Define custom topology
- Latest Dynatrace
- 5-min read
- Published Apr 09, 2021
We continue with our Easy Shipping LTD logistics example, in which trucks and truck-mounted containers send telemetry data to Dynatrace.
The example data stream conforms to the Dynatrace metric line protocol format.
truck.fuel.total,trucknr=99,model=mac-granite 10234truck.fuel.usage,trucknr=99,model=mac-granite 17truck.operation.hours,trucknr=99,model=mac-granite 23766truck.fuel.total,trucknr=12,model=mac-anthem 234truck.fuel.usage,trucknr=12,model=mac-anthem 10truck.operation.hours,trucknr=12,model=mac-anthem 13766container.temperature,containernr=234321,trucknr=99 40container.temperature.dev,containernr=234321,trucknr=99 0container.temperature,containernr=111111,trucknr=12 39container.temperature.dev,containernr=111111,trucknr=12 2.5
Define new entity type
To define a new entity type, provide the entity name and specify its extraction rules.
 Define entity name
Define entity name
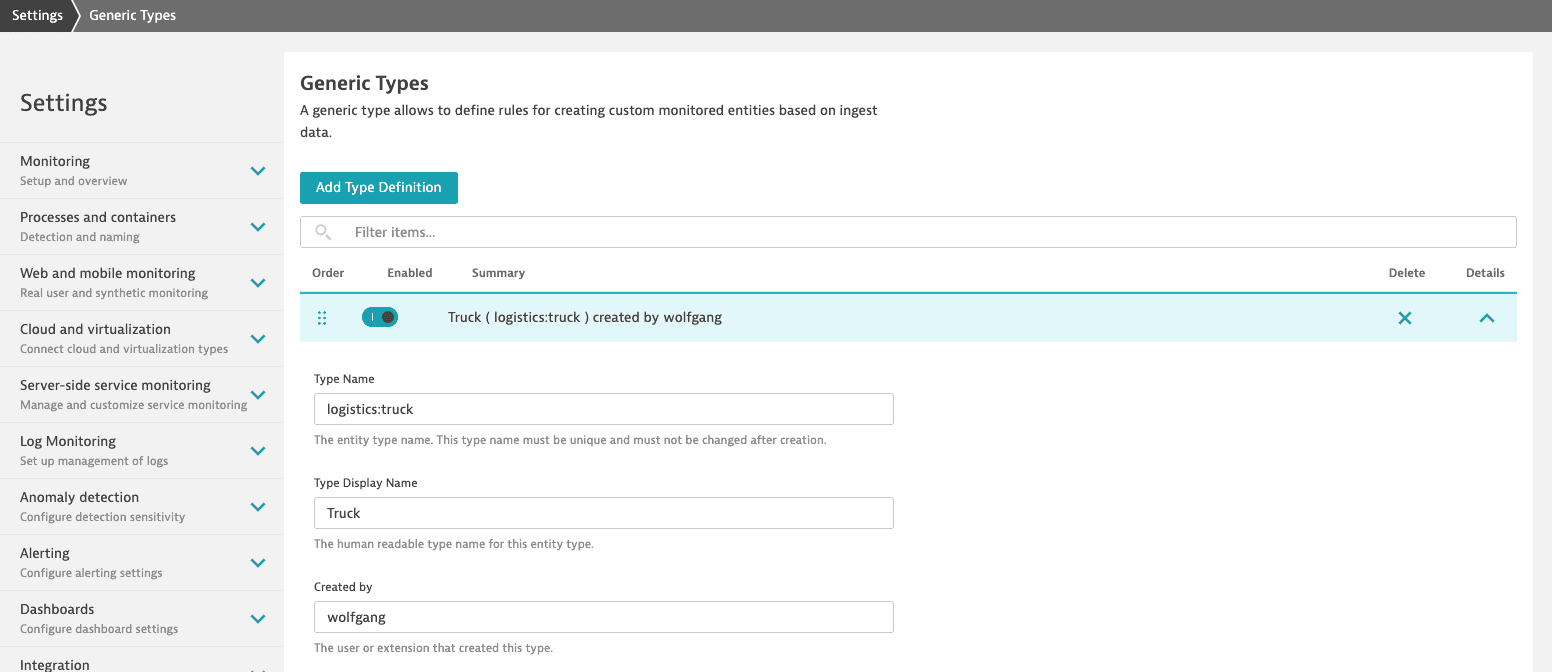
Based on the example above, define a new entity type Truck within a Dynatrace environment.
- Go to Settings > Topology model > Generic types.
- Select Add type definition to start defining your own custom
truckentity type. - Set Type name to a unique type name that will serve as the entity identifier.
To make sure it's unique for your whole Dynatrace environment, prefix Type name with your topology-specific domain (for example,
logistics:truck). - Set Type display name to a human-friendly display name.
- Set Created by to the creator's name (a person or extension).
Example
 Specify extraction rules
Specify extraction rules
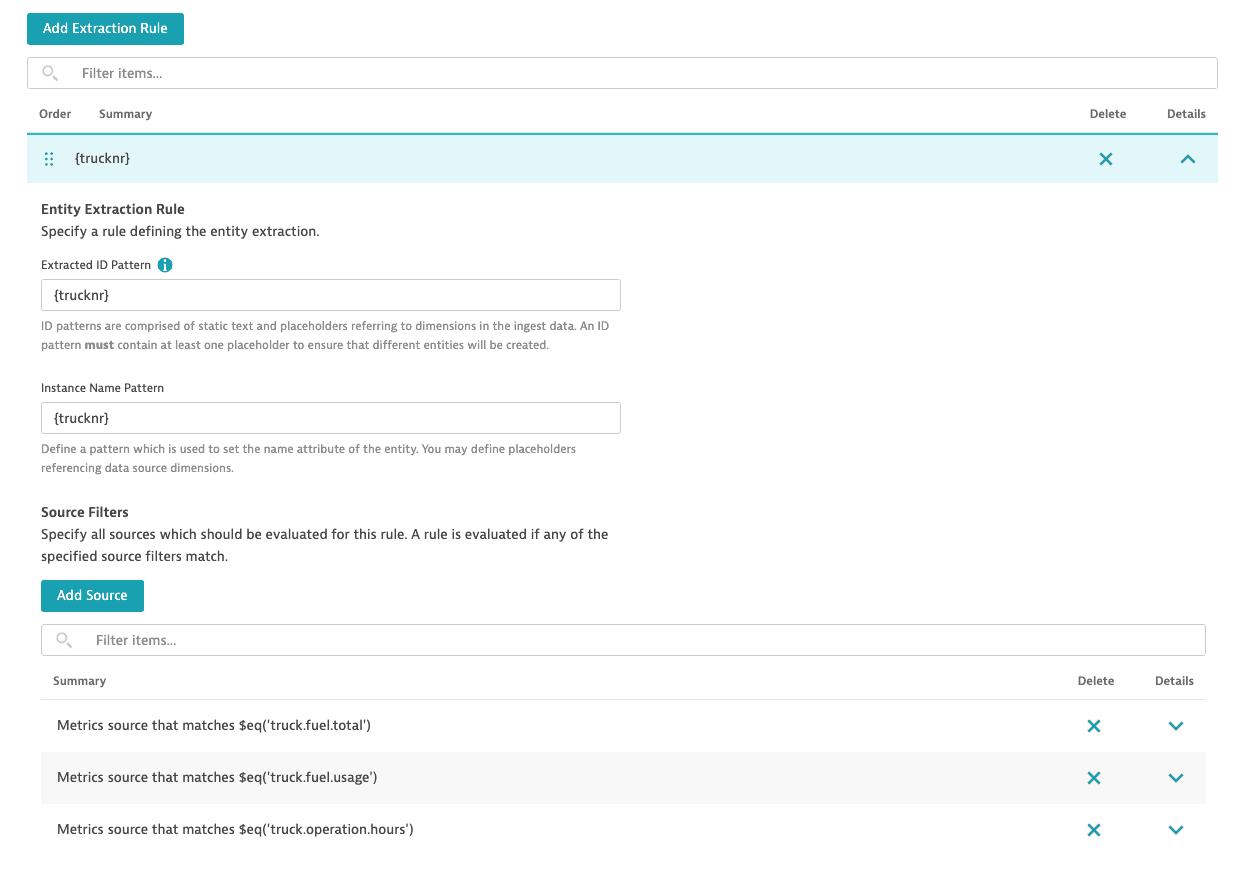
Teach Dynatrace how your new entity type should be automatically matched and how to identify unique entity instances (trucks).
-
Select Add extraction rule.
-
To specify the extraction rule for the instance identifier for your new entity type, set Extracted ID pattern to
{trucknr}.
You must use a{placeholder}referring to the dimension name to make sure the instance identifier is unique. The dimension value will become the instance identifier. -
To specify the extraction rule for the instance name for your new entity type, set Instance name pattern to
{trucknr}. The dimension value will become the instance name.Example
-
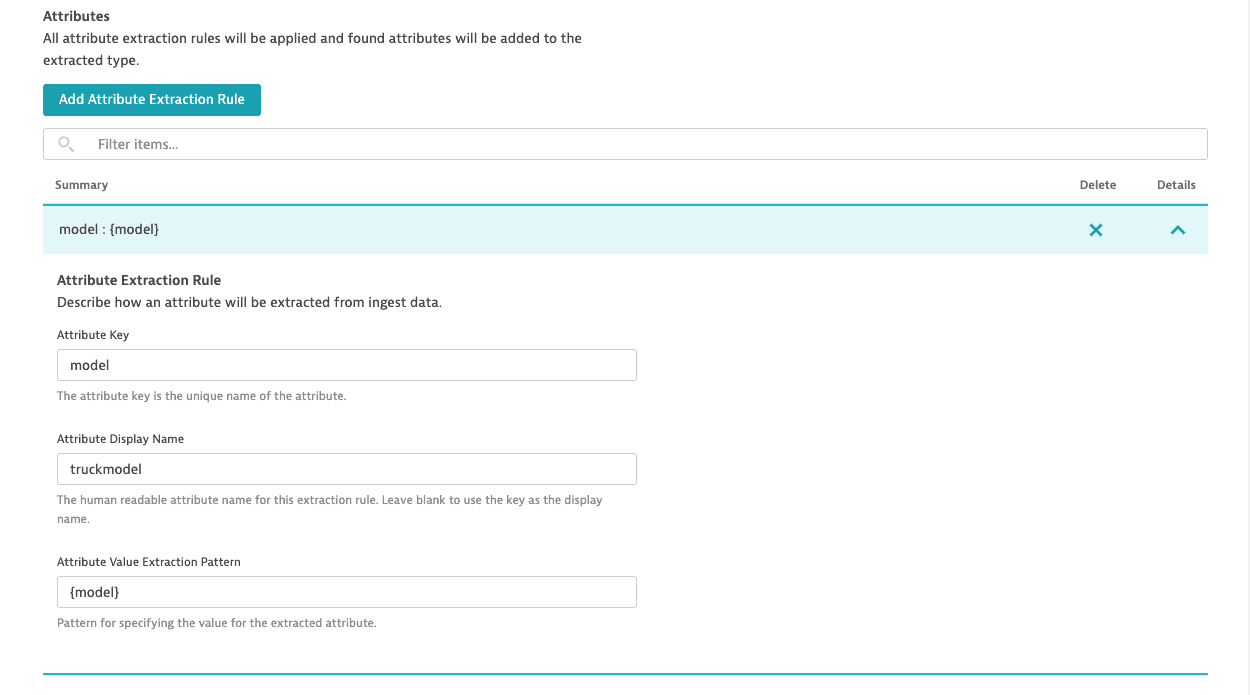
To specify the extraction rule for the entity attribute, select Add attribute extraction rule. In this example, each truck's data is reported with the
modeldimension, which is the truck attribute:- Attribute key
The unique identifier of the rule to extract the attribute value. - Attribute display name
You can leave it blank to use the key as the display name. - Attribute value extraction pattern
Add the placeholder for the{model}dimension. The dimension value will become the attribute name.
Example
- Attribute key
 Repeat for additional entities
Repeat for additional entities
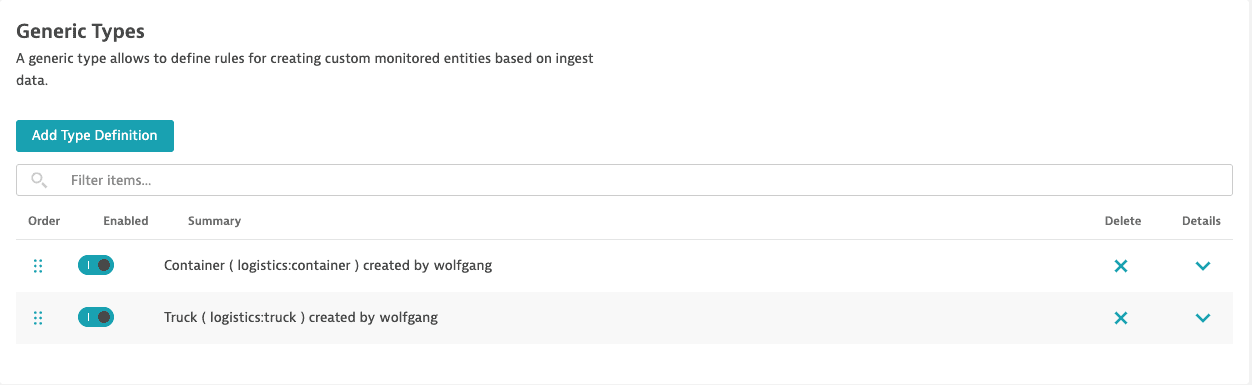
Repeat the above steps to define additional entities. In this case, we still need to define the container entity type, specify its extraction rules (containernr), and specify extraction rules for its attributes (trucknr).
After you configure your own domain types on top of your incoming metrics or log streams, Dynatrace will automatically extract and create new instances of trucks and containers whenever a truck or container starts sending its telemetry data.
Result
Define entity relationships
To complete the topology definition, define a relationship between the truck and the carried container. Without this relationship, the truck- and container-related measurements will be reported separately by Dynatrace with no topological relationship.
To extract a relationship between a given entity type and another entity type, we need to find a joined data stream. In our example, it's the container temperature measurement that contains both identifying values, the truck number and the container number. For example:
container.temperature,containernr=111111,trucknr=12 39
With a joined data stream, we now can define a relationship between a truck and a container.
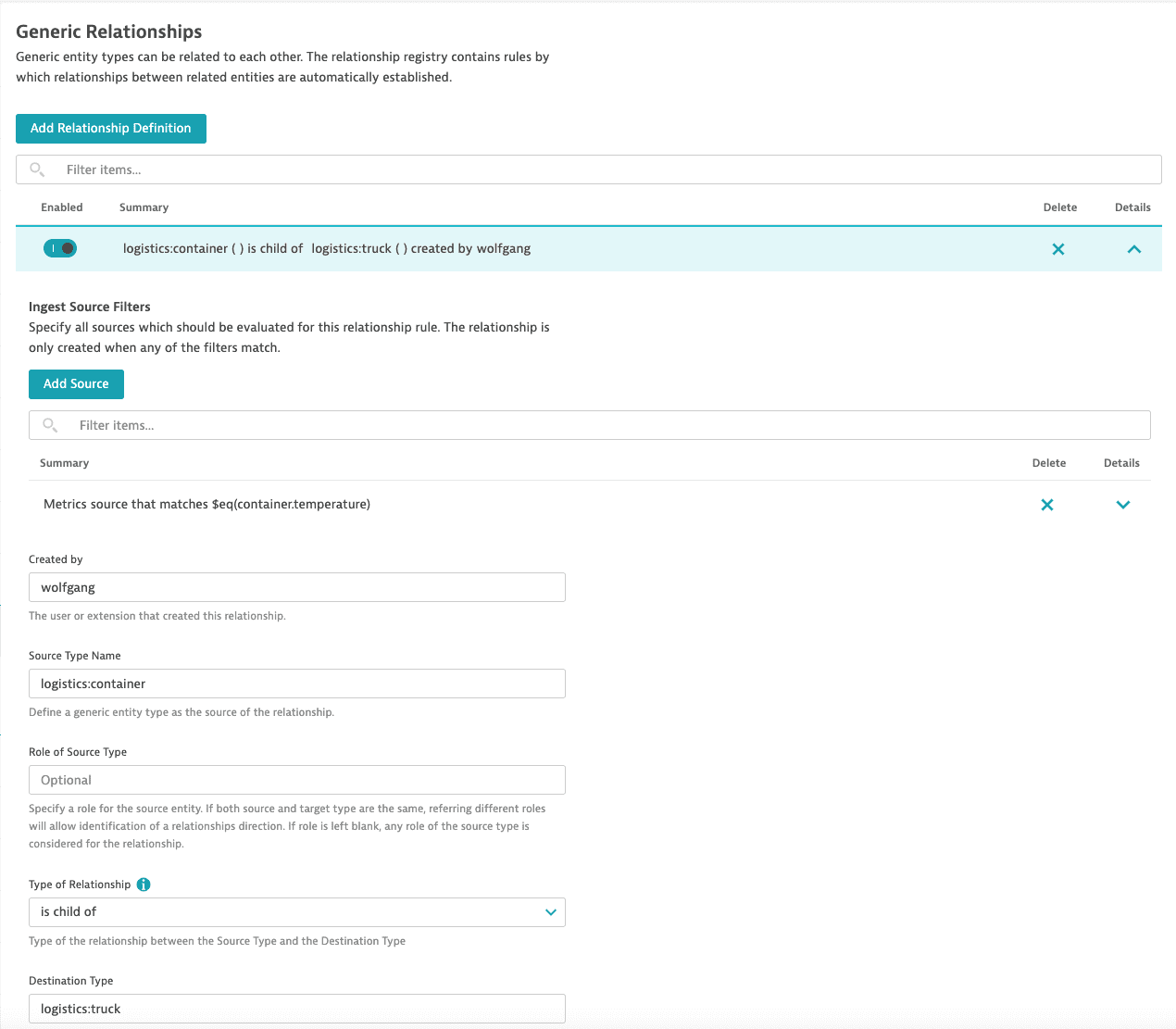
- Go to Settings > Topology model > Generic relationships.
- Select Add relationship definition.
- Select Add source.
- Define the source:
- Set Ingest datasource type to
Metrics - Set Condition to
$eq(container.temperature)
This is a filter that will match the joining metric name. In this example,$eq(container.temperature)is used to match thecontainer.temperaturemetric. - Set Source type name to
logistics:container - Set Destination type to
logistics:truck - Set Type of relationship to
is child of
This defines the relationship between Source type name (logistics:container) and Destination type (logistics:truck), meaning, in this case, thatlogistics:containeris child oflogistics:truck.
- Set Ingest datasource type to
- Select Save changes.
Result
Optional roles
The use of roles (such as client and server, or caller and callee) is optional. In our example, we don`t need to specify those roles as the joining data source contains two different entity types.
Roles are necessary if you want to connect two instances of the same entity type by a joining measurement.
An example here would be a measurement line that shows the response time of a service calling another service. For example:
service.responsetime,caller=service1,callee=service2 39
With the above example, two service instances of the same service type should be extracted and combined with a call relationship.
In this case, one extraction rule has to be identified with a role (caller) and the other extraction with a different role (callee).
During the extraction of the relationship, the caller and callee role can then be used to specify the direction of the resulting relationship.