Custom queries, segmentation, and aggregation of session data
- Classic
- How-to guide
- 37-min read
Dynatrace captures detailed user session data each time a user interacts with your monitored application. This data includes all user actions and high level performance data. Using either the Dynatrace API or Dynatrace User Sessions Query Language (USQL), you can easily run powerful queries, segmentations, and aggregations on this captured data. To assist you, this topic provides detail about keywords and functions, syntax, working with Real User Monitoring tables, automated queries, and more.
User Sessions Query Language isn't SQL, and Dynatrace doesn't store user session data in a relational database. User Sessions Query Language is a Dynatrace-specific query language, though it does rely on some SQL concepts and the syntax is similar, which makes it easy to get started.
Select your preferred approach:
User session queries via the Dynatrace web UI
- Go to
 Query User Sessions.
Query User Sessions. - Enter the query, and select Run query.
Timeframe selector with USQL
With the timeframe selector, user session data can be filtered based on a selected analysis timeframe. Select a new timeframe.

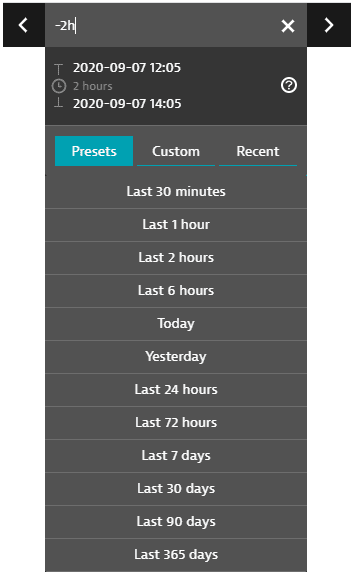
Timeframe selector controls
The global timeframe selector serves as a time filter that, in most cases, enables you to select a specific analysis timeframe that persists across all product pages and views as you navigate through your analysis.
-
The Presets tab lists all standard timeframes available. Select one to change your timeframe to that preset.
-
The Custom tab displays a calendar. Click a start day, click an end day, and then click Apply to select that range of days as your timeframe.
- Selected calendar intervals are set to end on start of the next day (with the time set to
00:00). For example, if you select September 3 to September 4 on the calendar, the timeframe starts on September 3 at time00:00and ends on September 5 at time00:00, so you never miss the last minute of the time range. You can edit these displayed times.
- Selected calendar intervals are set to end on start of the next day (with the time set to
-
The Recent tab displays recently used timeframes. Select one to revert to that timeframe.
-
The < and > controls shift the timerange forward or backward in time. The increment is the length of the original timerange. For example, if the current timerange is
Last 2 hours(the two-hour range ending now), click < to shift the timerange two hours back, to-4h to -2h(the two-hour range ending two hours ago). -
Hover over the timeframe to see the start time, duration, and end time.
Timeframe selector expressions
If you select the current timeframe in the menu bar, an editable timeframe expression is displayed.
- Reading from left to right, a timeframe expression has a start time, a
tooperator, and an end time. - If there is no explicit end time, the
toandnoware implied. For example,-2his the same-2h to now. - Supported units:
s,m,h,d,w,M,q,y(you can also use whole words such asminutesandquarter)
Autocomplete with USQL
Auto-completion is available for query statements based on the currently entered text. Auto-complete is context-sensitive and based on the current cursor context. It intelligently anticipates what text you may want to type next.
Autocomplete information returned from the API contains a list of suggestions, with the most likely values sorted to the top of the list, along with the necessary adjustment to the query text and the resulting cursor position after the adjustment. This allows you to place the cursor at a more useful position once text has been added, such as inside brackets when you select a function.
The fields list only contains valid fields or functions for the selected table, and its context-sensitivity shows only numeric fields when the cursor is placed inside a function-call that only works on numerical data, such as SUM(), or AVG().
Field-values are only suggested for enumeration based fields. No actual query to Elasticsearch is done for auto-completion.
Dynatrace Environment API
You can execute API calls using your preferred client. Find the related API documentation in User sessions API.
To execute these calls, you need the User sessions (DTAQLAccess) permission assigned to your API token. To learn how to obtain and use your token, see Dynatrace API - Tokens and authentication.
Timeframes in Environment API
User session data should always be accessed with a timeframe. It can be costly to access large timeframes because of the high number of potential single matches to queries.
The timeframe is usually not part of the query itself but is sent in separate parameters of the API call. You can find details in the API documentation.
You can, however, use the time fields like starttime and endtime to select a timeframe. You can also use these fields in functions, for example, to find out what time during the day most user sessions start, as in HOUR(starttime).
Keywords and functions
The following keywords have been defined to access user session data:
AND, AS, ASC, BETWEEN, BY, DESC, DISTINCT, FALSE, FROM, GROUP, IN, IS, JSON, LIMIT, NOT, NULL, OR, ORDER, SELECT, STARTSWITH, TRUE, WHERE, LIKE, FILTER
The following functions have been defined to access user session data:
SUM, MAX, MIN, AVG, MEDIAN, COUNT, YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, DATETIME, TOP, PERCENTILE, KEYS
Keywords, functions, and column names are case-insensitive. String-matches in WHERE conditions are case-sensitive.
Syntax
A typical query is built from the following keywords:
SELECT <columns> FROM <table> WHERE <condition> GROUP BY <grouping> ORDER BY <ordering>
However, the only mandatory elements are SELECT <columns> and FROM <table>.
Example
SELECT browserType, userId, city, AVG(userActionCount) AS "Average user action count", AVG(duration) AS "Average duration", count(*) AS "Sessions", SUM(totalErrorCount) AS "Errors" FROM usersession WHERE ip between '52.179.11.1' and '52.179.11.255' GROUP BY browserType, userId, city
Frequently used keywords
SELECT <columns>
Selects one or more columns from the specified data table or performs aggregation functions from the set of supported functions.
columns: [DISTINCT] <column>, <column>, ... | function(<parameter>) |<column> AS <alias> | JSON
Example
SELECT country, city, browserfamily FROM usersessionSELECT DISTINCT country, city, useractioncount FROM usersessionSELECT country, city, avg(duration) AS average FROM usersession GROUP BY country, city
FUNNEL
Allows you to use a predefined funnel format for a query. Can be used to chart the flow of specific user actions. Can also be combined with custom session properties and other conditions.
It changes the syntax of any query to the following:
SELECT FUNNEL (<condition> AS <alias>, <condition>, ...) FROM <table> WHERE <condition>
- For
FUNNELqueries, don't useSELECT *functions or keywords likeJSON. - Currently,
GROUP BY,ORDER BY, orLIMITstatements are not allowed in the funnels. FUNNELdoes not support ordering. There's no guarantee thatuseraction1happened beforeuseraction2for theSELECT FUNNEL (useraction.name = "useraction1", useraction.name = "useraction2") FROM usersessionquery. This query is only the equivalent of twoSELECTstatements, as explained in the examples below.
Example 1
Instead of running the following three queries:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name = "AppStart"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name = "AppStart" AND useraction.name = "searchJourney"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name = "AppStart" AND useraction.name = "searchJourney" AND useraction.name = "bookJourney"
The following single query returns the same result:
SELECT FUNNEL (useraction.name = "AppStart", useraction.name = "searchJourney", useraction.name = "bookJourney")FROM usersession
Example 2
To list the number of users that successfully booked the journey:
SELECT FUNNEL (useraction.name="login", useraction.name = "searchJourney", useraction.name = "bookJourney")FROM usersession
FROM <table>
You can only specify one table. Tables for user session data are as follows.
usersessioncontains information on user sessions.useractionstores data on user actions.usereventprovides information on user events, such as page changes or rage events.usererrorcontains more data on error events, which are errors and crashes.
Example
SELECT country, city, browserfamily FROM usersessionSELECT name, starttime, endtime, duration FROM useraction ORDER BY duration DESC
WHERE <condition>
You can combine multiple conditions using Boolean logic and parentheses within the WHERE clause, such as WHERE (city = 'Barcelona' AND country = 'Spain') to include only cities named Barcelona that are in Spain.
condition: (condition AND condition) | (condition OR condition) | field IN(...) |field IS <value> | field IS NULL | field = <value> | field > <value> | field < <value> |field <> <value> | field IS NOT <value> | field BETWEEN <value> AND <value> | ...
However, only the right-hand side of conditions can contain a value, so you can't compare between two fields.
Examples
SELECT country, city, browserfamily FROM usersession WHERE country = 'Albania' AND screenWidth > 1000SELECT TOP(country, 20), TOP(city, 20), TOP(duration, 10), AVG(duration) AS averageFROM usersessionWHERE duration BETWEEN 1000 AND 2000GROUP BY TOP(country, 20), TOP(city, 20), TOP(duration, 10)
GROUP BY <grouping>
Whenever fields are aggregated, you must specify corresponding GROUP BY keywords to indicate how the aggregation is to be performed.
grouping: <column>, ...
Example
SELECT city, count(*) FROM usersession GROUP BY citySELECT MONTH(starttime) as month, count (*) FROM usersessionGROUP BY month
LIMIT <limit>
Allows you to limit the number of returned results. For example, you can select only the top 10 results when it is combined with ordering.
The framework always applies an upper limit to prevent system overload. If LIMIT is not used, 50 results are returned by default.
Example
SELECT city, starttime FROM usersession ORDER BY starttime DESC LIMIT 10
LIMIT can also be used to increase the number of results in cases where the LIMIT clause is missing, because then a default limit is applied.
ORDER BY <ordering>
Allows you to order the results by columns, in either ascending or descending order. The order is ascending if not specified.
The ordering is done by frequency. For example, the top 5 returned cities are the most frequently occurring ones. By specifying a field in the ORDER BY clause, you can add a sort-by value for strings, dates, and numbers.
Ordering by enums or by function values such as AVG and SUM orders the returned results, but you may not get the top items. For example, if you request the top 5 results by AVG(duration), requesting only 10 may add results even at the top.
ordering: <column> ASC | <column> DESC | <column>, ...
Example 1
SELECT useraction.name, starttime FROM usersession ORDER BY starttime DESC
Example 2
You can achieve ordering of counts by adding the DISTINCT keyword.
SELECT DISTINCT city, COUNT(*) FROM usersession ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC
Example 3
You can achieve ordering of functions in the select list by stating the column name only or the alias defined in the SELECT.
SELECT avg(duration) AS average, count(*) as number, day(startTime) as startDayFROM usersession where duration < 2000GROUP BY startTimeORDER BY average
or
SELECT avg(duration) AS average, count(*) as number, day(startTime) as startDayFROM usersession where duration < 2000GROUP BY startTimeORDER BY number DESC, average ASC
LIKE
Allows you to compare data with an expression by using wildcard characters to match the specified pattern. You can use the following characters:
%or*: Matches any string of 0 or more characters?: Matches any single character
String values are case-sensitive. For example, SELECT city FROM usersession WHERE userId LIKE "*dynatrace*" matches me@dynatrace.com but not me@dynaTrace.com. To avoid this, use the ? wildcard character as in this example: SELECT city FROM usersession WHERE userId LIKE "*dyna?race*"
Escape wildcard characters
To escape a wildcard character, add a backslash \ before it. For example, \%, \*, and \? are treated as standard string literals %, *, and ?.
To escape a backslash \ itself, add another backslash \ before it. The resulting \\ entry is treated as a single backslash \.
If you add two backslashes \\ before a wildcard character (resulting in entries like \\%, \\*, or \\?), such an entry is treated as one escaped backslash \ and one wildcard character. For example, the \\* entry matches \abc, \123ABC, or \.
Summary of how to escape wildcard characters:
| Entry | Treated as | Matches |
|---|---|---|
\% | % | % |
\* | * | * |
\? | ? | ? |
\\ | \ | \ |
\\% | \ and any string of zero or more characters | \abc, \123ABC, \, etc. |
\\* | \ and any string of zero or more characters | \abc, \123ABC, \, etc. |
\\? | \ and any single character | \a, \1, \A, etc. |
Examples of how to escape wildcard characters:
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE userId LIKE "AU\%40KWM"
The query matches userId that equals AU%40KWM.
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE userId like "AU\*40KWM"
The query matches userId that equals AU*40KWM.
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE userId LIKE "AU\?40KWM"
The query searches for a userId that equals AU?40KWM.
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE userId LIKE "AU\\%40KWM"
The query has one escaped backslash \ and one wildcard character %, so the query matches a userId such as AU\40KWM, AU\abcd40KWM, AU\ab12340KWM, or AU\777_12340KWM.
Queries with 11+ LIKE conditions with non-trailing wildcards are rejected
USQL queries that have 11 or more LIKE conditions with * or % at the beginning or inside the search pattern (but not at the end) are rejected from execution.
Usually, we simply count the number of LIKE conditions used in the query. For example, there are five LIKE conditions in the query below—we count each occurrence of LIKE in the WHERE clause and the CONDITION function.
SELECT CONDITION(COUNT(userSessionId), WHERE useraction.name LIKE '*search.html'),CONDITION(COUNT(userSessionId), WHERE useraction.name LIKE '*booking-payment1.html')FROM usersessionWHERE city LIKE "%York"OR city LIKE "S*Francisco"AND city LIKE "L*inz"
However, when the FUNNEL function is used, the calculation becomes more complicated. For this function, we internally transform one query into several queries. After that transformation, we count the number of LIKE conditions in those internally transformed queries.
For example, the following query:
SELECT FUNNEL (useraction.name LIKE "*start", useraction.name LIKE "Jou%rney", useraction.name LIKE "bookJourn*ey") FROM usersession
is changed to the following three queries:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name LIKE "*start"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name LIKE "*start" AND useraction.name LIKE "Jou%rney"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usersession where useraction.name LIKE "*start" AND useraction.name LIKE "Jou%rney" AND useraction.name LIKE "bookJourn*ey"
This means there are actually six LIKE conditions in the FUNNEL query above.
FILTER
Allows you to filter for functions that have numeric values, thereby displaying only specific results from aggregations.
Example
SELECT useraction.application,AVG(usersession.doubleProperties.bookings)FILTER > 1500FROM usersessionWHERE usersession.doubleProperties.bookings IS NOT NULLGROUP BY useraction.application
The WHERE and FILTER functions aren't interchangeable. While you can use the WHERE clause only on absolute values, the FILTER function works on aggregated values as well.
Frequently used functions
MIN(field)
Queries the minimum value of a numeric or date field.
Example
SELECT MIN(duration), MAX(duration), AVG(duration), MEDIAN(duration)FROM usersession
MAX(field)
Queries the maximum value of a numeric or date field.
Example
SELECT MIN(duration), MAX(duration), AVG(duration), MEDIAN(duration)FROM usersession
AVG(field)
Queries the average value of a numeric or date field. May be NaN if the field is always null.
Example
SELECT MIN(duration), MAX(duration), AVG(duration), MEDIAN(duration)FROM usersession
MEDIAN(field)
Queries the median value of a numeric or date field.
Example
SELECT MIN(duration), MAX(duration), AVG(duration), MEDIAN(duration)FROM usersession
SUM(field)
Computes the sum of a numerical field.
Example
SELECT TOP(name, 20), SUM(duration) FROM useractionGROUP BY name
COUNT(field), COUNT(*), COUNT(DISTINCT field)
Counts the number of rows that match.
COUNT(*): Counts the number of matching items.COUNT(<field>): Counts the number of matching items where<field>is not null.COUNT(DISTINCT <field>): Counts the number of different values for<field>within the selected items.
Example
SELECT country, COUNT(*), COUNT(city), COUNT(DISTINCT city)FROM usersessionGROUP BY country
Results returned by the COUNT(DISTINCT <field>) function are approximate to prevent high memory usage. If COUNT(DISTINCT <field>) is used on a high-cardinality field, results might be even more rough. High-cardinality fields are those fields that have only few duplicates.
Results based on extrapolated data can be even more generalized; see Limitations for more information.
High-cardinality fields
| Table | Fields |
|---|---|
usersession | ip , userSessionId , internalUserId , userId |
Dynatrace rejects and doesn't execute the queries with COUNT(DISTINCT <field>) that might consume a lot of memory. This happens for all extremely high-cardinality fields, for example, for the dateTime fields like usersession.startTime, usersession.endTime, or useraction.networkTime.
Extremely high-cardinality fields
| Table | Fields |
|---|---|
usersession | startTime , endTime , replayEnd , clientTimeOffset, duration , replayStart |
useraction | domContentLoadedTime , startTime , firstPartyBusyTime , documentInteractiveTime , navigationStart , totalBlockingTime Deprecated, largestContentfulPaint , visuallyCompleteTime , cdnBusyTime , endTime , domCompleteTime , networkTime , loadEventStart , serverTime , firstInputDelay , responseStart , thirdPartyBusyTime , duration , loadEventEnd , responseEnd , frontendTime , requestStart |
userevent | startTime |
usererror | startTime |
Example
SELECT country, COUNT(*), COUNT(city), COUNT(DISTINCT city)FROM usersessionGROUP BY country
TOP(field, n)
Returns the top <n> results from a field. The default is 1 (the top value) if n is not specified.
Example
SELECT TOP(name, 20), SUM(duration)FROM useractionGROUP BY name
If TOP(<field>, n) is selected and the results are grouped, but <field> is not part of the grouping, the top-n elements return as a list within a single field.
SELECT TOP(country, 20), TOP(city, 3), COUNT(*)FROM usersessionGROUP BY country
YEAR(datefield), MONTH(datefield), DAY(datefield), HOUR(datefield), MINUTE(datefield)
Returns the given element extracted from a date field.
YEAR: The four-digit year.MONTH: The month number, between 1 and 12DAY: The day of the month, between 1 and 31.HOUR: The hour value, between 0 and 23.MINUTE: The minute value, between 0 and 59.
Example
SELECT starttime,DATETIME(starttime), YEAR(starttime), MONTH(starttime), DAY(starttime), HOUR(starttime), MINUTE(starttime)FROM usersessionORDER BY starttime DESC
DATETIME(datefield [, format [, interval]])
Formats the selected date field with the given format string. The default format is yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm.
The allowed letters within the format string are:
y: yearM: monthd: day of monthH: hour (0-23)h: hour (1-12)m: minutes: secondE: day of week (Mon-Sun)
The year|month|week intervals are for a single interval. For d (days), h (hours), m (minutes), or s (seconds), you can use a number followed by the letter for the format string, such as 5m. For example, SELECT DISTINCT DATETIME(starttime, 'HH:mm', '5m'), COUNT(*) FROM usersession counts sessions in five-minute time blocks.
Example
SELECT DATETIME(starttime, 'yyyy-MM') FROM usersessionSELECT DISTINCT DATETIME(starttime, 'HH:mm', '5m'), COUNT(*) FROM usersession
Similar to other date functions (YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, and MINUTE), you can use DATETIME to format a result (even the result of other functions like MAX, MIN, AVG, or CONDITION), create histograms, or retrieve a list of timestamps where there are results, for example, the days of a week when an application was used.
Examples
SELECT application, DATETIME(MAX(starttime)) AS LastUsedTime FROM useraction GROUP BY applicationSELECT DATETIME(starttime, "HH") AS hourOfDay, COUNT(*) FROM usersession GROUP BY hourOfDaySELECT application, DATETIME(starttime, "E") AS daysOfWeek FROM useraction GROUP BY applicationSELECT DATETIME(CONDITION(MAX(startTime), WHERE name = "index.jsp")) FROM useraction
CONDITION(function, condition)
Allows you to combine multiple functions with various conditions.
The allowed functions within the format string are as follows:
MIN()MAX()AVG()SUM()PERCENTILE()MEDIAN()COUNT()
You can combine multiple conditions using Boolean logic and parentheses with the CONDITION function, such as CONDITION(COUNT(*), WHERE city = 'Barcelona' AND country = 'Spain') to include only cities named Barcelona that are in Spain.
CONDITION(function, condition)condition:(condition AND condition) | (condition OR condition) | field IN(...) |field IS <value> | field IS NULL | field = <value> | field > <value> | field < <value> |field <> <value> | field IS NOT <value> | field BETWEEN <value> AND <value> | ...
You can also use the FILTER clause filter for functions that have numeric values, thereby displaying only specific results from aggregations.
SELECT CONDITION(COUNT(usersessionId), WHERE userActionCount > 2 AND useraction.name = "search.jsp") FILTER > 1000, city FROM usersession GROUP BY city
Example
SELECT CONDITION(COUNT(usersessionId), WHERE userActionCount > 2 AND useraction.name = "search.jsp") FROM usersessionSELECT CONDITION(SUM(usersession.duration), WHERE name = "index.jsp") AS c1, CONDITION(SUM(usersession.duration), WHERE name = "search.jsp") AS c2, CONDITION(SUM(usersession.duration), WHERE name IS NOT "index.jsp" AND name IS NOT "search.jsp") AS c3 FROM useraction WHERE (duration > 1000 OR usersession.userActionCount > 4)SELECT CONDITION(SUM(usersession.duration), WHERE name = "index.jsp") AS c1 FROM useraction WHERE (duration > 1000 OR usersession.userActionCount > 4) ORDER BY c1SELECT DATETIME(CONDITION(MIN(startTime ), WHERE useraction.application = "RUM Default Application" ), "yyyy-MM-dd" ) FROM usersession
PERCENTILE
Represents a value below which there's a percentage of data points lower in value. Useful in detecting the speed of your application for customers who receive the slowest response time.
Example
SELECT name, usersession.country, usersession.browserFamily,AVG(duration),MEDIAN(duration),PERCENTILE(duration, 99)FROM useractionWHERE useraction.name = "easytravel/rest/login"GROUP BY usersession.country, usersession.browserFamily, nameORDER BY usersession.continent
KEYS(customProperty)
Returns keys of user action or user session properties according to the property data type defined in the argument.
Check the table below to understand whether keys of user action properties or keys of user session properties are returned.
| KEYS(customProperty) | Table | Action properties | Session properties |
|---|---|---|---|
KEYS(<dataType>Properties) | useraction | ||
KEYS(<dataType>Properties) | usersession | ||
KEYS(useraction.<dataType>Properties) | useraction | ||
KEYS(useraction.<dataType>Properties) | usersession | ||
KEYS(usersession.<dataType>Properties) | useraction | ||
KEYS(usersession.<dataType>Properties) | usersession |
The <dataType> part of the function can take the following values:
stringlongdoubledate
Example 1
SELECT KEYS(stringProperties) FROM useraction WHERE application = "easyTravel demo application"SELECT KEYS(useraction.longProperties) FROM usersession WHERE applicationType="WEB_APPLICATION" ORDER BY keys(useraction.longProperties)SELECT KEYS(usersession.stringProperties) FROM useraction WHERE usersession.city ="Berlin"
For fetching distinct keys of action or session properties, use DISTINCT KEYS(customProperty).
Example 2
SELECT DISTINCT KEYS(stringProperties) FROM useraction WHERE useraction.application = "easyTravel demo application" ORDER BY keys(stringProperties)SELECT DISTINCT KEYS(doubleProperties) FROM usersession
Mathematical operations
The following operations are supported as part of queries:
- operations on numbers
- operations on numeric and dateTime fields
- operations on certain functions such as
YEAR,MONTH,DAY,HOUR,MINUTE - operations on numeric values and display them in different uses of measurement
Syntax
Number/NumericField/DateTimeField/Function OPERATOR Number/NumericField/DateTimeField/Function
Function: YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR or MINUTE
Operator: +, -, *, /, %, or MOD
Example
SELECT 7 + 80 * 100, duration + startTime, MONTH(startTime) - 1FROM usersession
Conditions
All conditions must start with an identifier, such as a field name, and must be compared against a value. Two fields can't be compared against each other.
Quoted text is always case-sensitive.
Basic operators
The basic operators for comparison are =, !=, <>, <, >, <=, >=, IS, and IS NOT.
To check if the value of a field is present, compare the field against NULL.
Example
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE userActionCount > 3
Ranges
Ranges are handled by keywords such as BETWEEN or NOT BETWEEN, <lowerLimit>, and <upperLimit>.
Example 1
SELECT DISTINCT ip FROM usersessionWHERE ip BETWEEN '192.168.0.0' AND '192.168.255.255'
Example 2
SELECT startTime FROM useractionWHERE NOT startTime BETWEEN $NOW - DURATION("2h") AND $NOW
Example 3
SELECT ip, browserType, userId, cityFROM usersessionWHERE NOT ip BETWEEN '52.179.11.1' AND '52.179.11.255'
Sets
The IN keyword can be used shorten "WHERE" <field> = val1 OR <field> = val2 OR <field> = val3.
Example
SELECT userId FROM usersession WHERE city IN ("NEW YORK", "San Francisco")
String conditions
The "STARTSWITH" string condition checks whether a string or an enum field starts with the specified text.
Example
SELECT city FROM usersession WHERE userId STARTSWITH "dynatrace"
Datetime values
When conditions are run on a datetime field, the following value formats are supported:
| Format | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| — | Unix timestamp as a number in milliseconds | 1514152800000 |
yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssZ | ISO datetime with the time zone | 2017-12-24T21:00:00+01:00 |
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss | Date with optional time | 2017-12-24 21:00 |
yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss | Date with optional time | 2017/12/24 21 |
MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss | Date with optional time | 12/24/2017 |
dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss | Date with optional time | 24.12.2017 21:00:00 |
For the formats where time is optional, the following time formats are supported:
| Format | Example |
|---|---|
HH:mm:ss | 08:20:59 |
H:mm:ss | 8:20:59 |
HH:mm | 08:20 |
H:mm | 8:20 |
HH | 08 |
H | 8 |
If the time is missing, the default 00:00:00 is assumed.
Sometimes, queries with datetime values might yield incorrect results due to the Daylight Saving Time conversion. If the date in the query is before the Daylight Saving Time end date (for example, before November 7, 2021 02:00), try using the ISO datetime with a time offset, for example, 2021-10-05T17:30:00+03:00.
Example
SELECT starttime FROM usersession WHERE starttime > "8.8.2018 8:00"
Condition optimization
IN
When your query contains multiple "equals" conditions for the same field via OR, use the IN function instead, as it's more performant. For example, you can rewrite the following query using the IN function.
Before
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usereventWHERE pageReferrer = "/some/page/referrer/1"OR pageReferrer = "/some/page/referrer/2"OR pageReferrer = "/some/page/referrer/3"OR pageReferrer = "/some/page/referrer/4"OR pageReferrer = "/some/page/referrer/5"
After
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM usereventWHERE pageReferrer IN ("/some/page/referrer/1","/some/page/referrer/2","/some/page/referrer/3","/some/page/referrer/4","/some/page/referrer/5")
NOT IN
To optimize the speed of your queries, use arrays for queries: instead of using several NOT, <>, or != operators, use the NOT IN operator.
Before
SELECT useraction.name, usersession.userIdFROM useractionWHERE name = "loading of page /"AND usersession.userId IS NOT NULLAND usersession.userId <> "Speed Travel Agency"AND usersession.userId <> "some user"AND usersession.userId <> "easyTravel - One step to happiness"AND usersession.userId <> "easyTravel - Booking - Finish"
After
SELECT useraction.name, usersession.userIdFROM useractionWHERE name = "loading of page /"AND usersession.userId IS NOT NULLAND NOT usersession.userId IN ("Speed Travel Agency","some user","easyTravel - One step to happiness","easyTravel - Booking - Finish")
Advanced syntax constructs
Query IP ranges
The IP field can be queried for ranges of addresses. Both BETWEEN ip > <lower ipaddress range> AND ip < <upper ipaddress range> or BETWEEN <lower ipaddress range> AND <lower ipaddress range> work.
Example
SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE ip > '211.44.94.0' AND ip < '212.113.5.0'SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE ip BETWEEN '211.44.94.0' AND '212.113.5.0'
Query timeframe selector
You can use the following keywords to select the start time and end time as defined in the timeframe selector.
TIME_FRAME_STARTTIME_FRAME_END
Example
SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE startTime >= $TIME_FRAME_START AND endTime < $TIME_FRAME_END
Timeframe selectors can be used to limit the timeframe on queries that are run on secondary tables (useraction). By default, the timeframe filter is applied on the usersession table, even if the query is run on any secondary table. To apply the filter on a secondary table as well, you can use the timeframe selector to add a condition on the startTime field of the secondary table. See the following example to fetch the name and duration of user actions that occurred only in the query timeframe:
Example
SELECT name, duration FROM useractionWHERE startTime BETWEEN $TIME_FRAME_START and $TIME_FRAME_END
Query relative timeframe
You can select a timeframe relative to the time when the query was run. The current time is expressed with the $NOW variable.
$NOW [+/-] DURATION("[number]TIME_UNIT")
The following time units are supported to express the duration:
y: yearq: quarterM: monthd: dayw: weekh: hourm: minutes: second
Example
SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE startTime >= $NOW - DURATION("1q") AND endTime <= $NOWSELECT * FROM useraction WHERE startTime BETWEEN $NOW - DURATION("2h") AND $NOWSELECT * FROM useraction WHERE usersession.startTime >= $TIME_FRAME_START - DURATION("2h") AND $NOW - DURATION("1h")
The timeframe selected in the Dynatrace web UI or Dynatrace API still applies to the results, even if timestamp-based filtering is used as part of your query.
Secondary tables for usersession, useraction, userevent, and usererror
When using SELECT with usersession, useraction, userevent, or usererror, columns from the other table can be accessed and included in the results by prefixing column names with the table name.
Example 1
Selecting a logical view of the usersession or the useraction table. Multiple values concatenate in the resulting column when adding information from useraction into a query on usersession.
SELECT city, useraction.name FROM usersessionSELECT usersession.city, name FROM useraction
You can use other secondary tables userevent and usererror in the same way.
SELECT usersession.country, name, page FROM usereventSELECT usersession.country, name, type FROM usererrorSELECT country, userevent.name, usererror.name FROM usersession
When you query from the usersession primary table, you can combine fields from other secondary tables (useraction, userevent, and usererror). You can use fields from the secondary tables in the WHERE condition too.
Example 2
SELECT city, useraction.name, userevent.page, usererror.type FROM usersessionSELECT city, usererror.name, userevent.page, useraction.duration FROM usersession WHERE usererror.name IS NOT NULL
Example 3
Listing all user sessions that contain a user event or a user action from the same application.
SELECT * FROM usersessionWHERE userevent.application = "a" OR useraction.application="a"
When you query from any of the secondary tables (useraction, userevent, or usererror), you can use fields only from the usersession primary table; you can't use fields from other secondary tables. For example, the query below fails, as the selected table is userevent, which means that only fields from userevent or usersession can be selected.
SELECT usersession.city, useraction.name, userevent.page, usererror.type FROM userevent
The same limitation applies to other secondary tables—useraction and usererror.
Example 4
The following queries won't fail, as only fields from the selected secondary table and from the primary table are used.
SELECT usersession.userId, name, duration FROM useractionSELECT usersession.userId, name, type FROM usererror
There is no way to connect secondary tables to each other and derive any relations between the useraction, userevent or, usererrortable, or in which order they happened. Therefore, it is not possible to say which useraction caused which usererror. The only connection we can make is to the usersession they belong to.
Applied conditions differ in meaning depending on the table. For example, consider that you want to list all user sessions that contain user actions with names a and b:
SELECT * FROM usersessionWHERE useraction.name = "a" AND useraction.name = "b"
This means, the session must contain a user action with name "a" and a user action with the name "b". Running the same query on the useraction table returns an empty result as the same user action can't have two different values for the name.
If you want to select user session data for a specific user action that matches several criteria, run the following query on the useraction table.
SELECT usersession.*, * FROM useractionWHERE useraction.name = "a" AND useraction.duration > 1000
In this case, each user action in the result satisfies both conditions.
Let's take a look at another query.
SELECT COUNT(usersession.userSessionId)FROM usersessionWHERE userevent.name = 'Page change'AND userevent.pageGroup = '/Booking'AND userevent.type = 'UserTag'
Because the query is run on the usersession table, the conditions are applied on the total set of user events that belong to a single session. This means that any user session with user events that satisfy the conditions is reflected in the count. For example, if a user session contains three user events that each satisfy one of the given conditions, the user session is reflected in the count.
If you run the same query on the userevent table, the conditions are applied on each individual user event. This means that only user sessions that have at least one user event that satisfies all conditions are reflected in the count.
SELECT COUNT(usersession.userSessionId)FROM usereventWHERE userevent.name = 'Page change'AND userevent.pageGroup = '/Booking'AND userevent.type = 'UserTag'
Filtering using fields of a secondary table
Be careful when filtering using the fields of one of the secondary tables. Consider the examples below.
Example 1
SELECT useraction.name FROM usersession WHERE useraction.name="abc"
This query returns a list of all user sessions that contain at least one user action named abc. The result contains a list of all user actions for each session because the query is run on the usersession level.
Example 2
SELECT name FROM useraction WHERE name="abc"
This query retrieves a list of only those user actions that are named abc.
SELECT * FROM table
Example
SELECT * FROM usersessionSELECT useraction.* FROM usersessionSELECT city, useraction.* FROM usersessionSELECT *, useraction.* FROM usersession
An asterisk * by itself selects columns from the main table, not the secondary table. For example, fields from useraction are not included in SELECT * FROM usersession, unless you include useraction.*.
JSON export
The JSON keyword adds an additional column that contains the data about the requested entry (a user session, user action, user event, or user error) in JSON format.
If you select the usersession primary table, the full JSON strings for the matching user sessions are returned, regardless of the selected columns.
Example 1
The query below returns the matching user sessions as JSON in an additional column, including the data from all secondary tables.
SELECT usersessionId, browserFamily, useraction.name, useraction.duration, JSONFROM usersession LIMIT 5
If you select a secondary table (useraction, userevent, or usererror), the full JSON strings for the matching sub-entry (a user action, user event, or user error) are returned.
Example 2
The query below returns the matching user actions as JSON in an additional column, without the data from the usersession table or other secondary tables.
SELECT name, duration, JSONFROM useraction LIMIT 5
See also Export user sessions.
Escaping strings
String literals can be put within single or double quotes. However, if you want to use the same quotation mark inside the string, simply double it.
Example
SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE userId = "some 'custom' name for ""my user"""SELECT * FROM usersession WHERE userId = 'some ''custom'' name for "my user"'
Funnel charting
Funnel charting allows you to track steps through your digital service and investigate the areas of struggle faced by your users. In conjunction with Session Replay, this functionality allows you to see at which point your user is struggling in your application.
Example
SELECT FUNNEL(useraction.name = "AppStart (easyTravel)" AS "Open easytravel",useraction.name = "searchJourney" AS "Search journey",useraction.name = "bookJourney" AS "Book journey",useraction.matchingConversionGoals = "Payment" OR useraction.matchingConversionGoals = "booking-finished" AS "Booked")FROM usersession
You can also filter for a specific segment. An example of this is using Session properties to extract the list of high priority customers.
Example
SELECT FUNNEL(useraction.name = "AppStart (easyTravel)" AS "Open easytravel",useraction.name = "searchJourney" AS "Search journey",useraction.name = "bookJourney" AS "Book journey",useraction.matchingConversionGoals = "Payment" OR useraction.matchingConversionGoals = "booking-finished" AS "Booked")FROM usersessionWHERE stringProperties.memberstatus="GOLD"
FUNNEL does not support ordering. There's no guarantee that useraction1 happened before useraction2 for the SELECT FUNNEL (useraction.name = "useraction1", useraction.name = "useraction2") FROM usersession query. This query is only the equivalent of two SELECT statements.
Available user session data tables and fields
For user session data, the following tables are available.
usersessioncontains information on user sessions.useractionstores data on user actions.usereventprovides information on user events, such as page changes or rage events.usererrorcontains more data on error events, which are errors and crashes.
Secondary tables for usersession, useraction, userevent, and usererror include a description of how data in one of those tables is available in the other.
The fields are described in User sessions API - User session structure.
You can also check the UserSession object in the API Explorer.
Run USQL queries for custom reports
A REST interface allows you to get results for your custom queries. All you need is to create a unique API token with the User session query language privilege. The ability to query user session data this way is useful in automated testing, data verification, and other automated functions. It includes the following endpoints:
/table: Returns the data as a flat table, even when grouping by various items and performing hierarchical aggregations against the user session data.
/tree: Returns the data as a full hierarchical tree based on the input.
The following query-parameters are available:
query: Needs to be encoded when put into a URL, for example, %20 instead of spaces.
startTimestamp/endTimestamp: Allows you to define points in time, passed as the number of milliseconds since the Unix epoch. If not specified, this defaults to the last two hours.
Examples
This code:
curl --location --insecure -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Api-Token _token_" \-XGET "https://{your-environment-id}.live.dynatrace.com/api/v1/userSessionQueryLanguage/table?query=select%20city,count(*)%20from%20usersession%20group%20by%20city"
provides the following result:
{"columnNames": ["city", "count(*)"],"values": [["Dublin", 23],["N. Virginia (Amazon)", 80],["Portland", 56]]}
This code:
curl --location --insecure -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Api-Token _token_" \-XGET "https://{your-environment-id}.live.dynatrace.com/api/v1/userSessionQueryLanguage/tree?query=select%20country,city,count(*)%20from%20usersession%20group%20by%20country,city"
provides the following result:
{"branchNames": ["country", "city"],"leafNames": ["count(*)"],"values": {"United States": {"Portland": [56],"N. Virginia (Amazon)": [83]},"Ireland": {"Dublin": [24]}}}
Learn more about user sessions API.
Convert queries into USQL custom metrics
You can convert some queries into USQL custom metrics for your web, mobile, and custom applications.
USQL custom metrics are available as user session custom metrics (USCMs) and user action custom metrics (UACMs). User action custom metrics are supported since Dynatrace version 1.260.
- Go to
 Query User Sessions.
Query User Sessions. - Enter the query, and then select Run query.
For a list of supported fields, see the detailed guides for your web, mobile, and custom applications. - Select Create custom metric.
- Enter the metric name, and then review the proposed settings.
Limitations
-
Dynatrace stores and retains Real User Monitoring (user actions and user sessions) for a limited period of time. See Data retention periods for details.
-
The default result set is 50 but the number of results can be increased to a maximum of 5000 by using the
LIMITkeyword. -
The number of potential maximum bucketed results is limited to a maximum of 100,000. The default is 10,000.
This affects howTOP()is applied whenDISTINCTorGROUP BYis used. If noTOP()is specified, 10,000 possible results are spread evenly across the specified columns. These default values can be overwritten by specifying aTOP()for each column. The multipliedTOP()-values can't exceed 100,000 results.Further limitations
- The
TOP()function can be used to increase the number of different values per aggregation. - The maximum number of different results per aggregation is limited to 1000.
- The following query uses at most 10,000 theoretical possible results:
select browserFamily, city, count * FROM usersession group by browserFamily, city - The following query includes
TOP()and can therefore use up to 100,000 (100 × 1000) theoretical possible results:select TOP(browserFamily, 1000), TOP(city, 100), count * FROM usersession group by browserFamily, city
- The
-
Joins aren't allowed.
-
Only one table is allowed per
SELECT. -
Searches for string-values with regular expressions aren't supported.
-
Two different fields can't be compared. For example
WHERE field1 = field2doesn't work. -
WHEREconditions only work on fields, so neitherWHERE truenorWHERE COUNT(*) > 3is supported. -
Only closed user sessions can be queried. Live user sessions aren't taken into account.
-
Ordering is partially supported.
For example, ordering by mathematical operation is not supported.
SELECT endTime - startTime AS duration FROM usersession ORDER BY duration -
For extensive timeframes and high-load environments, we might extrapolate the data from a sampled subset (extrapolation level). This takes place regardless of whether you use the Dynatrace API or the Dynatrace web UI. If you need 100% accurate data, reduce the timeframe or add additional conditions to further filter out the requested data.
-
Functions aren't allowed in the
GROUP BYclause. Therefore, if you want to group by month, specify an alias. -
FUNNELcan't be used with theSELECT *functions, keywords such asJSON, and theGROUP BY,ORDERandLIMITstatements. -
For mathematical operations, support for
GROUP BY,ORDER BY, and other operations on functions is not available. -
A maximum of 10 conditions can be applied to
FUNNEL. -
Certain fields, such as
duration, always return integer values instead of decimal values when mathematical operations, such as a division, are performed on them. This is because these fields are stored and displayed as integer values. For example,SELECT duration FROM usersessionreturns a duration of4800, andSELECT duration/1000 FROM usersessionreturns a duration of5.
 Session Segmentation
Session Segmentation