Upgrade role-based permissions to Dynatrace IAM policies
- 11-min read
Dynatrace version 1.252+
Starting with Dynatrace version 1.252+, Dynatrace supports defining user and group permissions using IAM policies alongside classic role-based access control. This page guides you through using environment-level permissions in policy statements, enabling fine-grained access control across management zones, host groups, and extensions. Dynatrace security policies support role-based permissions, allowing you to control all access to your environment. You can use security policies to define user/group permissions in your environment via the Dynatrace web UI or the Dynatrace API.
As you migrate your role-based permissions to IAM framework, note that role-based permissions and security policies are additive. For example, if an environment permission is assigned to a user, and then you assign this user to an IAM group with a policy-based role restricted to a management zone, the environment permission still grants access to a whole environment, including all management zones.
Environment permissions
To ease migration to security policies, you can use existing environment permissions in your policy statements and bind them to groups.
Example 1: Policy for an application developer
For example, to create a policy for a typical application developer, you'd want to provide them with a set of permissions as shown in the following code examples:
- Access to all settings in
devandhardeningALLOW environment:roles:manage-settingsWHERE environment:management-zone IN ("dev", "hardening"); - Read access in
prodALLOW environment:roles:viewerWHERE environment:management-zone IN ("prod");
Example 2: Monitoring parts of the environment
-
Create a policy granting full access to the environment.
ALLOW environment:roles:viewer, environment:roles:manage-settings;A user from a group to which this policy is bound has full access to the environment.
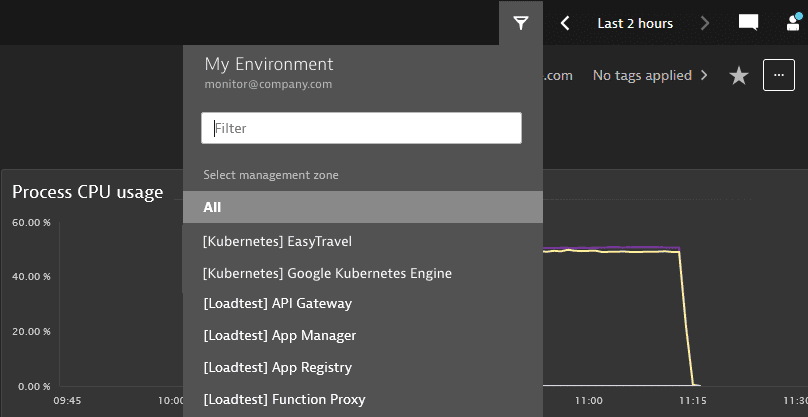
-
Modify the policy to limit access to selected management zones based on name prefix (in this example,
“[Kubernetes]”).ALLOW environment:roles:viewer, environment:roles:manage-settingsWHERE environment:management-zone startsWith "[Kubernetes]";Now the user has access only to the management zones with names starting with
“[Kubernetes]”.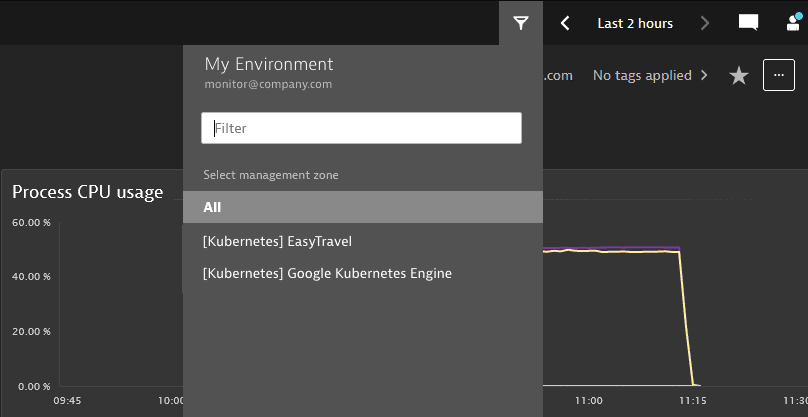
Learn how to create policies.
Management zone permissions
To create policy limited to a specific management zone, use the environment:management-zone attribute in your policy statement. For example, to limit log viewing to a selected management zone, use the following statement:
ALLOW environment:roles:logviewerWHERE environment:management-zone IN ("my-management-zone");
Role names
Use the following role names in your policy statements.
| Current role name | IAM role name | Management zone condition |
|---|---|---|
| View environment | roles:viewer | |
| Manage monitoring settings | roles:manage-settings | |
| Manage capturing of sensitive request data | roles:configure-request-capture-data | |
| Install OneAgent | roles:agent-install | |
| Manage security problems | roles:manage-security-problems | |
| View security problems | roles:view-security-problems | |
| Replay sessions without masking | roles:replay-sessions-without-masking | |
| Replay sessions with masking | roles:replay-sessions-with-masking | |
| View logs | roles:logviewer | |
| View sensitive request data | roles:view-sensitive-request-data |
As with classic role-based permissions, the viewer role is implicitly included in all roles. For example, a policy with a manage-settings role also allows a user to access the web UI.
Policy statement syntax
In its most basic form, a policy statement for environment permissions starts with the ALLOW keyword. Then it is followed by environment:roles, a role name, and a management zone name.
ALLOW environment:roles:<role name> WHERE environment:management-zone = "<name of management zone>";
A statement can include an optional management zone condition. This allows a role in a number of management zones.
ALLOW environment:roles:<role name> WHERE environment:management-zone IN ("<name of management zone 1>", "<name of management zone n>");