Grail security table migration guide
- Latest Dynatrace
- How-to guide
Dynatrace introduces a new security.events table in Grail, improving how security event data is consumed, stored, and queried. This guide explains the benefits, access control adjustments, ingestion and query changes, and required user actions.
The migration to the new security.events table is expected to be completed by the end of December 2025. To prevent any disruptions in your workflows, please ensure your migration is finalized before this deadline.
Refer to this guide for detailed instructions on completing the transition.
Why migrate?
The new security.events table enhances security data management with:
-
Simpler security event queries – You can directly retrieve security events with the
fetch security.eventscommand (see DQL examples for security data). -
No-code query support – Dashboards and notebooks enable security event analysis via user-friendly filters, requiring no previous DQL knowledge (see Explore security events).
-
Stronger access control – Separate permissions ensure table-level and record-level security without impacting other event tables (see Permissions in Grail).
-
Improved query performance – Queries only scan security events, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
-
Enhanced data ingestion – Supports native nested JSON and introduces dedicated fields for raw event data access.
What’s changing and what you need to do
With the introduction of the security.events table, some updates take place automatically, while others require manual action. See below for an overview.
Automatic updates
- Default data access policies – Updated to include security events.
- Dynatrace-generated security events – Written to old and new tables until the migration is complete.
- Dynatrace-provided processors and pipelines – Will be migrated and will work seamlessly with the new ingest scope.
 Dashboards,
Dashboards,  Notebooks,
Notebooks,  Workflows, and ready-made documentation samples – Adjusted to query the new security events table.
Workflows, and ready-made documentation samples – Adjusted to query the new security events table.
Manual updates required
-
Custom access policies – Update manually to grant permissions for the new
security.eventstable (see Access control updates). -
Third-party product ingest URLs – Change the ingest endpoint from
/events.securityto/security.events(see Data ingestion updates). -
Custom processing pipelines – Manually migrate sources via
 Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Security events (see Data ingestion updates).
Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Security events (see Data ingestion updates). -
Custom queries – Modify DQL queries to reference
security.eventsinstead ofevents(see DQL query updates). -
Migrating the connections for the integration apps/extensions - If you've already installed and configured security integrations, you need to do one of the following:
-
Reconfigure the third-party URL to point to
/security.events. This allows existing connections to continue working and display data from the new table. -
Recreate the connections and follow the on-screen setup instructions, which already include the updated endpoint.
-
Access control updates
-
(Automatic) Default access policies are automatically updated:
-
All Grail data read access– Read all Grail data, including security events. -
Read Security Events– Read security events only. -
OpenPipeline Ingest– Continue ingesting security events using existing permissions.
-
-
(Manual) Custom policies require manual changes:
-
New:
// previous security events within the events data tableALLOW storage:buckets:read WHERE storage:bucket-name IN ("default_security_events", "default_security_custom_events");ALLOW storage:events:read;// new table permissionsALLOW storage:buckets:read WHERE storage:table-name = 'security.events';ALLOW storage:security.events:read; -
Previously:
ALLOW storage:buckets:read WHERE storage:bucket-name IN ("default_security_events", "default_security_custom_events");ALLOW storage:events:read;
-
-
(Manual) For more granular access control, use the new buckets:
-
Read Dynatrace-generated events:
- New:
default_securityevents_builtin - Previously:
default_security_events
- New:
-
Read externally ingested events:
- New:
default_securityevents - Previously:
default_security_custom_events
- New:
-
Data ingestion updates
Dynatrace-generated events are stored in both the legacy and new tables until migration is complete. However, Kubernetes Security Posture Management-related events are no longer duplicated and are now available exclusively in the new security.events table. All other Dynatrace-generated events continue to be written to both tables during the migration period.
-
(Automatic) Dynatrace-provided processors and pipelines work seamlessly with the new ingestion scope.
-
(Manual) Update third-party product ingest URLs:
-
Default pipeline:
- New:
/platform/ingest/v1/security.events - Previously:
/platform/ingest/v1/events.security
- New:
-
Custom pipeline:
- New:
/platform/ingest/v1/security.events/<custom_ingest_source> - Previously:
/platform/ingest/v1/events.security/<custom_ingest_source>
Example new default and custom pipelines
New default and custom pipelines via Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Security events (New):
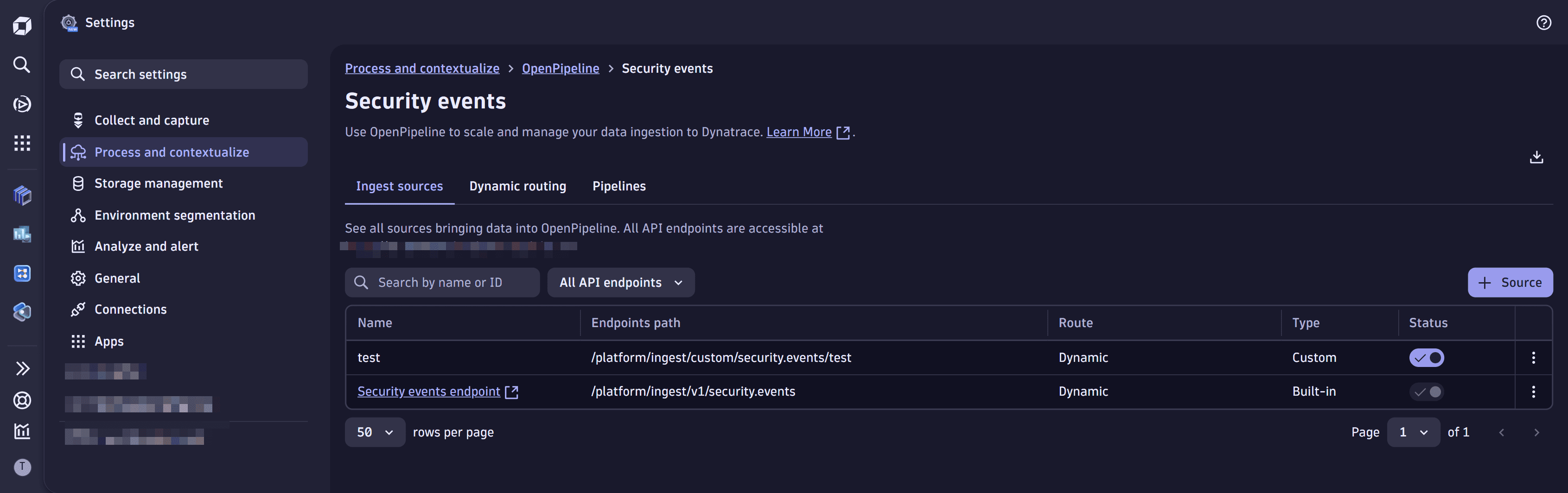
- New:
-
-
(Manual) Migrate custom ingest sources via
 Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Security events.
Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Security events. -
(Manual) Copy over and adjust, if required, the existing custom processors in your custom pipelines into the new
security.eventsOpenPipeline ingest scope.
DQL query updates
-
(Automatic)
 Dashboards,
Dashboards,  Notebooks,
Notebooks,  Workflows, and ready-made documentation samples delivered with Dynatrace apps and extensions now reference
Workflows, and ready-made documentation samples delivered with Dynatrace apps and extensions now reference security.events. -
(Automatic) The pre-built queries in Dynatrace apps are updated automatically where applicable.
-
(Manual) Update your custom queries in
 Dashboards,
Dashboards,  Notebooks, and
Notebooks, and  Workflows to fetch from
Workflows to fetch from security.eventsinstead ofevents.-
To query only recent data, switch completely to querying
security.events. -
To query both historical and new security events, modify queries to fetch from both tables.
-
To query only historical data, you can continue using the old queries.
To bulk-update multiple queries in
 Dashboards,
Dashboards,  Notebooks, or
Notebooks, or  Workflows, download the document JSON file and use a text editor for find and replace actions.
Workflows, download the document JSON file and use a text editor for find and replace actions. -
Example query updates
Query all security events
- New:
fetch security.events
- Previously:
fetch events | filter event.kind == "SECURITY_EVENT"
Query Dynatrace-generated events
- New:
fetch security.events | filter dt.system.bucket=="default_securityevents_builtin"
- Previously:
fetch events | filter dt.system.bucket=="default_security_events"
Query ingested events
- New:
fetch security.events | filter dt.system.bucket=="default_securityevents"
- Previously:
fetch events | filter dt.system.bucket=="default_security_custom_events"
Query ingested events in both old and new security event tables
// Fetch all migrated security eventsfetch security.events| filter dt.system.bucket!="default_securityevents_builtin"| append [// Fetch all security events that were not migratedfetch events| filter event.kind == "SECURITY_EVENT"// Exclude the by Dynatrace generated security events as they are written in both tables| filter dt.system.bucket!="default_security_events"]