Automatically applied tags API - GET an auto-tag
- Reference
- Published Aug 09, 2019
Deprecated
This API is deprecated. Use the Settings API with the Automatically applied tags (builtin:tags.auto-tagging) schema instead.
Gets parameters of the specified automatically applied tag.
The request produces an application/json payload.
| GET | SaaS | https://{your-environment-id}.live.dynatrace.com/api/config/v1/autoTags/{id} |
| GET | Environment ActiveGate | https://{your-activegate-domain}:9999/e/{your-environment-id}/api/config/v1/autoTags/{id} |
Authentication
To execute this request, you need an access token with ReadConfig scope.
To learn how to obtain and use it, see Tokens and authentication.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | In | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | The ID of the required auto-tag. | path | Required |
| includeProcessGroupReferences | boolean | Flag to include process group references to the response. Process group references aren't compatible across environments. When this flag is set to | query | Optional |
Response
Refer to JSON models to find all JSON models that depend on the type of the model.
Response codes
| Code | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | Auto | Success |
Response body objects
The AutoTag object
Configuration of an auto-tag. It defines the conditions of tag usage and the tag value.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| description | string | The description of the auto-tag. |
| entitySelectorBasedRules | Entity | A list of entity-selector based rules for auto tagging usage. If several rules are specified, the OR logic applies. |
| id | string | The ID of the auto-tag. |
| metadata | Configuration | Metadata useful for debugging |
| name | string | The name of the auto-tag, which is applied to entities. Additionally you can specify a valueFormat in the tag rule. In that case the tag is used in the For example you can extend the |
| rules | Auto | The list of rules for tag usage. When there are multiple rules, the OR logic applies. |
The EntitySelectorBasedAutoTagRule object
The entity-selector-based rule for auto tag usage. It allows tagging entities via an entity selector.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| enabled | boolean | The rule is enabled ( |
| entitySelector | string | The entity selector string, by which the entities are selected. |
| normalization | string | Changes applied to the value after applying the value format. Default is LEAVE_TEXT_AS_IS. The element can hold these values
|
| valueFormat | string | The value of the entity-selector-based auto-tag. If specified, the tag is used in the For example, you can extend the |
The ConfigurationMetadata object
Metadata useful for debugging
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| clusterVersion | string | Dynatrace version. |
| configurationVersions | integer[] | A sorted list of the version numbers of the configuration. |
| currentConfigurationVersions | string[] | A sorted list of version numbers of the configuration. |
The AutoTagRule object
A rule for the auto-tag.
Defines the conditions of tag usage.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| conditions | Entity | A list of matching rules for the auto-tag. The tag applies only when all conditions are fulfilled. |
| enabled | boolean | Tag rule is enabled ( |
| normalization | string | Changes applied to the value after applying the value format. Default is LEAVE_TEXT_AS_IS. The element can hold these values
|
| propagationTypes | string[] | How to apply the tag to underlying entities:
The element can hold these values
|
| type | string | Type of entities to which the rule applies. The element can hold these values
|
| valueFormat | string | The value of the auto-tag. If specified, the tag is used in the For example, you can extend the You can use the following placeholders here:
|
The EntityRuleEngineCondition object
A condition defines how to execute matching logic for an entity.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comparisonInfo | Comparison | Defines how the matching is actually performed: what and how are we comparing. The actual set of fields and possible values of the operator field depend on the type of the comparison. Find the list of actual objects in the description of the type field or see JSON models. |
| key | Condition | The key to identify the data we're matching. The actual set of fields and possible values depend on the type of the key. Find the list of actual objects in the description of the type field or see JSON models. |
The ComparisonBasic object
Defines how the matching is actually performed: what and how are we comparing.
The actual set of fields and possible values of the operator field depend on the type of the comparison. Find the list of actual objects in the description of the type field or see JSON models.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| negate | boolean | Reverses the comparison operator. For example it turns the begins with into does not begin with. |
| operator | string | Operator of the comparison. You can reverse it by setting negate to Possible values depend on the type of the comparison. Find the list of actual models in the description of the type field and check the description of the model you need. |
| type | string | Defines the actual set of fields depending on the value. See one of the following objects:
The element can hold these values
|
| value | string | The value to compare to. |
The AnyValue object
A schema representing an arbitrary value type.
The ConditionKey object
The key to identify the data we're matching.
The actual set of fields and possible values depend on the type of the key. Find the list of actual objects in the description of the type field or see JSON models.
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| attribute | string | The attribute to be used for comparison. The element can hold these values
|
| type | string | Defines the actual set of fields depending on the value. See one of the following objects:
The element can hold these values
|
Response body JSON models
{"description": "sampleDescription","entitySelectorBasedRules": [{"enabled": true,"entitySelector": "type(HOST) AND cpuCores(4)"}],"name": "sampleAutoTag","rules": [{"conditions": [{"comparisonInfo": {"caseSensitive": false,"negate": false,"operator": "BEGINS_WITH","type": "STRING","value": "sample"},"key": {"attribute": "SERVICE_DATABASE_NAME"}},{"comparisonInfo": {"negate": false,"operator": "EXISTS","type": "STRING"},"key": {"attribute": "SERVICE_WEB_SERVER_NAME"}},{"comparisonInfo": {"caseSensitive": false,"negate": false,"operator": "BEGINS_WITH","type": "STRING","value": "sample"},"key": {"attribute": "PROCESS_GROUP_CUSTOM_METADATA","dynamicKey": {"key": "kubernetes.io/limit-ranger","source": "KUBERNETES"},"type": "PROCESS_CUSTOM_METADATA_KEY"}}],"enabled": true,"propagationTypes": ["SERVICE_TO_HOST_LIKE"],"type": "SERVICE","valueFormat": "myTagValue {Service:DetectedName}"}]}
Example
In this example, the request inquires about the properties of the Infrastructure - Linux auto-tag, which has the ID 7c82c170-b380-4fa7-992a-453f3e73047b.
The configuration has the following settings:
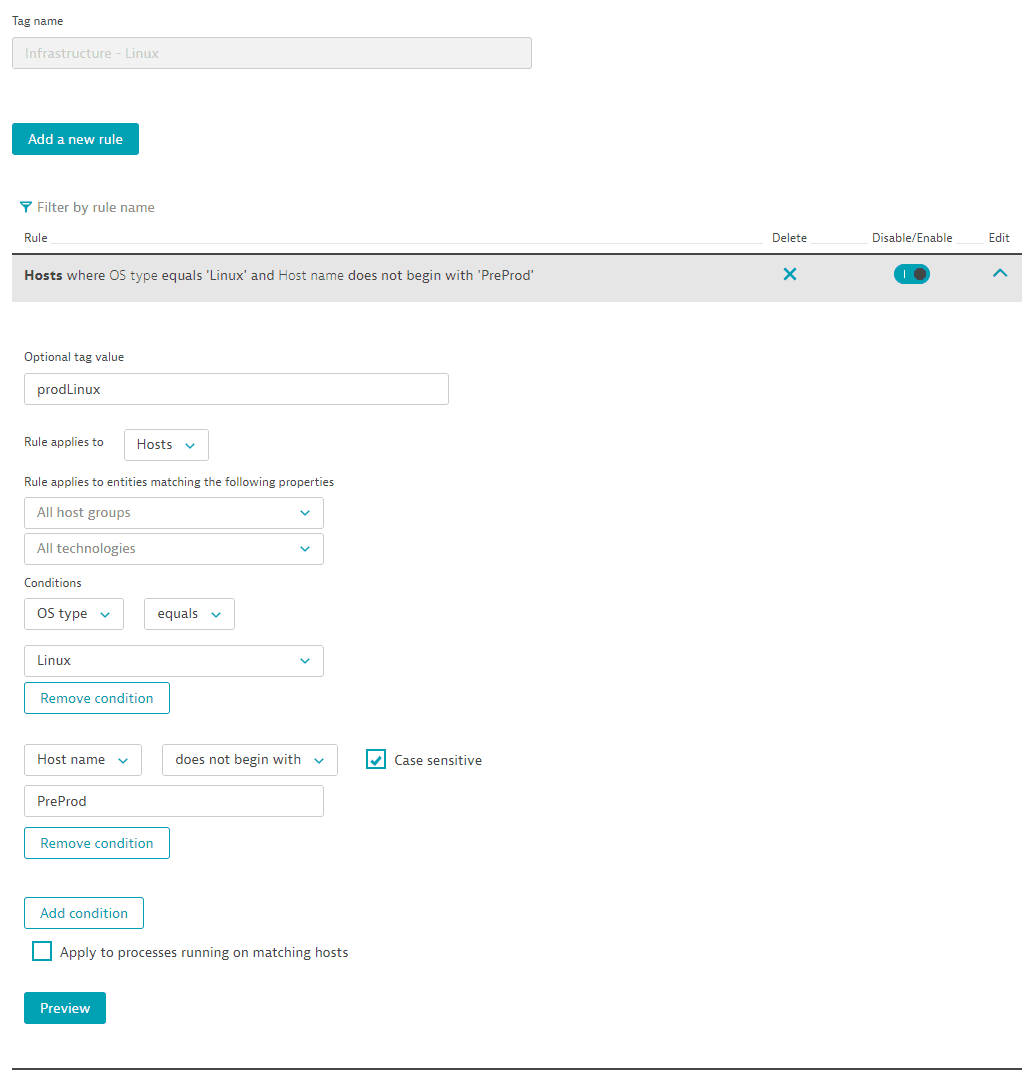
The API token is passed in the Authorization header.
Curl
curl -X GET \https://mySampleEnv.live.dynatrace.com/api/config/v1/autoTags/7c82c170-b380-4fa7-992a-453f3e73047b \-H 'Authorization: Api-Token dt0c01.abc123.abcdefjhij1234567890'
Request URL
https://mySampleEnv.live.dynatrace.com/api/config/v1/autoTags/7c82c170-b380-4fa7-992a-453f3e73047b
Response body
{"metadata": {"configurationVersions": [7],"clusterVersion": "1.176.0.20190808-181828"},"id": "7c82c170-b380-4fa7-992a-453f3e73047b","name": "Infrastructure - Linux","rules": [{"type": "HOST","enabled": true,"valueFormat": "prodLinux","propagationTypes": [],"conditions": [{"key": {"attribute": "HOST_OS_TYPE"},"comparisonInfo": {"type": "OS_TYPE","operator": "EQUALS","value": "LINUX","negate": false}},{"key": {"attribute": "HOST_NAME"},"comparisonInfo": {"type": "STRING","operator": "BEGINS_WITH","value": "PreProd","negate": true,"caseSensitive": true}}]}]}
Response code
200