Stream syslog to Dynatrace with Fluentd (Logs Classic)
- Tutorial
- 3-min read
Log Monitoring Classic
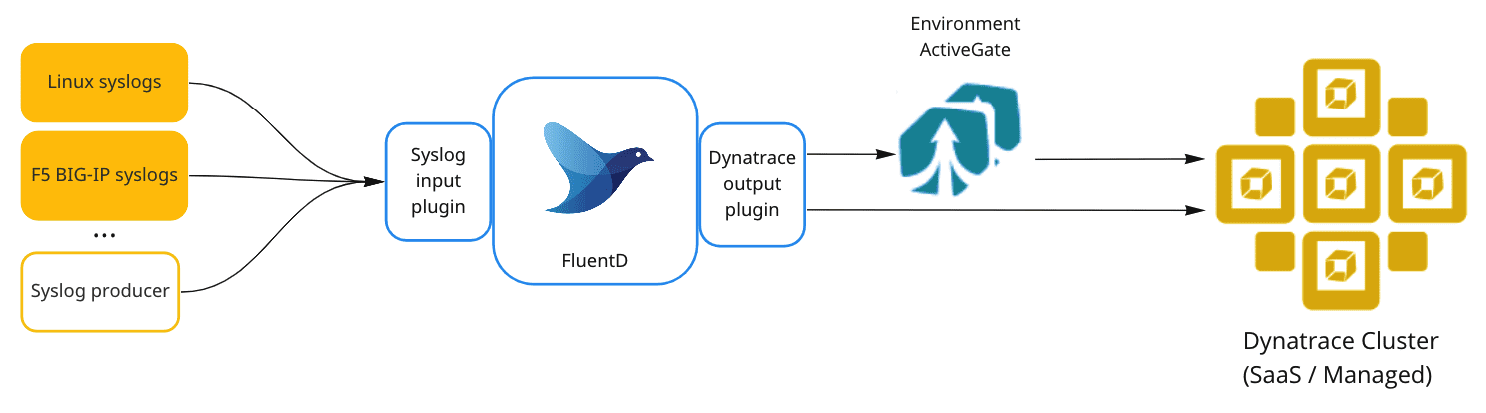
You can send Syslog to Dynatrace using Fluentd. Configure Fluentd to send Syslog to Dynatrace Log ingestion API.
Capabilities
- Syslog is a standard protocol for message logging and system logs management. Routers, printers, hosts, switches and other devices across platforms use Syslog to log users' activity, system and software lifecycle events, status, or diagnostics.
- During network monitoring, the remote Syslog server listens to the client's log messages and consolidates the logging data that can be then processed using the capabilities of Dynatrace Log Management and Analytics powered by Grail and Dynatrace AI-driven root cause analysis.
Configuration
Set up the flow from Syslog producer over Fluentd to Dynatrace with the following steps:
- Get a Dynatrace API token with the
logs.ingest(Ingest Logs) scope. - Deploy Fluentd according to your preferences.
- Deploy Fluentd. Fluentd can also run as a DaemonSet in a Kubernetes cluster. Built-in resiliency ensures data completeness and consistency even if Fluentd or an endpoint service temporarily goes down.
- Enable Fluentd to accept incoming Syslog messages.
- The in_syslog input plugin enables Fluentd to retrieve records via the Syslog protocol on UDP or TCP. It is included in Fluentd's core so no additional installation is needed in this step.
- Use the Dynatrace Fluentd plugin to stream logs to the Dynatrace cluster. The open-source Dynatrace Fluentd plugin uses Log ingestion API to send logs to Dynatrace.
- Point your devices to send syslogs to Fluentd.
Send syslogs to a remote endpoint
In the examples below, you can send syslogs to a remote endpoint, which is Fluentd.
Example 1
Configure Rsyslog on Linux Ubuntu to forward syslogs to a remote server, Fluentd.
You need to add the following line to the syslog daemon configuration file /etc/rsyslog.conf (UDP protocol):
*.* @<fluentd host IP>:5140
- The
*.*instructs the daemon to forward all messages to the specified Fluentd instance listening on port 5140.<fluentd host IP>needs to point to the IP address of Fluentd. - If you use TCP, type two
@symbols, (@@), as follows:
*.* @@<fluentd host IP>:5140
Example 2
Configure the F5 BIG-IP system to log to a remote syslog server (11.x - 17.x). Refer to the F5 BIG-IP documentation for procedures regarding remote Syslog configuration.
Add attributes to syslogs in Fluentd
The Dynatrace software intelligence platform and the Davis AI engine depend on context-rich, quality data. You can provide the context for your data ingested via Log ingestion API that supports a set of keys and semantic attributes. You can also provide custom attributes that don't require indexing in the Dynatrace Grail database.
Example 1
Add the log.source attribute based on the source of syslogs in Fluentd.
The syslog message often needs additional context to differentiate sources during analysis. In this example, there are two separate syslog endpoints exposed in Fluentd: one for the Linux syslogs, and the other one for F5 syslogs. This helps decorate log streams with meaningful log.source attribute. The Fluentd configuration file needs to look like this:
<source>@type syslogport 5140bind 0.0.0.0tag system-linux</source><source>@type syslogport 5141bind 0.0.0.0tag system-f5</source>
You need to add log.source attribute based on the fluentd tag.
<filter system-linux.**>@type record_transformer<record>log.source "linux syslogs"</record></filter><filter system-f5.**>@type record_transformer<record>log.source "f5 syslogs"</record></filter>
Refer to the Fluentd record_transformer filter plugin documentation for more details.