Live Debugger
- Latest Dynatrace
- Overview
- 1-min read
Live Debugger is a cloud-native, live data collection application that gives you instant access to the code-level data you need to troubleshoot and debug quickly in any environment, from dev to production.
- You can access the necessary and relevant data without adding additional code, waiting for redeploy, or attempting to reproduce issues locally.
- Using non-breaking breakpoints, you can instantly see the complete state of your app, including stack trace, variable values, and more, all without stopping or breaking your running code.
- Dynatrace SaaS environment with a Dynatrace Platform Subscription (DPS) that includes Code Monitoring.
- OneAgent version 1.309+ with Java Live-Debugger and Node.js Live-Debugger OneAgent features enabled.
- Monitoring Modes: Full-Stack, Infrastructure, or Discovery (with container code-module injection).
- Code modules: Java and Node.js.
Activate the Live Debugger feature
These steps should only be performed once. After enabling the Live Debugger feature for the first time, a restart of any affected process is required.
To activate the Live Debugger feature
-
Go to
 Settings > Collect and capture > General monitoring settings > OneAgent features.
Settings > Collect and capture > General monitoring settings > OneAgent features. -
Enable the Java Live-Debugger, Node.js Live-Debugger, or both, depending on your needs.
-
Restart any process that is affected.
Start live debugging an application
To use the Live Debugger, you must opt-in to Observability for Developers. You can enable it for specific process groups, Kubernetes namespaces, clusters, or for the entire environment.
Go to ![]() Settings > Collect and capture > Observability for Developers > Enable Observability for Developers.
Settings > Collect and capture > Observability for Developers > Enable Observability for Developers.
- On Process group overview, select Settings.
- Go to Collect and capture > Observability for Developers > Enable Observability for Developers.
- Go to
 Kubernetes.
Kubernetes. - Select a namespace or cluster.
- Select in the top-right corner, then select Connection settings, or, if not available Anomaly detection settings.
- Go to Observability for Developers > Enable Observability for Developers.
To start your live debugging session, open Live Debugger and go to Customize your debug session by selecting Debug Configuration in the upper-left corner of the application.
To scope the instances you would like to debug, you can add one or more filters from the Facets/Categories, use the search bar, or choose a filter within the application properties.
Fetch source code
- Windows: 7, 8, 8/1 aren't supported.
- Mac: All versions are supported.
Each debug session must contain the application source code you're about to debug. Live Debugger lets you quickly load sources from your local file system and Git provider. When you integrate your source code into Live Debugger, it remains between your code repository and your local browser.
There are two main ways to import your source code:
Automatic fetching
Live Debugger can connect to a repository and automatically fetch the source code for the selected instance.
Your repository may be automatically fetched for the selected instance based on your git permissions, if your admin has already set it up.
To learn more about automatic fetching, see Integrate with your version control.
Manual fetching
Live Debugger lets you easily load your relevant source code into the application.
- Select the
+icon on the upper-right corner of the Set up your session page to open a list of the supported git providers from which you can fetch sources. - Live Debugger includes a desktop application that can access source repositories from your local file system. This allows you to fetch source code from locally hosted Git providers. When selecting your source code, you can find the desktop application's installation file in Live Debugger.
Live Debugger integrates directly with the cloud editions of the following Git providers, both on-premises and SaaS:
- Github
- BitBucket
- GitLab
- Azure DevOps
Git On-Premise integration
To enable Live Debugger to integrate with your On-premise or locally hosted Git provider
- Go to Settings > Dynatrace Apps > Git On-Premise Servers.
- Select Add item.
- Git Provider: Specify your Git provider.
- Server URL: Provide your server's HTTP/HTTPS URL.
- Select Save changes.
- To use BitBucket On-Premises, install the desktop application (see the Manual Fetching section above).
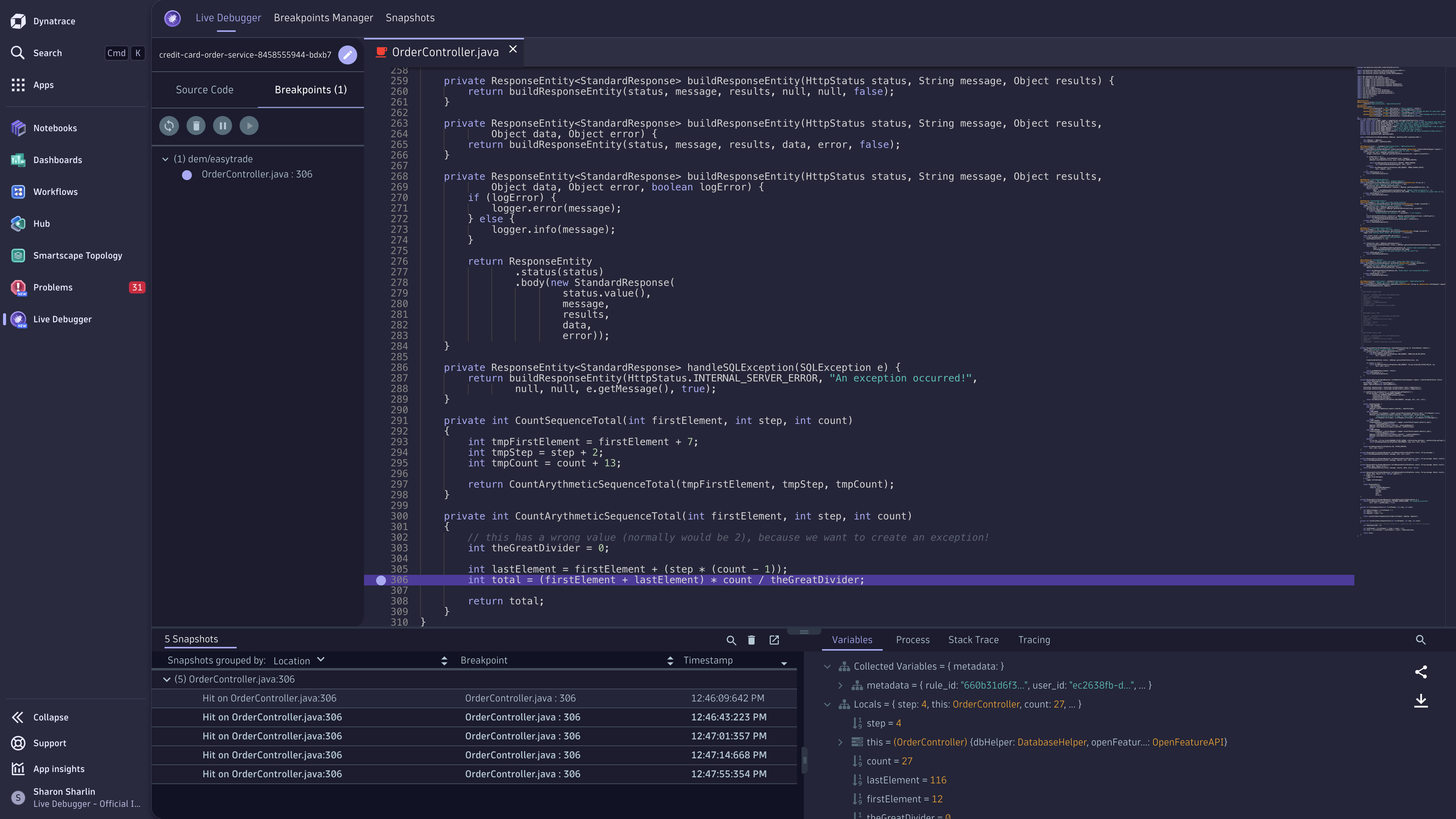
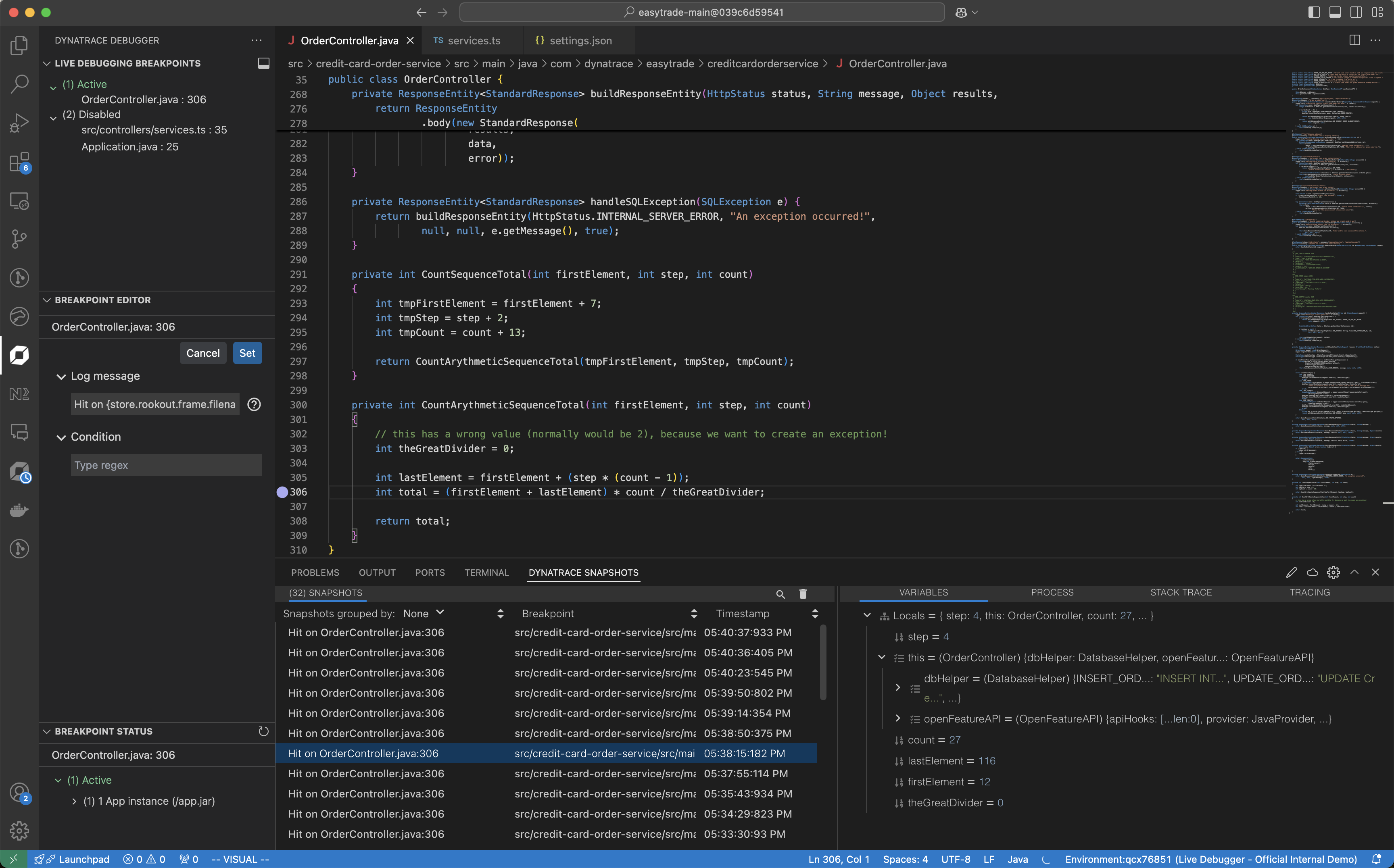
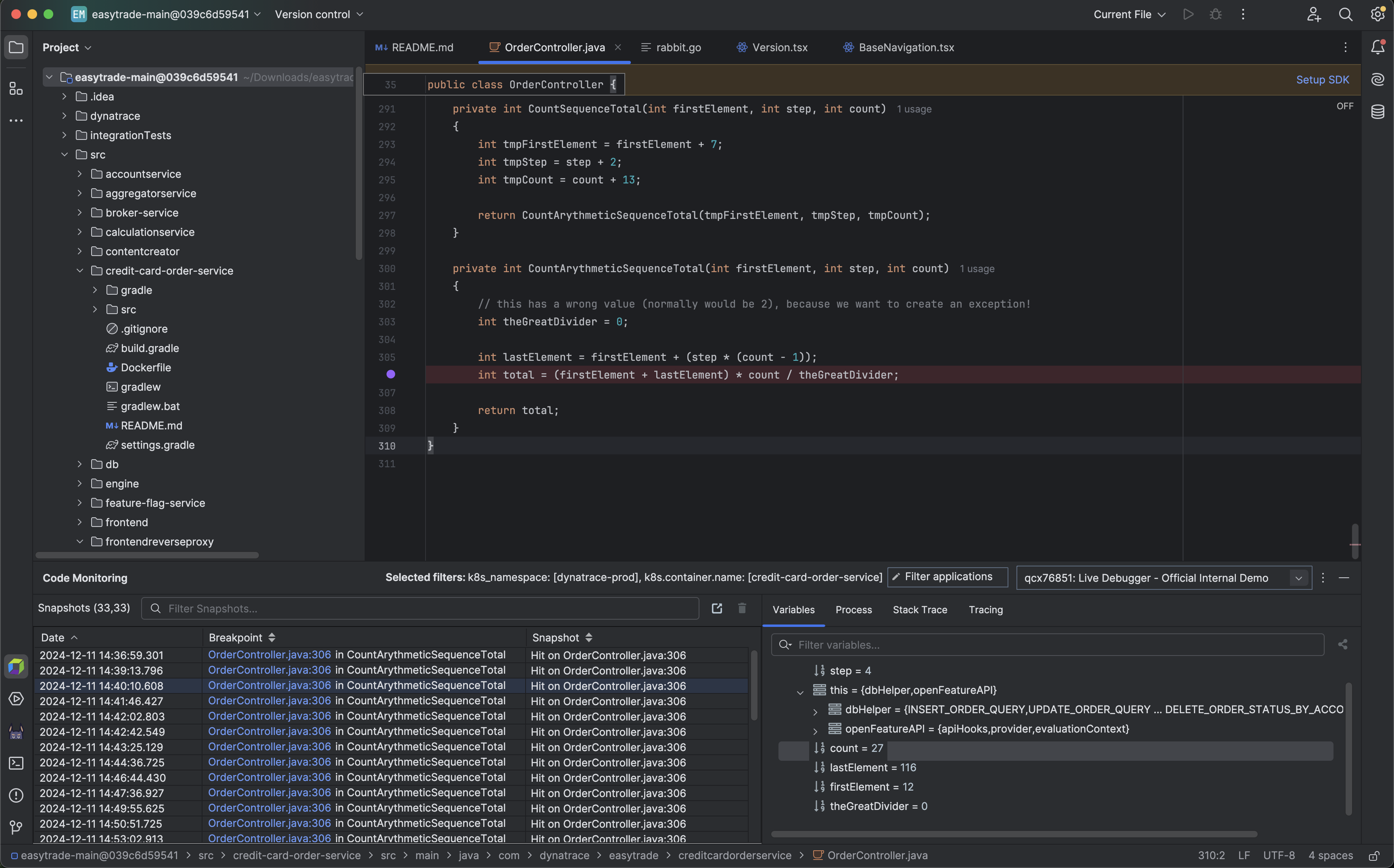
Place a non-breaking breakpoint
To get real-time code-level data
- Select the service you want to debug.
- Navigate to the file system.
- Set a non-breaking breakpoint on the line of code you want to debug.
Non-breaking breakpoints are reference breakpoints for the lines of code from which you want to collect debug data. These breakpoints won't stop your code from running. Instead, they will carry the debug data collection request. Placing these breakpoints and receiving the derived snapshots won't affect your application or its users.
After placing a non-breaking breakpoint, ensure your code has been triggered, so the data will be collected and appear immediately in the application.
See the debug data
Once the non-breaking breakpoint is triggered, the collected data will be displayed as snapshot items in the lower-left panel. By selecting a specific snapshot, you can view
- All local variables and their values
- Process information
- The complete stack trace leading to the breakpoint
- Tracing information from the running application
You can also debug code up the stack from the stack trace view, including third-party components.
 Live Debugger
Live Debugger