in Elasticsearch store at DATASTORE_PATH/elasticsearch. Data is replicated across cluster nodes. Replication factor is set to three.
RUM: Session Replay
Minimum size of required Session Replay storage volume is entirely load-dependent. A maximum size isn't required.
The Session Replay data storage directory is a dedicated file store at DATASTORE_PATH/server/replayData an is used exclusively for Session Replay data. For more information about storage size recommendations, see Configure the secondary disk.
Log Monitoring Classic
Log Monitoring Classic enables you to store all logs centrally within external storage. This makes log data available independent of log files themselves.
For storing log files centrally, you already use Elasticsearch store at DATASTORE_PATH/elasticsearch to store log files on your Dynatrace Managed cluster. Replication factor is set to two. To configure log storage, see Log ingest rules (Logs Classic).
Memory dumps
Memory dumps are immediately deleted from the disk once they're uploaded to ActiveGate. When an upload isn't possible, memory dumps up to 20 GB are stored on the disk for up to 2 hours.
Metrics Classic
The following interval granularity levels are available for dashboarding and API access:
| Timeframe | Interval granularity |
|---|---|
| 0–14 days | 1 minute |
| 14–28 days | 5 minutes |
| 28–400 days | 1 hour |
| 400 days–5 years | 1 day |
Data is stored in Metrics repository at DATASTORE_PATH/cassandra. Data is replicated across cluster nodes. Replication factor is set to three.
To provide accurate calculations for timeseries metrics, Dynatrace uses the P2 algorithm to calculate the quantiles dynamically. This algorithm is known to yield good results and it works well with values in the long tails of value distributions. However, the aggregation algorithm is neither associative ((a + b ) + c == a + ( b + c )) nor commutative (a + b + c == c + b + a). For some metrics, for example, response times, this might lead to different quantile values each time the algorithm runs or when the data is aggregated in different ways, for example, one metric is split by URL and another by browser.
OneAgent and ActiveGate diagnostics
OneAgent diagnostics and ActiveGate diagnostics are optional features that enable you to collect and analyze support archives for anomalies.
Support archives are created by Dynatrace OneAgent or Dynatrace ActiveGate and stored in Cassandra, where they are automatically deleted after 30 days. When you allow Dynatrace to analyze an issue, an additional copy of the support archive is stored in the configured AWS S3 bucket. Results of the issue analysis and the support archive are also automatically deleted from the AWS S3 bucket after 30 days. Dynatrace OneAgent and Dynatrace ActiveGate do not keep copies of created support archives.
You can delete OneAgent or ActiveGate diagnostics issues at any time. If you delete an issue, the related support archive and analysis report are deleted from Cassandra and the AWS S3 bucket immediately. The analysis result in Dynatrace Health Control is deleted after 30 days.
Security data Classic
Vulnerabilities
-
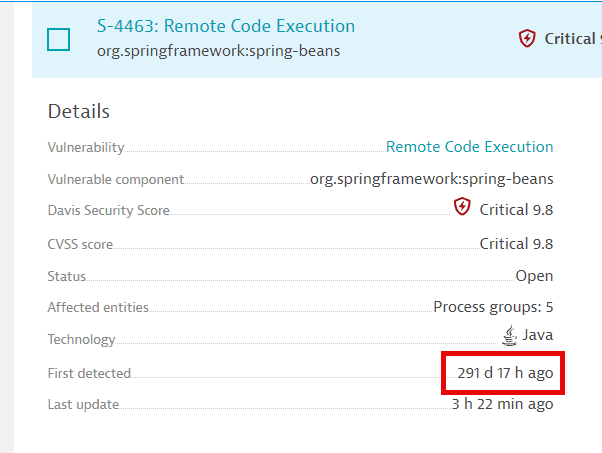
Open third-party vulnerabilities and code-level vulnerabilities are stored as long as they are open, regardless of the timeframe.
-
The storage time for resolved third-party and code-level vulnerabilities depends on when vulnerabilities are resolved:
- If a vulnerability is resolved before 365 days since it was first opened, it's deleted after 365 days.
- If a vulnerability is resolved after 365 days since it was first opened, it's deleted on its closest anniversary of the date when it was first opened.
Examples:
First opened First resolved Reopened Resolved again Delete date 2022-05-12 2023-05-06 2023-05-13 2022-05-12 2023-08-06 2024-05-13 2022-05-12 2023-08-06 2024-01-01 2024-02-08 2024-05-13
Events
Third-party vulnerability evolution events and code-level vulnerability evolution events are stored for 365 days and can only be queried up to the timestamp of when the vulnerability was first detected.
Attacks
Attacks are stored for 550 days.
Because retention is managed in monthly intervals, the exact duration may vary slightly depending on when the attack occurred and when cleanup is performed.