Observe Argo CD deployment and application health with Dashboards and SDLC events
- Latest Dynatrace
- Tutorial
- 7-min read
- Preview
In this use case, you'll
- Integrate Argo CD and Dynatrace.
- Use Dashboards to observe Argo CD deployments and application health.
- Use this information to optimize deployments with Argo CD.
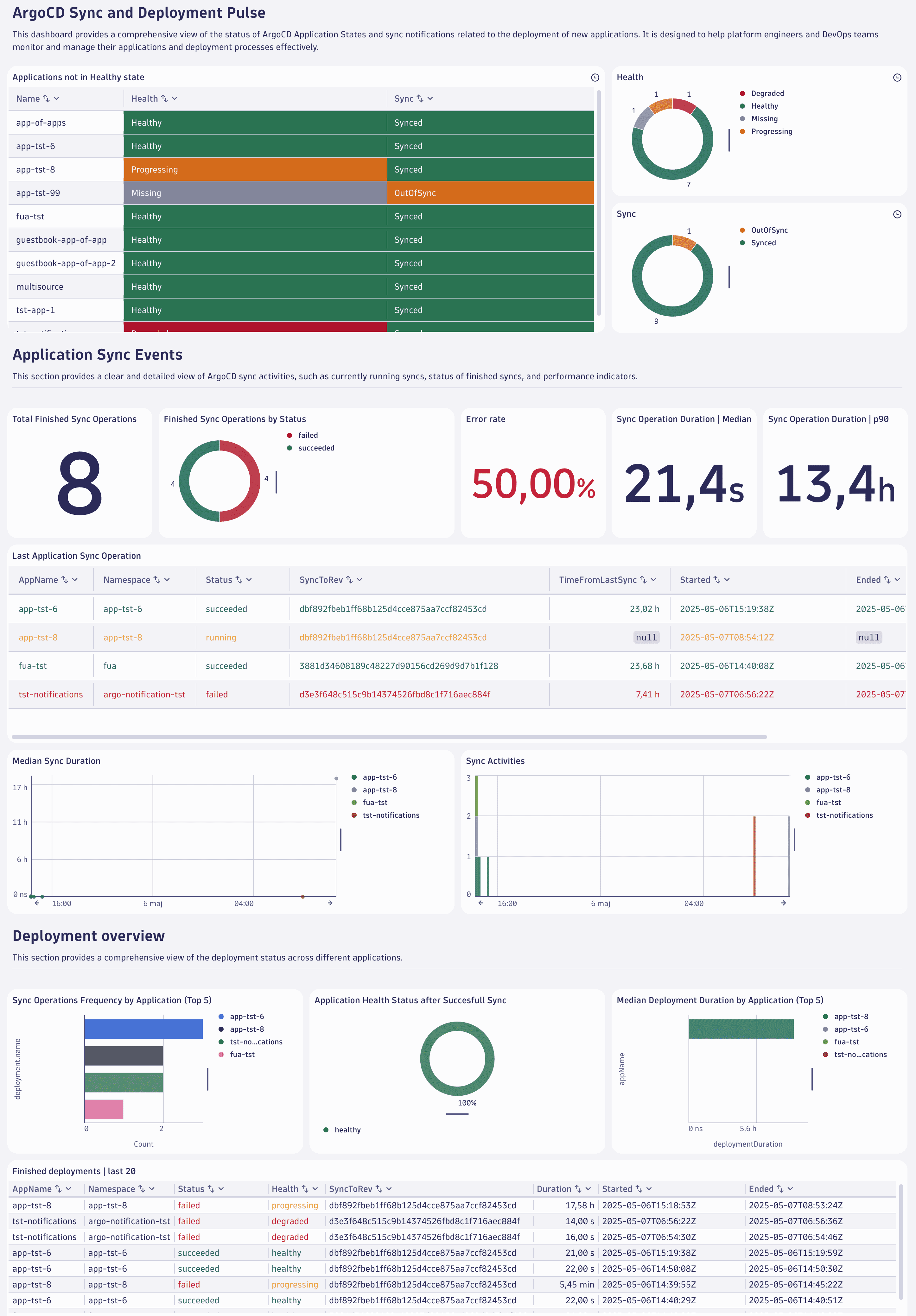
Below is an example of what your Argo CD dashboard could look like.
Concepts
- Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) events
- Why were Argo CD notifications changed into SDLC events?
The main benefits are data normalization, being tool-agnostic, and not relying on specific tools. As a result, Dynatrace Dashboards, Apps, and Workflows can build on SDLC events with well-defined properties rather than tool-specific details.
Target audience
This tutorial is intended for platform engineers who manage the Internal Development Platform (IDP), including Argo CD, in GitOps-based deployments.
Learning outcome
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to
- Forward Argo CD notifications to Dynatrace.
- Send Prometheus metrics to Dynatrace.
- Normalize the ingested event data.
- Use Dashboards to analyze the data and derive improvements.
If you prefer, you could follow the Argo CD tutorial directly on GitHub.
Prerequisites
Install Dynatrace Configuration as Code via Monaco
How-to
1. Setup: Prepare the Monaco configuration
-
Create an OAuth client for the Dynatrace Monaco CLI with the following permissions
- Run apps:
app-engine:apps:run - View OpenPipeline configurations:
openpipeline:configurations:read - Edit OpenPipeline configurations:
openpipeline:configurations:write - Create and edit documents:
document:documents:write - View documents:
document:documents:read
- Run apps:
-
Store the retrieved client ID and secret as separate environment variables.
$env:OAUTH_CLIENT_ID='<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>'$env:OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET='<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>' -
Clone the Dynatrace configuration as code sample repository and go to
argocd_observabilitydirectory.git clone https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-configuration-as-code-samples.gitcd dynatrace-configuration-as-code-samples/argocd_observability -
Edit the
manifest.yamlby exchanging your environment ID<YOUR-DT-ENV-ID>placeholder with your Dynatrace environment ID at the name property and within the URL of the value property.manifestVersion: 1.0projects:- name: pipeline_observabilityenvironmentGroups:- name: groupenvironments:- name: <YOUR-DT-ENV-ID>url:type: valuevalue: https://<YOUR-DT-ENV-ID>.apps.dynatrace.comauth:oAuth:clientId:name: OAUTH_CLIENT_IDclientSecret:name: OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET
2. Setup: Check the OpenPipeline configuration for SDLC events
These steps modify the OpenPipeline configuration for SDLC events. If your OpenPipeline configuration contains only default/built-in values, you can directly apply the Monaco configuration. If you have any custom ingest sources, dynamic routes, or pipelines, you'll first need to download your configuration and manually merge it into the Monaco configuration.
Step 3 will indicate if a configuration merge is needed or if you can apply the provided configuration directly.
-
Go to
 Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Events > Software development lifecycle.
Settings > Process and contextualize > OpenPipeline > Events > Software development lifecycle. -
Check the Ingest sources, Dynamic routing, and Pipelines.
- Under Ingest sources, are there any other sources than Default API?
- Under Dynamic routing, are there any other routes than Default route?
- Under Pipelines, are there any other pipelines than events.sdlc?
-
If the answer to one of those questions is "yes", follow the steps below. Otherwise, skip ahead to step 4.
-
Download the OpenPipeline configuration.
monaco download -e <YOUR-DT-ENV-ID> --only-openpipeline -
Open the following files:
- Your downloaded configuration file,
download_<DATE>_<NUMBER>/project/openpipline/events.sdlc.json. - The provided configuration file,
pipeline_observability/openpipline/events.sdlc.argocd.json.
- Your downloaded configuration file,
-
Merge the contents of
events.sdlc.jsonintoevents.sdlc.argocd.json, and then save the file.
-
-
Apply the Monaco configuration.
The configuration consists of
- Dashboards to analyze Argo CD activities.
- OpenPipeline configuration to normalize Argo CD notifications into SDLC events.
Run this command to apply the provided Monaco configuration:
monaco deploy manifest.yaml
3. Setup: Create an access token
To generate an access token:
- Go to
 Access Tokens.
Access Tokens. - Select Generate new token.
- Enter a name for your token.
Dynatrace doesn't enforce unique token names. You can create multiple tokens with the same name. Be sure to provide a meaningful name for each token you generate. Proper naming helps you to efficiently manage your tokens and perhaps delete them when they're no longer needed. - Select the required scopes for the token.
- Select Generate token.
- Copy the generated token to the clipboard. Store the token in a password manager for future use.
You can only access your token once upon creation. You can't reveal it afterward.
-
Select these scopes:
- OpenPipeline - Ingest Software Development Lifecycle Events (Built-in) (
openpipeline.events_sdlc) - OpenPipeline - Ingest Software Development Lifecycle Events (Custom) (
openpipeline.events_sdlc.custom)
- OpenPipeline - Ingest Software Development Lifecycle Events (Built-in) (
4. Setup: Configure Argo CD notifications
Argo CD notifications provide a flexible way to alert users about essential changes in the state of their applications managed by Argo CD. To configure the Argo CD notifications, you need to create a notification secret, apply the configuration, and subscribe applications to notifications.
-
Create notification secret.
-
Update the
argocd-notifications-secretwith:apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: argocd-notifications-secretstringData:dt-base-url: https://{your-environment-id}.live.dynatrace.comdt-access-token: <YOUR-ACCESS-TOKEN> -
Apply the configuration.
kubectl apply -f <secret_file_name>.yaml -n argocd
-
-
Create a notification template and trigger.
-
If you don't have any notification configurations, create a new configuration map called
argocd-notification-cmas shown below. Otherwise, extend your config map configuration by adding the example's service, template, and trigger sections.apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata:name: argocd-notifications-cmdata:service.webhook.dynatrace-webhook: |url: $dt-base-urlheaders:- name: "Authorization"value: Api-Token $dt-access-token- name: "Content-Type"value: "application/json; charset=utf-8"template.dynatrace-webhook-template: |webhook:dynatrace-webhook:method: POSTpath: /platform/ingest/custom/events.sdlc/argocdbody: |{"app": {{toJson .app}}}trigger.dynatrace-webhook-trigger: |- when: app.status.operationState.phase in ['Succeeded'] and app.status.health.status in ['Healthy', 'Degraded']send: [dynatrace-webhook-template]- when: app.status.operationState.phase in ['Failed', 'Error']send: [dynatrace-webhook-template]- when: app.status.operationState.phase in ['Running']send: [dynatrace-webhook-template]Here is an explanation for the naming in the configuration.
dynatrace-webhookis the name of the service,$dt-access-tokenrefers to the Dynatrace access token, and$dt-base-urlis a reference to the Dynatrace event ingest endpoint stored in theargocd-notifications-secret secret.dynatrace-webhook-templateis the template's name, anddynatrace-webhookrefers to the service created above.dynatrace-webhook-triggeris the trigger's name, anddynatrace-webhook-templaterefers to the template created above.
-
Apply the configuration with this command.
kubectl apply -f <config_map_file_name>.yaml -n argocd -
Subscribe applications to notifications.
Modify the annotations of the Argo CD application by using either the Argo CD UI or the Argo CD application definition with the following annotations:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1kind: Applicationmetadata:annotations:notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.dynatrace-webhook-trigger.dynatrace-webhook: ""The added
notifications.argoproj.ionotification annotation subscribes the Argo CD application to the notification setup you created above.
-
5. Setup: Send Argo CD Prometheus metrics to Dynatrace
Argo CD exposes different sets of Prometheus metrics for different services. Configure your Argo CD services to expose this information so that it can be collected by Dynatrace. You can use either Dynatrace ActiveGate, which is installed on the Kubernetes cluster that hosts Argo CD, or the Dynatrace OTel Collector.
To use Dynatrace ActiveGate
-
Enable Prometheus metrics monitoring.
- Go to Kubernetes and select the monitored cluster with Argo CD installation.
- In the upper-right corner, go to > Connection settings.
- Choose Monitoring Settings.
- Enable Monitor annotated Prometheus exporters.
- Save.
-
In your Argo CD installation namespace, add the following two annotations for each of the services listed in the table below. Replace
{METRICS_PORT}with the corresponding port number.metrics.dynatrace.com/port: {METRICS_PORT}metrics.dynatrace.com/scrape: 'true'Service Metrics Port argocd-applicationset-controller 8080 argocd-metrics 8082 argocd-server-metrics 8083 argocd-repo-server 8084 argocd-notifications-controller-metrics 9001 argocd-dex-server 5558 View the histogram data ingest by going to
 Settings > Metrics > Histograms. The Ingest complete explicit bucket histograms setting that you need is automatically turned on.
Settings > Metrics > Histograms. The Ingest complete explicit bucket histograms setting that you need is automatically turned on.
6. Unlock enhanced deployment insights with Argo CD Dashboards
Now that you've successfully configured Argo CD and Dynatrace, you can use Dashboards and SDLC events to observe your Argo CD deployments.
Analyze
In Dynatrace, open the ArgoCD Application Lifecycle dashboard to
- Investigate running syncs and hotspots of many sync operations.
- Analyze the duration of sync operations.
- See deployment status and application health.
Optimize
Leverage those insights for the following improvement areas:
-
Improved performance: Optimizing syncs can reduce the time it takes to deploy changes, making your deployment process more efficient. Efficient syncs can also help better utilize resources, reducing the load on your infrastructure.
-
Enhanced Reliability: Optimizing syncs can minimize the chances of errors during deployment, leading to more stable and reliable releases. Ensuring that syncs are optimized can help maintain consistency across different environments.
Continuous improvements
Regularly review your Argo CD sync operations and adjust the configuration to ensure they're optimized for performance.
In Dynatrace, adjust the timeframe of the ArgoCD Application Lifecycle dashboards to monitor the long-term impact of your improvements.
Call to action
We highly value your insights on Argo CD observability. Your feedback is crucial in helping us enhance our tools and services. Visit the Dynatrace Community page to share your experiences, suggestions, and ideas directly in Feedback channel for CI/CD Pipeline Observability.
Further reading
 Dashboards
Dashboards OpenPipeline
OpenPipeline