Discover relevant troubleshooting guides with Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI helps you resolve problems faster by automatically surfacing relevant troubleshooting guides, such as notebooks or dashboards created by your team.
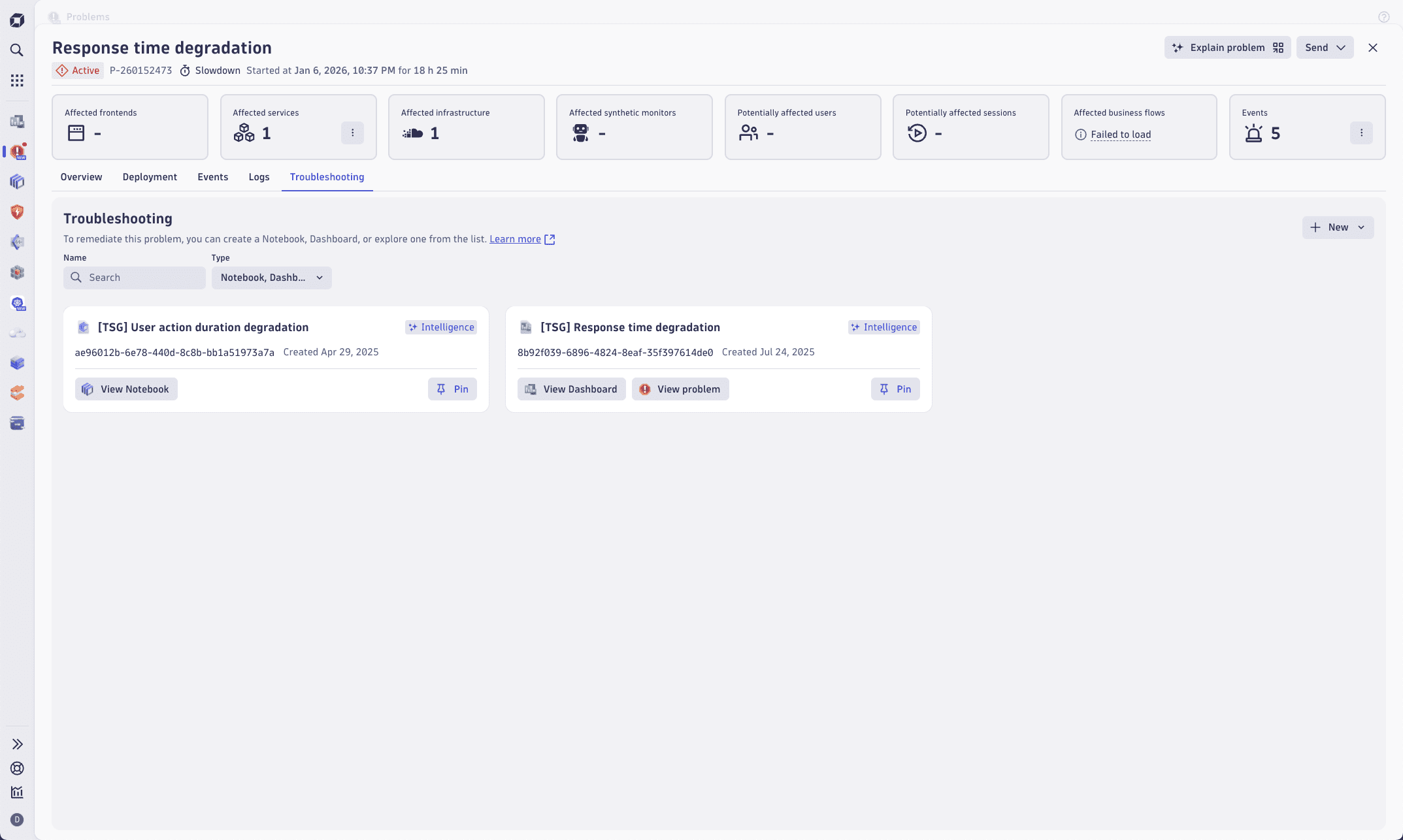
To reduce the mean time to repair (MTTR), you can leverage Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI document suggestions in  Problems to check if your team has created any troubleshooting guides for problems similar to the one you've encountered.
Problems to check if your team has created any troubleshooting guides for problems similar to the one you've encountered.
Who this is for
This article is for any users who want to quickly and effectively troubleshoot and remediate active problems in their environment.
What you will learn
In this article, you'll learn how Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI can suggest relevant troubleshooting guides to assist with problem remediation.
Before you begin
Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI periodically indexes notebooks and dashboards that have been labeled as troubleshooting guides and shared within the environment.
- By default, semantic vector indexing of the guides occurs every 6 hours.
- In order for Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI to index and suggest your document, you have to share it with all users in your environment. Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI won't index or suggest any private documents or documents shared only with specific users. To learn more about sharing documents, see Share documents.
Prior knowledge
Prerequisites
- Dynatrace SaaS environment.
- You have completed the Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI setup described in Getting started with Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI.
- You have document suggestions enabled in your environment. Document indexing enablement is a part of the Enable Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI on your environment guide.
- You have the
ALLOW davis-copilot:document-search:execute;permission. To learn how to set up the permissions, see Permissions in Grail.
Get document suggestions to remediate problems
-
Go to
 Problems and open the problem you need to resolve.
Problems and open the problem you need to resolve. -
On the problem details page, select Troubleshooting. You will be able to see any troubleshooting guides you have created for the problem, as well as any relevant documents suggested by Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI.
Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI only indexes documents that are recognized as troubleshooting guides. Dashboards and notebooks created directly from
 Problems are automatically recognized as troubleshooting guides and do not require the
Problems are automatically recognized as troubleshooting guides and do not require the [TSG]prefix.If you create a troubleshooting guide directly from
 Dashboards or
Dashboards or  Notebooks, you have to prefix the document title with
Notebooks, you have to prefix the document title with [TSG]to indicate it is a troubleshooting guide.Regardless of how the document was created, it still has to be shared at the environment level to be indexed by Dynatrace Intelligence generative AI.
-
Optional Provide the keywords or part of a keyword in the Name search field to filter the suggested documents by name.
-
Optional Select the Type (
Notebooks,Dashboards) to filter the suggested documents by type. By default, both types are selected for document suggestions. -
Select View … on the document you want to view. This action will take you to the troubleshooting guide for further investigation.
Pin documents directly to a problem
When you create a document from a problem details page, it is automatically pinned to that specific problem. Pinned documents aren't included in the suggested document list. Instead, the TSGs are linked to the problem from which they were created. This ensures that documents created within a problem remain attached and prevents scenarios where the AI might exclude them from the suggested list due to a lack of similarity.
The documents are pinned to problems by setting the id field within the document store. The pattern used for problem pinning consists of:
- A string
problem-TSG. - A dash
-. - A problem ID (
event.idin the Problem Grail record). - A dash
-. - A random UUID represented by a string.
You can see the general pattern in the example below:
problem-TSG-{problem_ID}-{random-UUID}
Since underscore _ present in a problem ID isn't supported by the document identifier, it needs to be replaced by a dash -, as seen in the example below:
problem-TSG-1589269324049748129-1747888020000V2-225b65bd-ab67-4efe-9d71-742de9b87387
The random UUID appended to the end of the pattern ensures the uniqueness of each document and allows multiple documents to be pinned to the same problem without conflicts.
Pinning documents to problems allows you to attach additional analysis results and domain-specific knowledge directly to the detected problems. You can pin a document to a problem via workflows or API for seamless external integrations.
Create and attach a notebook to a detected problem via Workflows
By using a JavaScript workflow action, you can automatically create and attach a document (notebook or dashboard) with your domain-specific analysis results to a detected problem.
- Go to Workflows
 and select to create a new workflow.
and select to create a new workflow. - Select the preferred trigger type.
- Select Add task.
- In the Choose action section, select Run JavaScript.
- In the Input section, enter the following script:
import { documentsClient } from "@dynatrace-sdk/client-document";import { credentialVaultClient } from '@dynatrace-sdk/client-classic-environment-v2';import { execution } from '@dynatrace-sdk/automation-utils';function generateGUID() {return 'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'.replace(/[xy]/g, function(c) {const r = Math.random() * 16 | 0, v = c === 'x' ? r : (r & 0x3 | 0x8);return v.toString(16);});}export default async function ({ execution_id }) {const ex = await execution(execution_id);const problem_event = ex.params.event;var problem_id = problem_event['event.id'];problem_id = problem_id.replace('_', '-'); // Replace the unsupported character// Create a new Notebook and pin it to the triggering problemtry {const notebookContent = {defaultTimeframe: { from: "now()-2h", to: "now()" },defaultSegments: [],sections: [{"id":"19ebed94-69a9-4a6e-b392-7bb7b0deb330","type":"markdown","markdown":"# Domain Analysis Results\n\nHere goes the external, domain-specific analysis results"}],};const generatedNotebook = await documentsClient.createDocument({body: {name: "[TSG] Domain Analysis Results",type: "notebook",description: "A notebook containing domain specific analysis results",id: "problem-TSG-" + problem_id + "-" + generateGUID(),content: new Blob([JSON.stringify(notebookContent)], { type: "application/json" }),},});// Make the document publicconst updated = await documentsClient.updateDocument({id: generatedNotebook.id,optimisticLockingVersion: generatedNotebook.version,body: {isPrivate: false,}})} catch (error) {console.error("Error creating notebook:", error);}return { };}
Once the newly created notebook is attached to the AI-detected problem, you'll be able to see it in the troubleshooting section. The document will also be suggested to you for similar problems in the future.