Oracle Database extension
- Latest Dynatrace
- Extension
Observe, analyze, and optimize the usage, health, and performance of your database.
Get started
Overview
This remote extension runs on an ActiveGate within your environment. It connects to each Oracle Database you want to monitor, executes a series of queries on various views, and sends the collected data to Dynatrace.
Dynatrace automatically detects all applications and microservices in your system and their Oracle Database usage.
Dynatrace uses AI to diagnose anomalies in real time and identify root causes in slow-performing or erroneous SQL statements. Code-level insights combined with database server monitoring provide comprehensive observability.
The Oracle Database extension provides server-side monitoring with availability and performance statistics, SQL statements, and log insights.
Use cases
- Understand all database dependencies of your applications, which database statements are executed, and their performance.
- Improve the performance of your application by reducing or optimizing typical database patterns like the 1+N query problem.
- Understand the resource impact that your applications have on your database.
- Understand the impact that resource shortages or other database issues have on your application by observing the database server itself.
- Manage and analyze DB audit logs to spot invalid login attempts.
- Track the health and performance of Oracle Database servers (either standalone or multi-tenant).
- Track the performance of the most time-consuming queries.
- Speed up application-problem diagnosis when it's caused by the database.
Requirements
- Decide which Oracle Database server you want to monitor. The Oracle Database extension supports Oracle Database versions 12.2+ with the following setups:
- Oracle standalone servers
- Oracle Multitenant (CDB/PDB)
- Oracle RAC
- Oracle AWS RDS
- Designate an ActiveGate group or groups that will remotely connect to your Oracle Database server to pull data. All ActiveGates in each group must connect to your Oracle database server.
-
Create a dedicated database user in your database instance with the necessary permissions. Dynatrace uses this user to run monitoring queries against your Oracle database.
-
Authenticate user accounts
Use a dedicated user account for monitoring. You can find user creation scripts on GitHub. These scripts create a user with the
CREATE_SESSIONrole andSELECTpermissions on the following performance views:Performance views
CDB_DATA_FILESCDB_TABLESPACE_USAGE_METRICSCDB_TABLESPACESCDB_TEMP_FILESGV_$ARCHIVE_DESTGV_$ARCHIVE_DEST_STATUSV_$ASM_DISK_STATV_$ASM_DISKGROUP_STATV_$BACKUP_SET_DETAILSGV_$CLUSTER_INTERCONNECTSGV_$CONTAINERSV_$CONTAINERSGV_$CON_SYS_TIME_MODELGV_$CON_SYSSTATGV_$DATABASEV_$DATABASEV_$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTIONGV_$DATAFILEV_$DATAFILEGV_$DATAGUARD_STATUSGV_$INSTANCEGV_$INSTANCE_PINGGV_$LIBRARYCACHEV_$LOGGV_$METRICGV_$METRICGROUPGV_$PARAMETERGV_$PDBSGV_$PGASTATV_$RECOVER_FILEV_$RECOVERY_FILE_DESTGV_$RESOURCE_LIMITV_$RMAN_BACKUP_JOB_DETAILSGV_$SESSIONV_$SESSIONGV_$SGASTATGV_$SQLV_$SQLGV_$SQLAREAV_$SQL_PLANGV_$SQL_PLANV_$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALLGV_$SYSSTATGV_$SYSTEM_EVENTGV_$SYSTEM_WAIT_CLASSV_$TABLESPACEV_$TEMPFILE
Alternatively, you can assign the
SELECT_CATALOG_ROLEto the monitoring user.From extension version
3.9.2+, the extension will attempt to query the local IP of the each node on RAC setups using theUTL_INADDR.get_host_addressfunction. As such, the following Access Control List permission will be required:BEGINDBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.create_acl (acl => 'dynatrace.xml',description => 'Allow DNS resolution checks to get RAC node IP addresses',principal => '<DYNATRACE_USER>',is_grant => TRUE,privilege => 'resolve',start_date => SYSTIMESTAMP,end_date => NULL);FOR instance_host IN (SELECT DISTINCT host_nameFROM gv$instance -- Retrieves all RAC node hostnames) LOOPDBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.assign_acl (acl => 'dynatrace.xml',host => instance_host.host_name, -- Assign ACL to each instance hostlower_port => NULL,upper_port => NULL);END LOOP;COMMIT;END;/This only applies for RAC databases or other multi-instance setups. The
UTL_INADDR.get_host_addressquery will only run if theracfeature set is enabled. These permissions are already included in the user creation scripts.For multitenant Oracle DB setups, ensure the extension is configured to point to the CDB. PDB discovery and monitoring occur automatically. In this case, explicit permissions to access data across all containers are required:
alter user <your_username> set container_data=all container = current;These privileges are already included in the user creation scripts.
Users of Databases who want to use Query Execution Plans must also provide permission for the
V$SQL_PLAN,V$SESSION,V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL, andV$SQLviews. These permissions are included in the user creation scripts. For more details, see the execution plan monitoring section.
-
Compatibility information
The following Oracle versions are supported:
- Oracle DB 12.2+
The following architectures are supported:
- Oracle standalone servers
- Oracle Multitenant (CDB/PDB)
- Configure monitoring for CDB to detect all PDBs.
- Oracle AWS RDS
- Oracle RAC
- Configure monitoring for the SCAN listener to detect all instances and databases.
Activation and setup
Follow these steps to set up server-side monitoring for Oracle databases.
If your Oracle Database server runs on a virtual machine or bare metal, install OneAgent on it to start collecting system performance metrics.
To monitor Oracle Database server's health and performance, activate the remote Oracle Database extension. The extension queries the database performance views to collect metrics and events.
Add DB instance
-
Go to Dynatrace Hub
 .
. -
Select and install Oracle Database extension. This enables the extension in your monitoring environment.
- Required permission: Change monitoring settings
-
Select Add DB Instance in
 Databases. This opens the Add DB Instance wizard.
Databases. This opens the Add DB Instance wizard. -
Select Oracle section in the wizard.
Select hosting type
Select a hosting type from the options. This choice determines which script generates the necessary database objects later in the process.
- From the Add DB Instance wizard, select the host type that matches your requirement.
- Select Next.
Select ActiveGate group
- Select the ActiveGate group to determine which ActiveGates will run the extension.
- Select Next step.
Accept license agreement
An Oracle Database extension requires that you accept the Dynatrace redistribution license agreement for Oracle JDBC Driver.
Create a connection
Set up the connection to your database instance. Provide the required credentials directly in the wizard or use secure alternatives:
- Name the connection, so you can identify it later.
- Add the details in the Configure connection section.
- Select connection. Use Select from existing hosts or Enter manually to add connection details.
- Add Database identifier, either Service Name or SID.
- Add Service name.
- Provide the Authenticate credentials for the
dynatracemonitoring user you have created directly or use secure alternatives.- Basic credentials: Authentication details passed to Dynatrace when activating monitoring configuration are masked to prevent them from being retrieved.
- Credential vault: Use vault credentials to securely store and retrieve database credentials.
- Select Next.
Install instance
- Add manual configurations based on the monitoring requirements.
- Select Create DB instance monitoring.
Get started for Oracle Database clients
Follow these steps to set up Dynatrace to monitor Oracle databases for both client-side.
-
If the application connecting to the Oracle Database server runs on a virtual machine or bare metal, install OneAgent on that machine to get started.
-
If the application that connects to the Oracle Database server runs as a workload in Kubernetes or OpenShift, set up Dynatrace on Kubernetes or OpenShift.
-
If the application runs as a workload in Kubernetes, set up Dynatrace on Kubernetes.
Activate the following OneAgent features to gain full tracing insights:
- Node.js Oracle DB
- PHP Oracle
Activate log monitoring
Activate log monitoring to get full log insight.
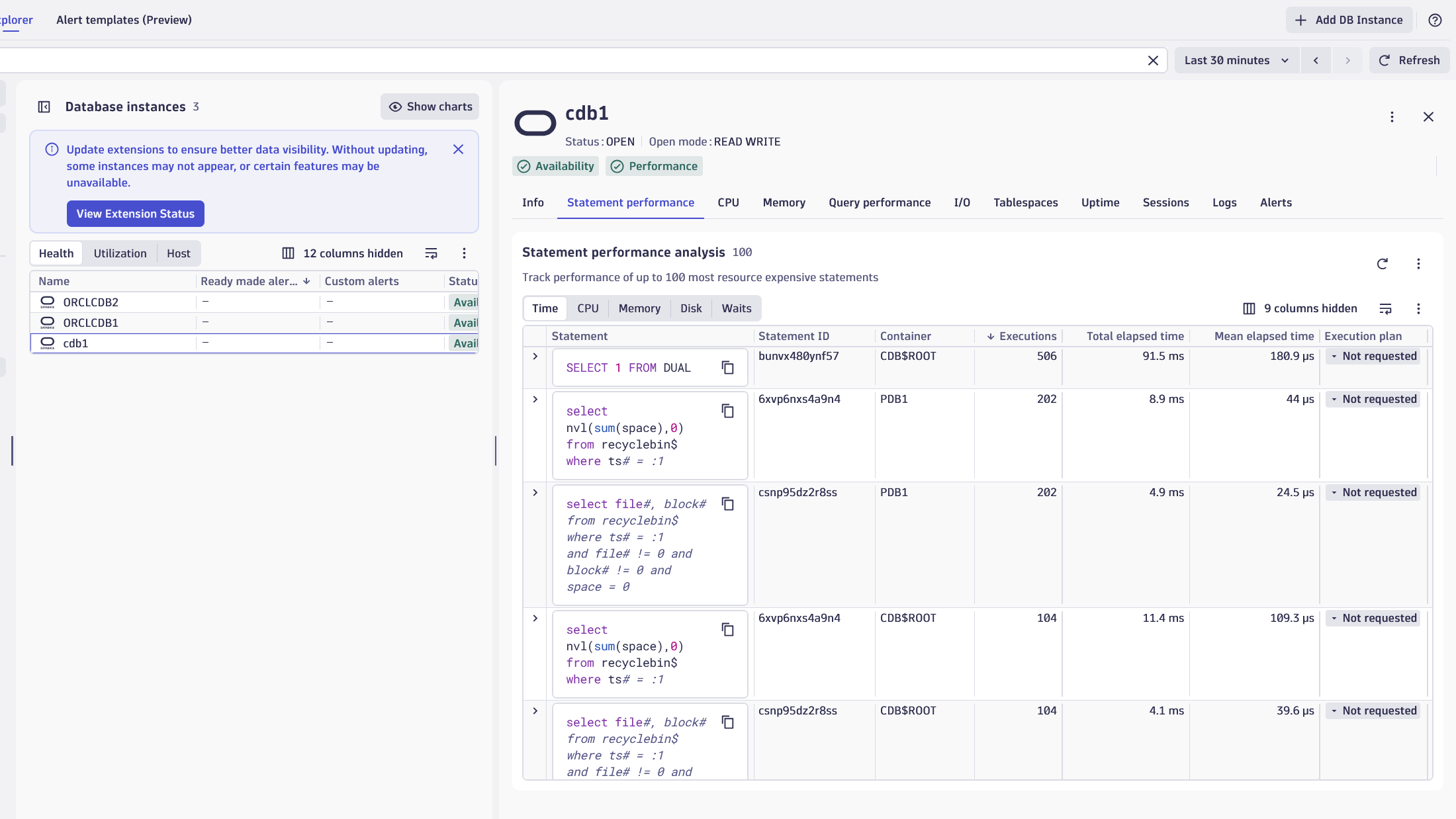
With the TopN feature set, the extension reports the most time-consuming queries on the Oracle Instance entity page, in a Logs card. Enabling this feature may expose sensitive data in the reported queries.
Details
Extension package
This extension package contains:
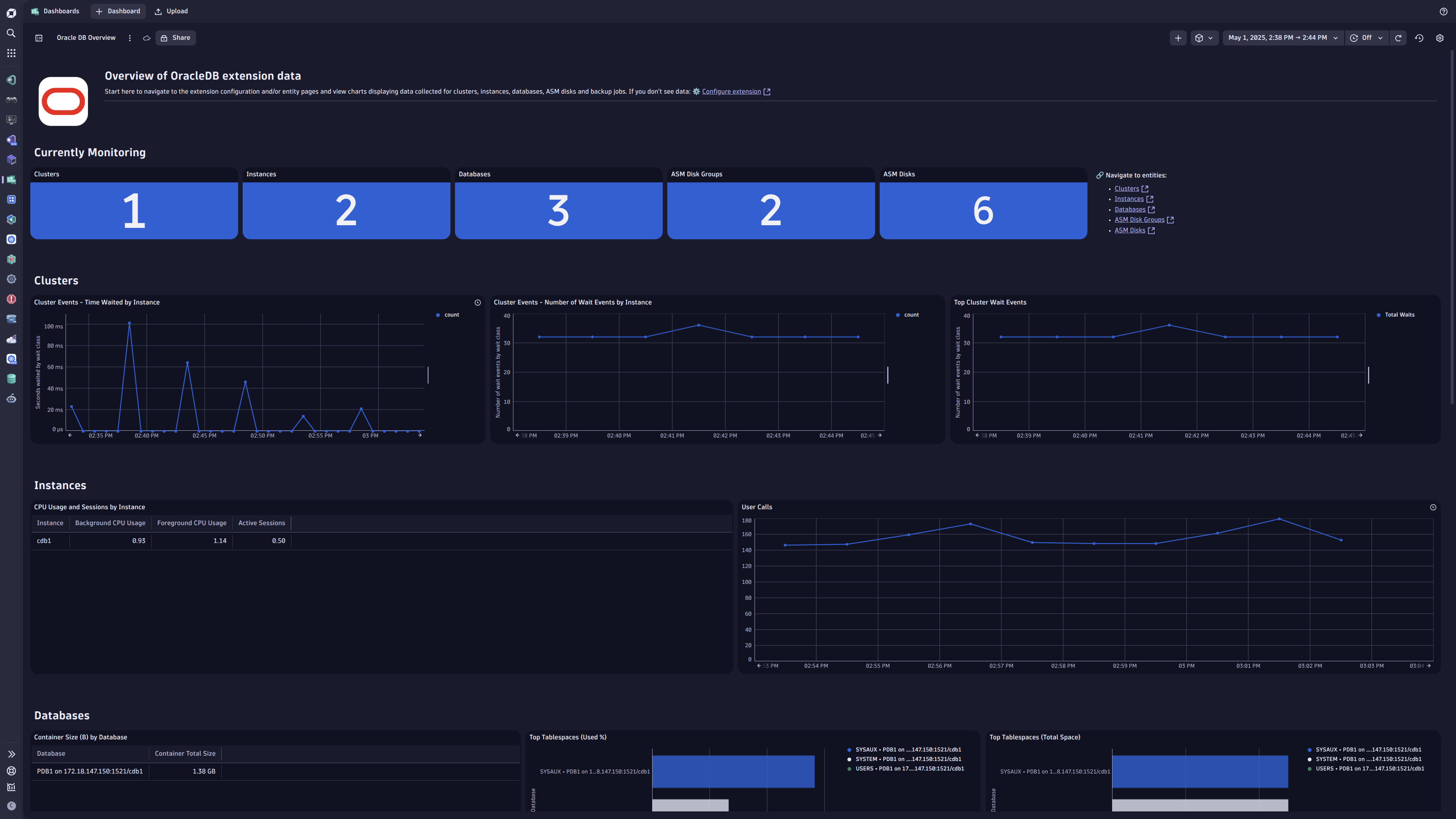
- Topology and relationship definitions for RAC Clusters, Backup Jobs, Databases, Instances, ASM Disks, and ASM Disk Groups.
- Classic and New Dashboard offering a monitoring overview for the Oracle Database environment.
- Alerts for failed backups, unavailable PDBs, unavailable instances, high tablespace usage, and more.
- Unified Analysis page for the above-mentioned topology.
Licensing and cost
There is no charge for obtaining the extension, only for the data that the extension ingests. The details of license consumption will depend on which licensing model you are using. This will either be Dynatrace classic licensing or the Dynatrace Platform Subscription (DPS) model.
Dynatrace Platform Subscription
With a Dynatrace Platform Subscription (DPS) license:
-
For metrics, license consumption is based on the number of metric data points ingested. This is billed as Metrics powered by Grail.
The following formula will provide the approximate annual data points ingested assuming all feature sets are enabled. Actual ingested metric data point volumes will depend heavily on your specific Oracle Database environment.
((55 * number of instances)+ (7 * number of databases)+ (8 * number of backup jobs per year)+ (5 * number of ASM disks)+ (3 * number of ASM disk groups))* 60 minutes * 24 hours * 365 days data points per year -
For logs, regular consumption for Log Analytics applies, see Log Analytics (DPS).
Classic licensing
With a Dynatrace classic license:
-
For metrics, metric ingestion consumes Davis Data Units (DDUs) at the rate of .001 DDUs per metric data point. Multiply the above formula for annual data points by .001 to estimate annual DDU usage.
-
For logs, regular DDU consumption for log monitoring applies. Depending on your licensing model, refer either to DDU consumption for Log Management and Analytics or DDUs for Log Monitoring Classic.
Execution plan monitoring
For SaaS customers with access to  Database Services Classic, the execution plan monitoring functionality is also available when analyzing statement performance.
Database Services Classic, the execution plan monitoring functionality is also available when analyzing statement performance.
For this feature to work, the DBMS_XPLAN package needs to be available, and the user configured in the Dynatrace extension needs to have permissions to call the DISPLAY_CURSOR function. As per the official documentation, this means that SELECT or READ permissions are required on the following views:
V$SQL_PLANV$SESSIONV$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALLV$SQL
In addition to this, the SELECT permission is also required for V$SQL_PLAN.
Sensitive data masking
Query performance tracking may expose sensitive data in reported statements. Dynatrace provides an optional mechanism that allows masking selected attributes. For details, see Log processing examples.
The configurations below provide an example of how sensitive data can be masked within tracked statements:
-
Create a new processing rule under Settings > Log Monitoring > Processing.
- Processor definition:
USING(INOUT content) | FIELDS_ADD(content: REPLACE_PATTERN(content, "(\"'\"):p1 (LD):p2 (\"'\"):p3", "${p1}${p2|sha1}${p3}"))
- Processor definition:
-
Alternatively, create/modify your custom extension to distribute such rules across your environment.
logProcessingRules:- ruleName: TopN statements maskingquery: event.group="query_performance"enabled: trueProcessorDefinition:rule: |USING(INOUT content) | FIELDS_ADD(content: REPLACE_PATTERN(content, "(\"'\"):p1 (LD):p2 (\"'\"):p3", "${p1}${p2|sha1}${p3}"))RuleTesting:sampleLog: |{"event.group": "query_performance","content": "/*dt:ownQuery*/SELECT DECODE(name, 'sessions', value) AS sessions_limit, DECODE(name, 'processes', value) AS processes_limit FROM v$parameter WHERE name IN('sessions', 'processes')"}
DQL and Logs
Audit log files tracking
Check log file's location
SELECT name, value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = 'audit_trail';
OSmeans that the audit logs are stored locally in the file.SELECT value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = 'audit_file_dest';
Specifies the log file's location.
Add OneAgent Log module security rules
Configure OneAgent Log module security rules to allow access to local files by adding the oracle.json file:
- on Linux/UNIX:
/var/lib/dynatrace/oneagent/agent/config/logmodule - on Windows:
%PROGRAMDATA%\dynatrace\oneagent\agent\config\logmodule
{"@version": "1.0.0","allowed-log-paths-configuration": [{"directory-pattern": "/u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/","file-pattern": "*.aud","action": "INCLUDE"}]}
OneAgent restart is not required. This configuration is applied within 1 minute.
Configure custom log source and log ingest rules
Custom log source
Use the log file location fetched via the query executed in the first step, for example, /u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/*.
Log ingest rules
An example configuration that includes only ORA-01017, which reports invalid username or password logon attempts, could be configured using:
Log content is any of: (.*)RETURNCODE:\[(\d+)\] "1017 AND Log source is any of:/u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/*
Accessing logs
Logs collected in the way described above can be accessed using the following DQL query:
fetch logs| filter matchesValue(log.source, "/u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/*")
Metrics extraction
Log processing rule
Configure the log processing rule to extract log attributes out of the log content:
- Rule name: preferred name
- Matcher:
matchesValue(log.source, "/u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/*") - Processor definition:
PARSE(content, "DATA ' RETURNCODE:['INT']' SPACE '\"' INT:ora.returncode LD") |PARSE(content, "DATA ' USERID:['INT']'SPACE CSVDQS:ora.userid LD") |PARSE(content, "DATA ' USERHOST:['INT']'SPACE CSVDQS:ora.userhost LD")
Metric extraction
Extract metrics from log entries to enable alerting:
- Metric key: for example,
log.oracle.invalid_credentials - Matcher:
matchesValue(log.source, "/u01/app/oracle/admin/oracle_standalone/adump/*") - Metric measurement:
Occurence of logs records - Dimensions: specify the log attributes to be used as metric dimensions
Feature sets
When activating your extension using monitoring configuration, you can limit monitoring to one of the feature sets. To work properly, the extension has to collect at least one metric after the activation.
In highly segmented networks, feature sets can reflect the segments of your environment. Then, when you create a monitoring configuration, you can select a feature set and a corresponding ActiveGate group that can connect to this particular segment.
All metrics that aren't categorized into any feature set are considered to be the default and are always reported.
A metric inherits the feature set of a subgroup, which in turn inherits the feature set of a group. Also, the feature set defined on the metric level overrides the feature set defined on the subgroup level, which in turn overrides the feature set defined on the group level.
cpu
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPU cores | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cpu.cores | Number of CPU cores |
| Background CPU usage (per second) | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cpu.backgroundTotal | CPU usage of background processes in centi seconds per second |
| Foreground CPU usage (per second) | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cpu.foregroundTotal | CPU usage of foreground processes in centi seconds per second |
queryPerformance
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection management time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.connectionManagement.count | Time spent on performing session connect and disconnect calls |
| PL SQL exec time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.plSqlExec.count | Time spent on running the PL/SQL interpreter |
| SQL exec time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.sqlExec.count | Time spent on executing SQL |
| SQL parse time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.sqlParse.count | Time spent on parsing SQL |
| DB Time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.dbTime.count | Time spent on performing Database user-level calls |
| DB CPU | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.queries.cpuTime.count | CPU time spent on performing database user-level calls |
waitEvents (detailed)
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number of wait events | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.wait.events.count | Total number of waits by wait event, excluding 'Idle' events. Only collects the top 20 most time consuming events. |
| Seconds waited | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.wait.events.time.count | Total amount of time waited by wait event, excluding 'Idle' events. Only collects the top 20 most time consuming events. |
tablespaces
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.totalSpace | Total size of tablespace, including extensibility. This covers both allocated an unallocated space as large as the tablespace can expand. |
| Free space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.freeSpace | Total free space available in the tablespace, in bytes. This includes space that is currently allocated and available for reuse and space that is currently unallocated. |
| Used space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.usedSpace | Total space in use within the tablespace, in bytes. |
| Tablespace usage | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.usage | The percentage of tablespace in use, relative to the total size (including extensibility). |
rac
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Instance ping | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.rac.instance_ping | Represents the current inter-instance ping of 8K messages as provided in GV$INSTANCE_PING. |
| — | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.rac.interconnects | — |
default
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster topology | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cluster_topology | A state metric whose dimensions represent all Oracle clusters and their linked instances and hosts |
| Database topology | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.database_topology | A state metric whose dimensions represent all Oracle instances and their linked databases |
| Instance status | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.status | A state metric representing the details of the connected Oracle instance. |
| Instance Uptime | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.uptime | The uptime of the Oracle instance in seconds. |
| Database status | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.db_status | A state metric representing details of the connected Oracle database. |
asm (detailed)
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Free space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk.free_mb | Free disk space available on this Oracle ASM Disk |
| Total space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk.total_mb | Total disk space available on this Oracle ASM Disk |
| Used space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk.usage | Percentage of disk space used on this Oracle ASM Disk |
| Reads | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk.reads.count | Number of reads from this Oracle ASM Disk |
| Writes | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk.writes.count | Number of writes to this Oracle ASM Disk |
TopN
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|
Datafiles
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
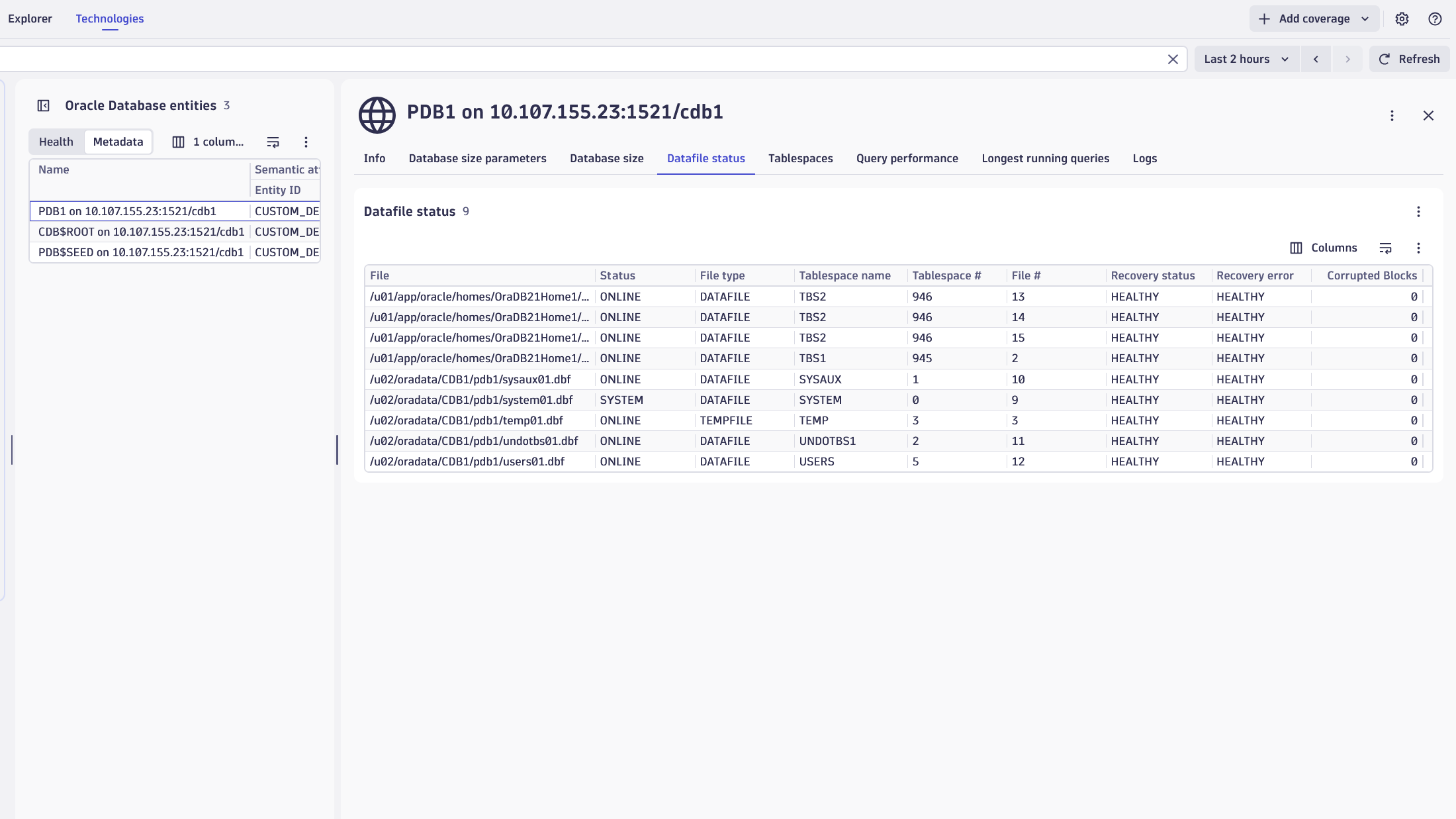
| Datafile status | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.datafile.status | State metric representing the status of Datafiles and Tempfiles across containers (database and any PDBs). |
| Datafile number of corrupted blocks | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.datafile.corrupted_blocks | Metric representing the number of corrupted blocks reported by V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTION for each Datafile |
waitEvents
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number of wait events by wait class | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.wait.count | Total number of waits by wait class, excluding 'Idle' events |
| Seconds waited by wait class | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.wait.time.count | Total amount of time waited by wait class, excluding 'Idle' events |
io
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical bytes read | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.io.bytesRead.count | Total size in bytes of disk reads by all database instance activity including application reads, backup, recovery, and other utilities |
| Physical bytes written | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.io.bytesWritten.count | Total size in bytes of all disk writes for the database instance including application activity, backup, recovery, and other utilities |
| Total wait time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.io.wait.count | Total time spent in all wait states except for Idle class |
Data guard
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dataguard severe events | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.dataguard.severeEvents | Counts the number of fatal and severe Data guard events occurred in the last day. If this count is greater than 0, check its dimensions to take action for the specific events. |
| NOLOGGING activity | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.dataguard.nologgingActivity | Counts the number of files which contain NOLOGGING activity in the last day. If the count is greater than 0 then the standby database is vulnerable; check the dimensions to find out which files must be refreshed on the standby. |
| Archive destination status | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.dataguard.archiveDestErrStatus | Counts the number of invalid or errored statuses of archive destinations. If the count is greater than 0, use the dimensions to understand the status and destination it refers to. |
| Seq. difference | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.dataguard.seqDifference | Tracks the difference in sequence number between the latest archived and applied redo log. Use this count along with the dimensions to identify gaps between the primary and archive destination. |
tablespaces (detailed)
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.totalSpace | Total size of tablespace, including extensibility. This covers both allocated an unallocated space as large as the tablespace can expand. |
| Free space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.freeSpace | Total free space available in the tablespace, in bytes. This includes space that is currently allocated and available for reuse and space that is currently unallocated. |
| Used space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.usedSpace | Total space in use within the tablespace, in bytes. |
| Allocated space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.allocatedSpace | Total space in use within the tablespace, in bytes. |
| Tablespace usage | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.usage | The percentage of tablespace in use, relative to the total size (including extensibility). |
Blocked sessions
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|
multitenancy
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-total_size | Shows the disk space (in bytes) used by the PDB, including both data and temp files. |
| Block size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-block_size | The current block size for the PDB |
| Diagnostic size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-diagnostic_size | Shows the current disk space usage (in bytes) of the diagnostic traces generated in the PDB. |
| Audit files size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-audit_files_size | Shows the current disk space usage (in bytes) by Unified Audit files (.bin format) in the current PDB. |
| Max size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-max_size | Shows the maximum amount of disk space (in bytes) that can be used by data and temp files in the PDB. If the value is 0 then there is no limit. |
| Max diagnostic size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-max_diagnostic_size | Shows the maximum amount of disk space (in bytes) that can be used by diagnostic traces generated in the PDB. If the value is 0 then there is no limit. |
| Max audit size | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.pdb-max_audit_size | Shows the maximum amount of disk space (in bytes) that can be used by Unified Audit files (.bin format) in the PDB. If the value is 0 then there is no limit. |
asm
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Free space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk_group.free_mb | Free disk space available on this Oracle ASM Disk Group |
| Total space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk_group.total_mb | Total disk space available on this Oracle ASM Disk Group |
| Used space | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.asm.disk_group.usage | Percentage of disk space used on this Oracle ASM Disk Group |
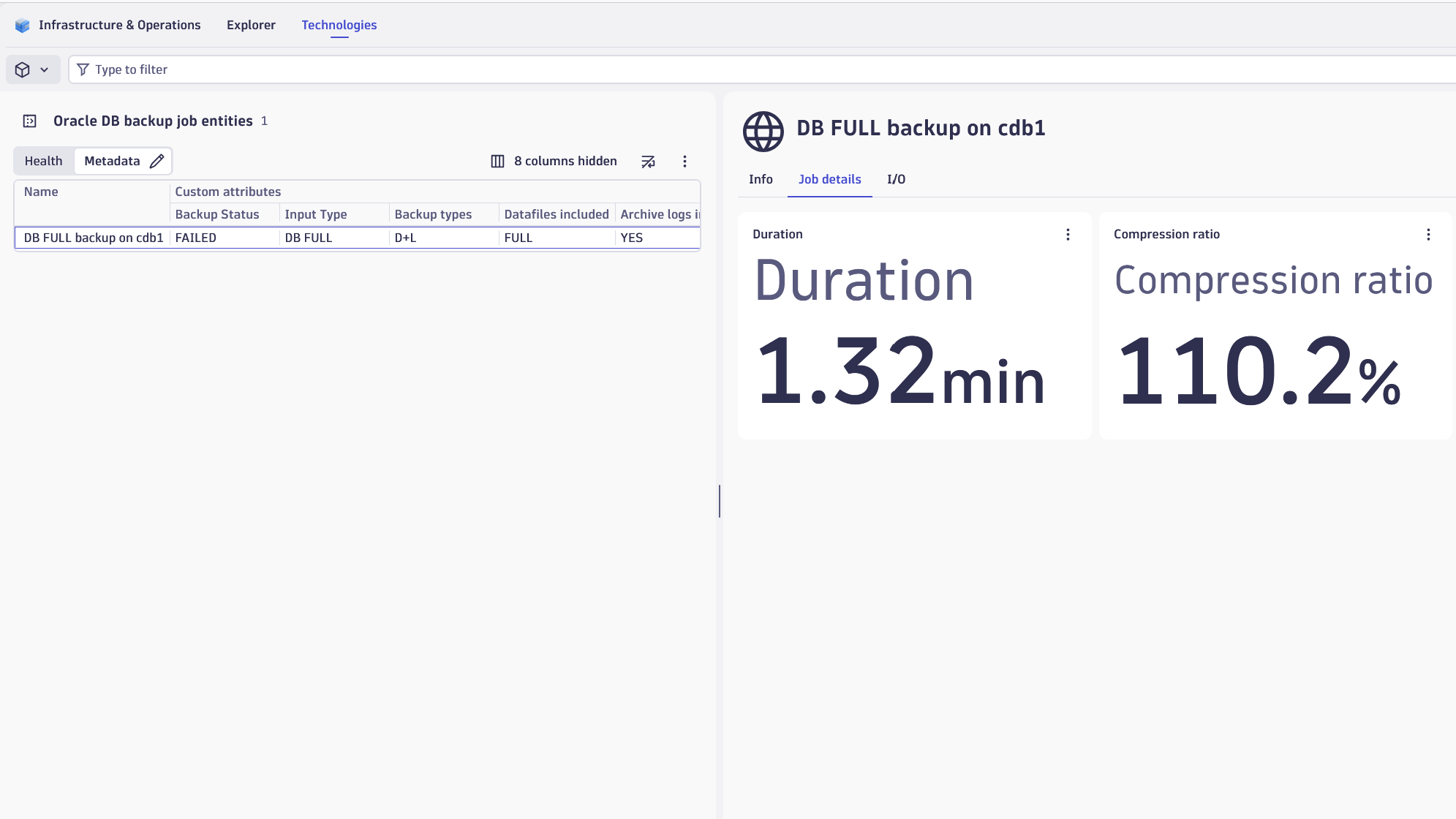
backupJob
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Input bytes | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-input_bytes | Sum of all input file sizes backed up. |
| Output bytes | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-output_bytes | Output size of all pieces generated. |
| Elapsed seconds | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-elapsed_seconds | Number of elapsed seconds. |
| Compression ratio | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-compression_ratio | Compression ratio. |
| Input bytes per second | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-input_bytes_per_second | Input read-rate-per-second. |
| Output bytes per second | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-output_bytes_per_second | Output write-rate-per-second. |
| Auto - backup count | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup-autobackup_count_number | Number of autobackups performed by this job. |
| Backup state | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup.state | A state metric representing the details of a Backup Job. |
| Time since last backup | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.backup.time_since | The time elapsed since the last backup completed successfully. |
memory
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PGA aggregate limit | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.pga.size.pgaAggregateLimit | Limit on the aggregate PGA memory consumed by the instance |
| PGA aggregate target | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.pga.size.pgaAggregateTarget | Target aggregate PGA memory available to all server processes attached to the instance |
| PGA memory used | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.pga.used | PGA memory consumed by work areas |
| Allocated PGA | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.pga.allocated | Current amount of PGA memory allocated by the instance |
| Shared pool free | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.sga.cacheBuffer.sharedPoolFree | Amount of free system global area (SGA) memory available in shared pool |
| Redo log space wait time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.sga.redoBuffer.redoLogSpaceWaitTime.count | Total elapsed time of waiting for redo log space request |
| Redo size increase | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.sga.redoBuffer.redoSizeIncrease.count | Total amount of redo generated in bytes |
| Redo write time | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.sga.redoBuffer.redoWriteTime.count | Total elapsed time of the write from the redo log buffer to the current redo log file |
| Logical reads | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.sessionLogicalReads.count | The sum of "db block gets" plus "consistent gets" |
| Physical reads | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.physicalReads.count | Total number of data blocks read from disk |
| Physical reads direct | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.physicalReadsDirect.count | Number of reads directly from disk, bypassing the buffer cache |
| Sorts in memory | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.memorySorts.count | Number of sort operations that were performed completely in memory and did not require any disk writes |
| Sorts on disk | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.diskSorts.count | Number of sort operations that required at least one disk write |
| DB Block gets from cache | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.dbBlockGetsFromCache.count | Number of times a consistent read was requested for a block from the buffer cache. |
| Consistent gets from cache | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.consistentGetsFromCache.count | Number of times a CURRENT block was requested from the buffer cache. |
| Physical reads into cache | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.physicalReadsCache.count | Total number of data blocks read from disk into buffer cache. |
| Library cache hit ratio | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.memory.libraryCacheHitRatio | Library cache hit ratio |
limits
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sessions utilization | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.limits.sessions_utilization | Utilization of sessions on the instance. This is a percentage of current utilization relative to the limit. |
| Processes utilization | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.limits.processes_utilization | Utilization of processes on the instance. This is a percentage of current utilization relative to the limit. |
sessions
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Active Sessions | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.sessions.active | Active sessions count |
| Blocked Sessions | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.sessions.blocked | Blocked sessions count |
| Total sessions | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.sessions.all | Total sessions count |
| User calls | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.sessions.userCalls.count | Total number of logins, parses, or execute calls |
| Deadlocks | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.sessions.deadlocks.count | Total number deadlocks |
FRA
| Metric name | Metric key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FRA Usage | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.fra.usage | The percentage disk utilization in the fast recovery area. |
| FRA limit | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.fra.limit | Maximum amount of disk space (in bytes) that the database can use for the fast recovery area. This is the value specified in the DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE initialization parameter. |
| FRA used | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.fra.used | Amount of disk space (in bytes) used by fast recovery area files created in current and all previous fast recovery areas. Changing fast recovery areas does not reset SPACE_USED to 0. |
| FRA reclaimable | com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.fra.reclaimable | Total amount of disk space (in bytes) that can be created by deleting obsolete, redundant, and other low priority files from the fast recovery area |
FAQ
How does this Dynatrace extension collect data from my databases?
This extension will run from your Dynatrace ActiveGates and connect to the configured databases. Once the connection has been established, the extension will regularly run queries on the database to gather performance and health metrics, reporting the results back to Dynatrace.
Only SELECT queries are executed to collect data, and the vast majority of these will be selecting GV$ or V$ views. To see exactly which queries are executed, download the extension yaml artifact by going to Release notes, opening a release and pressing the Download version button.
How often are these monitoring queries executed?
From version 3.2.0 onwards, query execution frequency is controlled by the configuration variables query-interval and heavy-query-interval. Most of the queries executed by the extension will run every query-interval minutes (with a default of 1 minute), while the queries under
asm (detailed)tablespacestablespaces (detailed)Blocked sessionsTopN
will run every heavy-query-interval minutes (with a default of 5 minutes).
For older versions, most queries run every minute, with exceptions for the heavy queries mentioned above, which run every 5 minutes.
How do I adjust query timeout?
By default, the extension's monitoring queries will timeout after 10 seconds. For a couple of selected queries, the long-running-query-timeout variable allows you to specify, in seconds, the timeout for the queries in the following feature sets:
asm (detailed)tablespacestablespaces (detailed)TopN
What is the difference between Feature set and Feature set (detailed)
The following feature sets have both a regular version and a detailed versions. These can be enabled or disabled in accordance to your specific use-case:
asmandasm (detailed)- Due to the high license consumption associated with monitoring thousands of ASM disks, the
asmfeature set captures only ASM disk group data, while theasm (detailed)feature set captures data for all disks. Both feature sets can be enabled at the same time.
- Due to the high license consumption associated with monitoring thousands of ASM disks, the
waitEventsandwaitEvents (detailed)- To control license consumption, the
waitEventsfeature set will collect wait time metrics aggregated by wait class, while thewaitEvents (detailed)feature set collects metrics for the top 20 wait events.
- To control license consumption, the
tablespacesandtablespaces (detailed)- Due to high the CPU consumption caused by joining tablespace metrics with datafile data, the
tablespacesfeature set does not collect thecom.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.allocatedSpacemetric coming fromCDB_DATA_FILES(whichtablespaces (detailed)does). Furthermore, thetablespacesfeature set only collects data for tablespaces with more than 50% used space (as reported byCDB_TABLESPACE_USAGE_METRICS), while thetablespaces (detailed)feature set collects metrics for all tablespaces. Only one of these feature sets should be enabled at any given time.
- Due to high the CPU consumption caused by joining tablespace metrics with datafile data, the
Why am I missing Dataguard metrics?
For some of the Dataguard metrics, not seeing any data is the correct behavior and it means the Data guard deployment is working as expected. The following metrics will only show datapoints in case there are issues which need further investigation:
- NOLOGGING activity will record a metric datapoint whenever there are operations executed against the database which will not generate redo log records. This requires investigation because from a Data guard perspective the mechanism is completely bypassed when such activity occurs, leaving the standby vulnerable until these files are manually refreshed.
- Dataguard severe events will record a metric datapoint whenever Data guard reports a fatal or severe event. In such a situation, the metric dimensions will carry the event message/description which should be further investigated on the Database instance.
- Archive destination status will record a metric datapoint whenever the Database's archive destinations are reporting an Invalid or Error status. The metric dimensions will show a description of the status as well as point to the archive destination which reported the error.
Why am I missing CPU usage metrics?
The com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cpu.backgroundTotal and com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.cpu.foregroundTotal metrics are collected from the GV$METRIC view filtering by metric group name System Metrics Long Duration (Group ID 2). Since metrics for this group are only populated at the CDB level, these two metrics will only be collected when the extension is configured to connect to the CDB and not the PDB.
If you are missing these two metrics, double-check your connection configuration and ensure that the extension configuration is pointing to the CDB.
Why are the tablespace usage metrics reported by Dynatrace different to what I am used to seeing?
While tablespace usage monitoring on Oracle DB is sometimes done by manually going through datafiles, in Dynatrace the metrics related to tablespace usage, com.dynatrace.extension.sql-oracle.tablespaces.*, all come from the DBA_TABLESPACE_USAGE_METRICS view. This view provides Oracle's own calculations on tablespaces' maximum and used space. The values reported for maximum space (and hence used space %) can be quite different from the datafile approach, as this view not only takes into account underlying storage available space, but also auto-extends. To learn how these metrics are calculated, see Oracle's table usage metrics.
Why do I see duplicate entities?
When monitoring RAC setups, node discovery is done automatically based on the data collected from the GV$ views. The monitoring configuration should be configured only for the listener in front of the cluster, and not for each individual cluster node. If you are seeing duplicate clusters or nodes, ensure that you have configured the extension to connect to the cluster listener, and not to each individual node.
Also, confirm that the extension is configured to connect to the CDB, and not the individual PDBs.
Why am I not seeing my databases?
When there is no data at all for a whole database, the most likely scenario is that there was some problem in the connection between the ActiveGate and the database server to be monitored.
-
First, ensure that the connection details (hostname/IP, port, service name/SID) were correctly configured and that the user account provided to the extension has the permissions to establish a session.
-
Next, confirm that a connection can be established from the ActiveGate server to the Database server, and that there are no firewalls blocking the connection. Use the Dynatrace DB connection check tool, to ensure the JDBC can establish a connection.
If you are missing data only for a specific metric, or set of metrics, it may be a problem related to the permissions granted to the user account. Ensure that all the required permissions highlighted on the Hub tile are provided. The ActiveGate logs will also indicate if an error occurred during the execution of monitoring query.
In some cases, a missing metric might indicate the extension was not properly configured (CDB vs. PDB, for example). Some metrics work at the CDB level, not the PDB, which can cause confusion. Double-check your connection configuration and ensure that the extension configuration is pointing to the CDB, as mentioned above.
Where do I look for diagnostic logs?
You can find detailed error messages in the ActiveGate logs. Most logs can be found under the ActiveGate logs directory on the server itself.
- Alternatively, you can collect diagnostics remotely, which include relevant logs.
Troubleshooting
- To troubleshoot this extension, use the guide(s) in the Dynatrace Community