Kubernetes
- Latest Dynatrace
- App
- 7-min read
The new Kubernetes experience is optimized for DevOps Platform Engineers and Site Reliability Engineers (SREs), focusing on the health and performance optimization of multicloud Kubernetes environments. The centerpiece of this experience is the  Kubernetes.
Kubernetes.
The underlying metrics, events, and logs are all powered by Grail, which supports flexible analytics through the Dynatrace Query Language in Notebooks, Dashboards, and Workflows.
Prerequisites
- Dynatrace SaaS environment powered by Grail and AppEngine
- DPS license with the Kubernetes Platform Monitoring capability on your Rate Card
- Sufficient permissions to use the
 Kubernetes within your Dynatrace environment
Kubernetes within your Dynatrace environment - ActiveGate version 1.327+ is a prerequisite for Kubernetes Enhanced Object Visibility.
- Older ActiveGate versions are supported in backward compatibility mode; in that mode, an additional Explorer (Classic) tab appears in the UI.
For more details, see getting started FAQs.
The new Kubernetes experience is not available for Managed or SaaS on non-Grail environments—you can continue to use Kubernetes Classic (accessible from the previous Dynatrace via Kubernetes).
Get started
 Kubernetes provides a comprehensive view of your environment, enabling you to automate monitoring and optimize the health and performance of your Kubernetes clusters and workloads. This page walks you through the main concepts underlying
Kubernetes provides a comprehensive view of your environment, enabling you to automate monitoring and optimize the health and performance of your Kubernetes clusters and workloads. This page walks you through the main concepts underlying  Kubernetes.
Kubernetes.
With  Kubernetes, you can:
Kubernetes, you can:
- Set up Kubernetes monitoring with Dynatrace.
- Explore cluster, node, and workload insights.
- Analyze health status with Davis AI.
- Detect and troubleshoot Kubernetes issues.
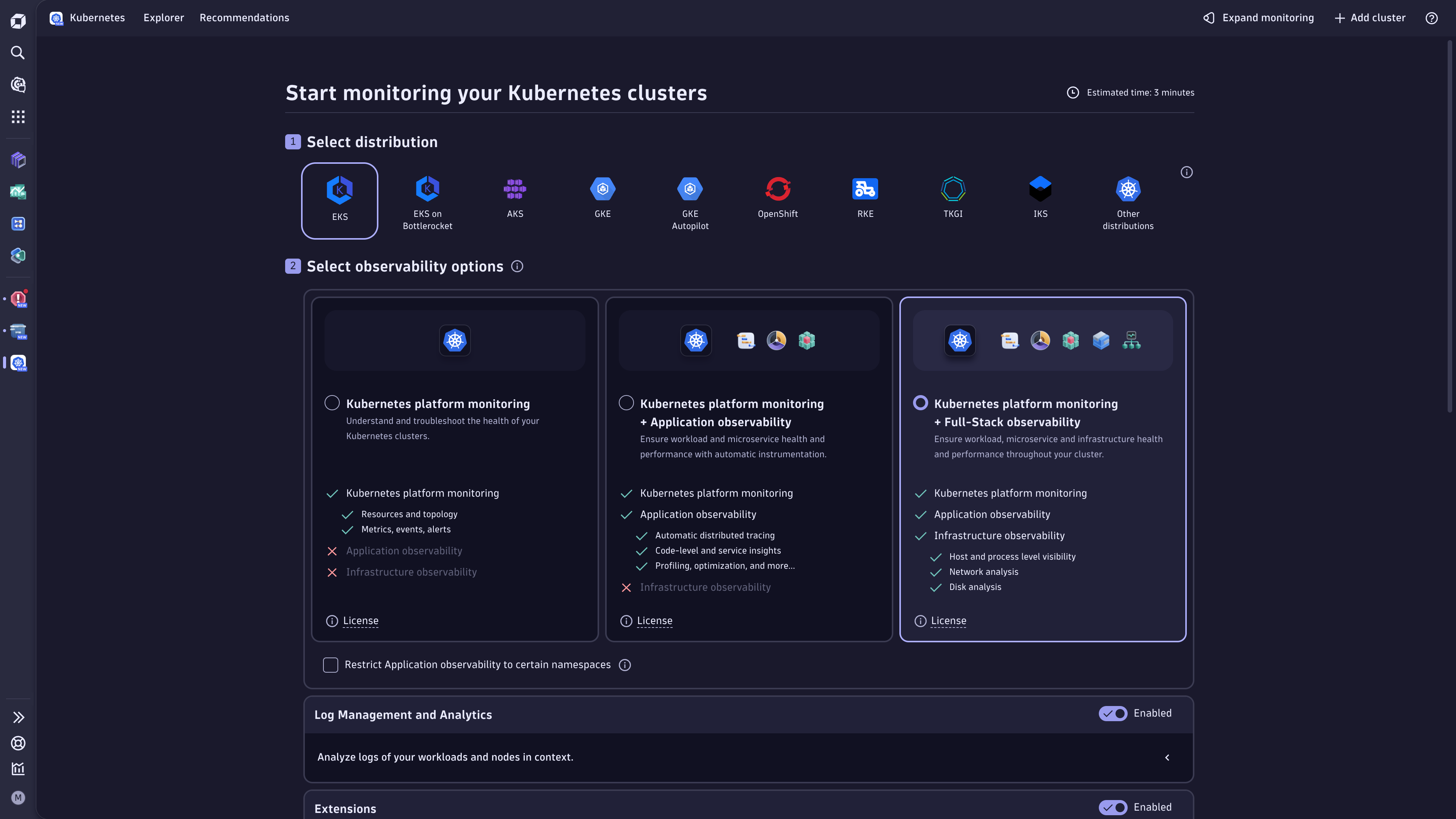
Setup and reference
Use the following guide to set up and configure Kubernetes monitoring in Dynatrace.
Explorer
Explorer is the shared Dynatrace interface for monitoring and analyzing different technology domains. It defines a common layout (sidebar, list, filter bar, health indicators, and detail panels) with consistent filtering, perspectives, drill‑down navigation, and unified analysis.
The sections below describe how Explorer appears in the Kubernetes app.
Basic structure
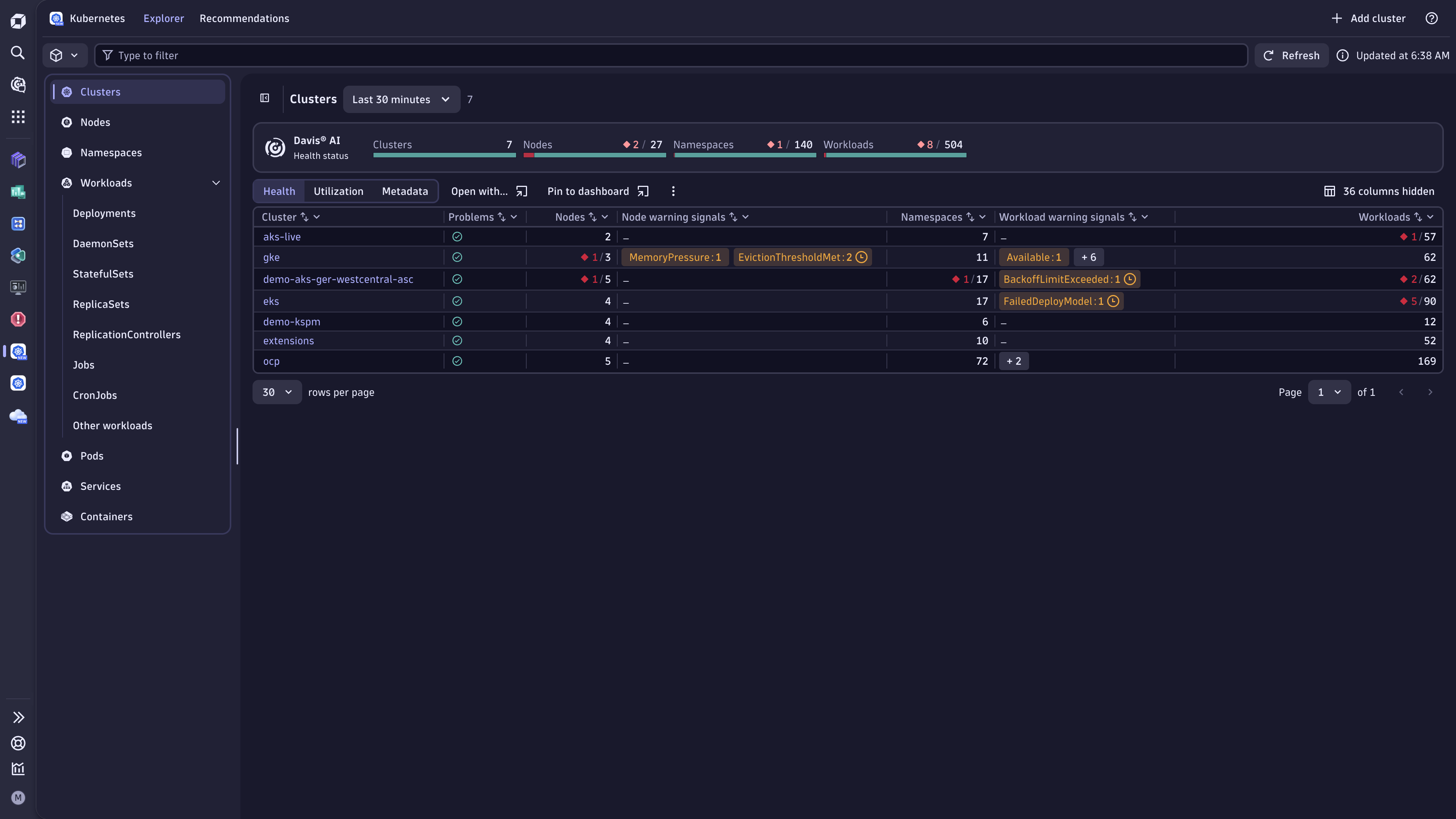
 Kubernetes offers insights into your entire Kubernetes environment, presenting valuable information across primary areas as indicated in the picture below.
Kubernetes offers insights into your entire Kubernetes environment, presenting valuable information across primary areas as indicated in the picture below.
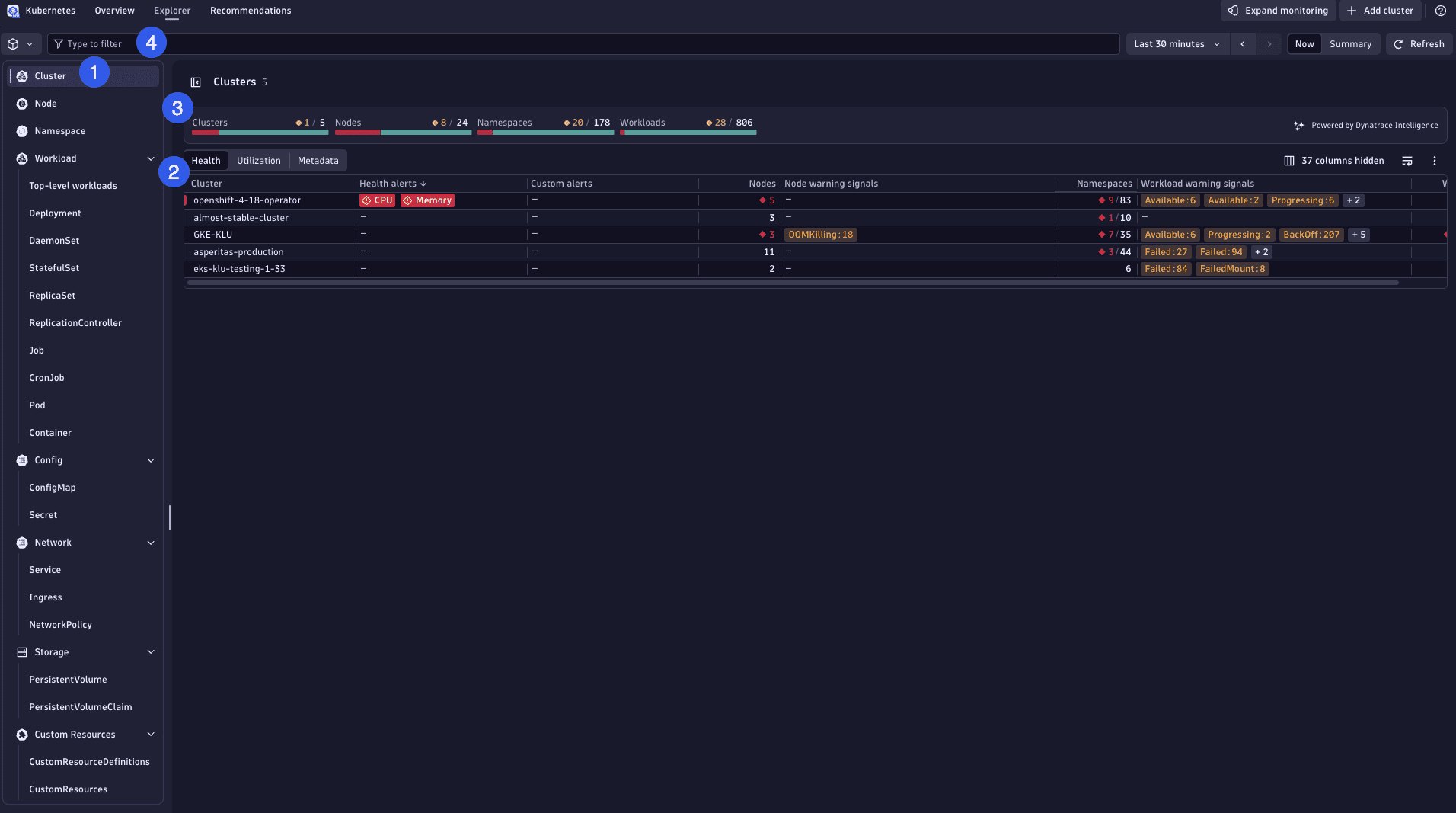
-
Sidebar (1)
Located on the left side, the sidebar groups all Kubernetes objects by type, including clusters, nodes, namespaces, workloads, pods, services, and containers.
-
Object list (2)
The central table displays all objects of the selected type, serving as the starting point for analysis and drill-down for your observability use cases.
-
Aggregated health bar (3)
Located above the object list, this bar provides an aggregated health status of the displayed objects and their child objects.
-
Filter bar (4)
The filter bar below the app header allows you to narrow down the object list view, focusing on specific objects or health statuses.
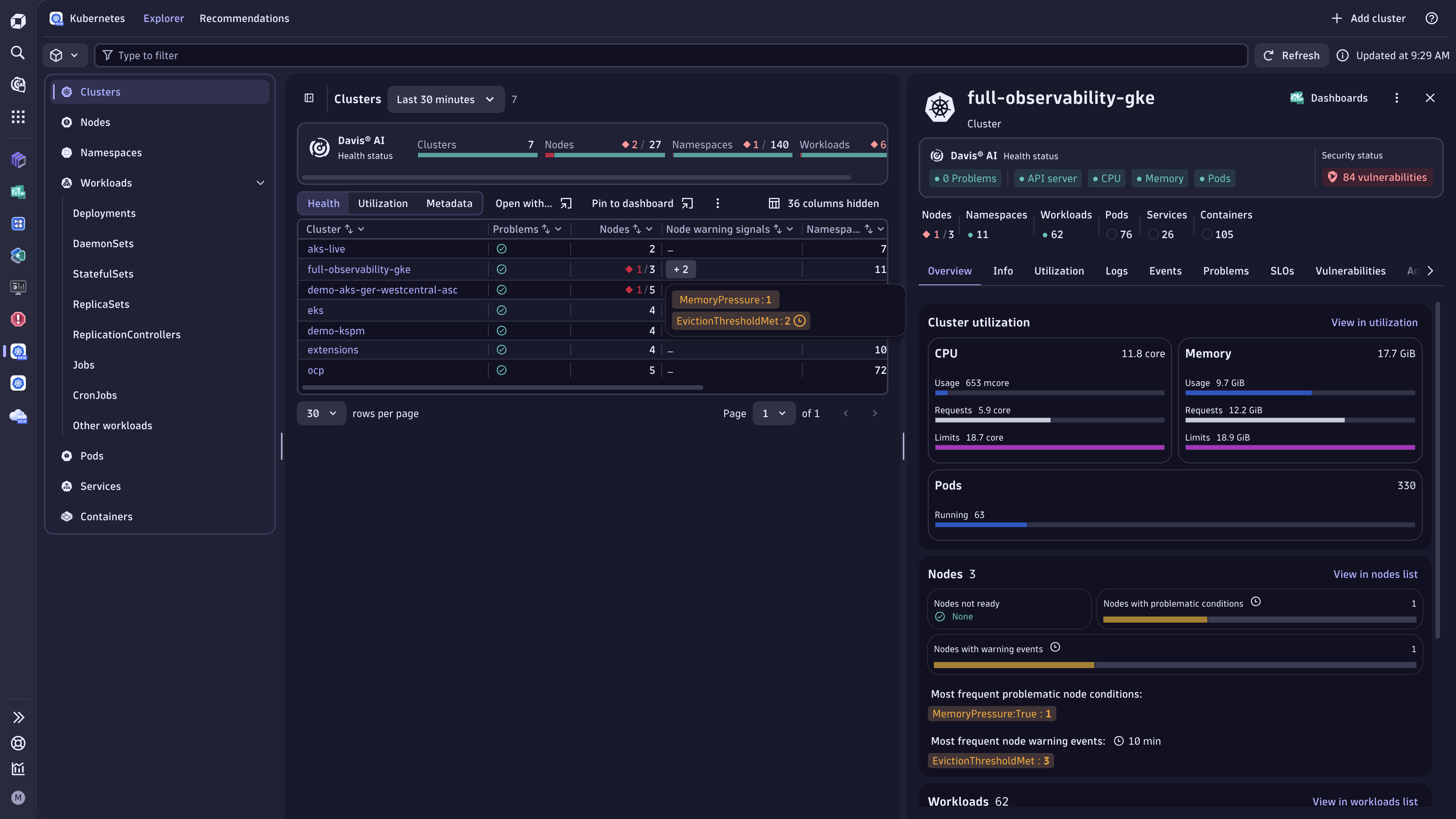
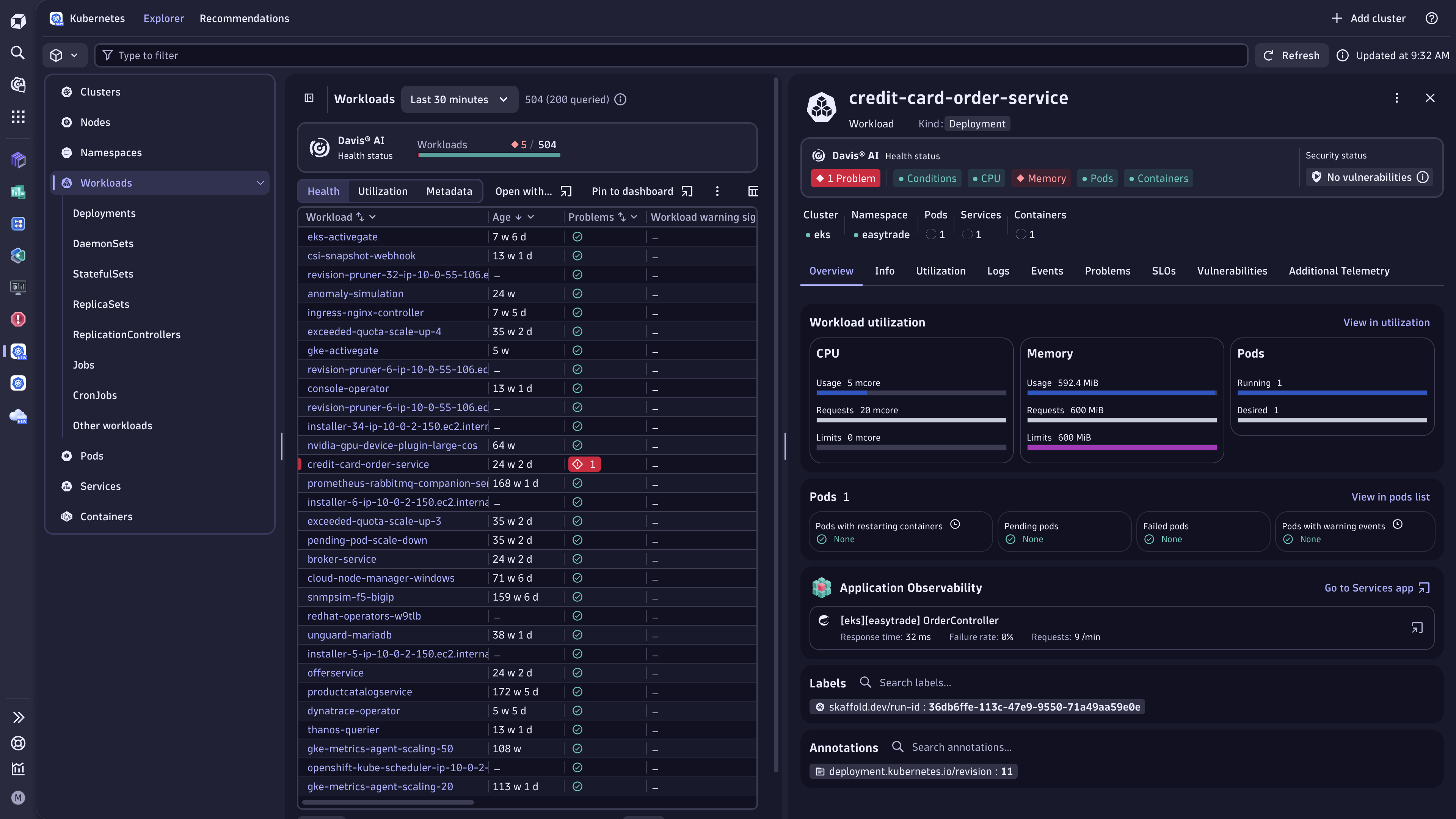
Detail view
Select a Kubernetes object from the list to open a detail view and focus on the specific object.
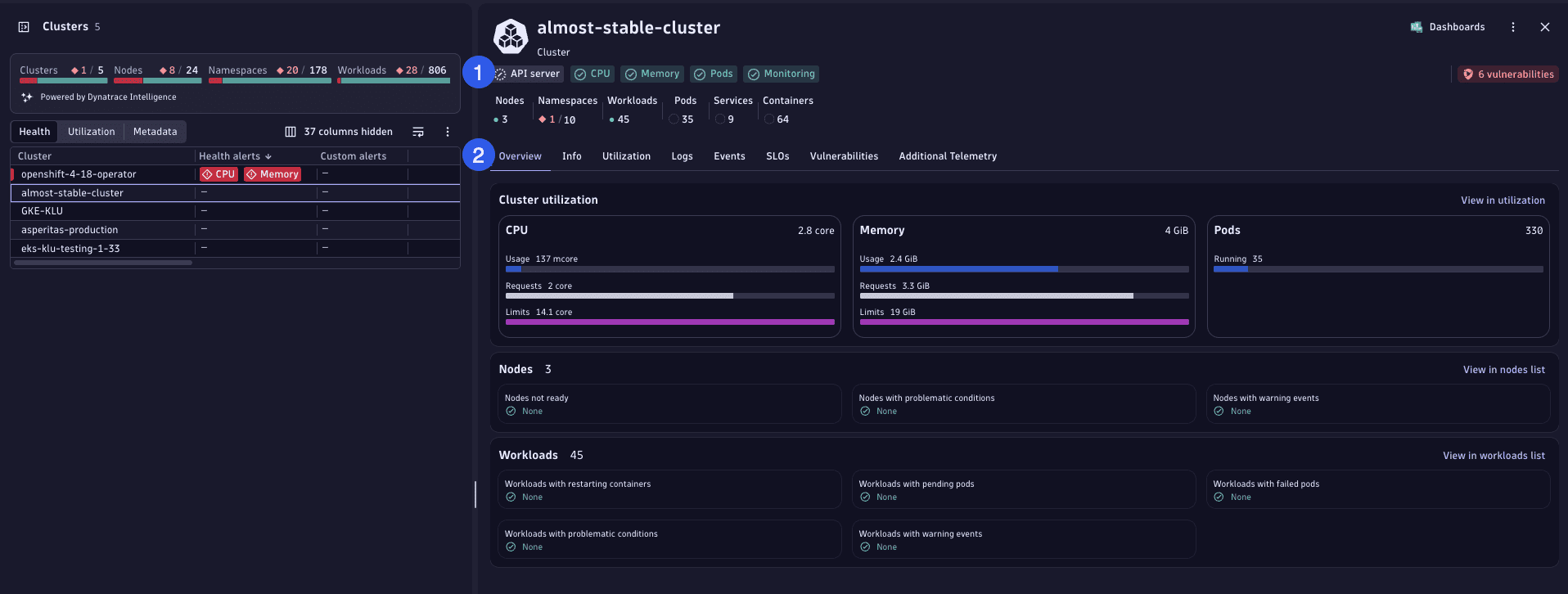
-
Top summary section (1)
The top pane provides a quick summary of the health and security status of the selected object and its child objects.
-
Main detail section (2)
The main section provides detailed insights of the given object, featuring tabs for analyzing health and utilization, as well as for exploring logs, events, ownership, and vulnerabilities. The data presented in the detailed view remains consistent regardless of any filters applied in the main interface.
Perspectives
Perspectives are located under the aggregated health bar. They support various use cases, such as health monitoring or resource optimization.
-
Selecting a perspective (1)
Choosing a perspective changes which columns are displayed in the table. For example:
- Health—shows health-related information and alerts.
- Utilization—focuses on CPU, memory, and other resource usage metrics.
-
Customizing columns (2)
You can add or remove columns within a selected perspective to match your analysis needs. Your personal configuration persists in your browser, and you can reset to the default layout at any time by selecting
next to the list of available perspectives (1).
Davis AI health status
The health status is based on the Kubernetes-focused custom alerts. Health indicators aggregate the states of these custom alerts per resource.
A Kubernetes object (such as a cluster) is considered unhealthy if any of its associated custom alert configurations are in an unhealthy state. By selecting a specific health indicator, you can gain further insights into the underlying reasons for this status.
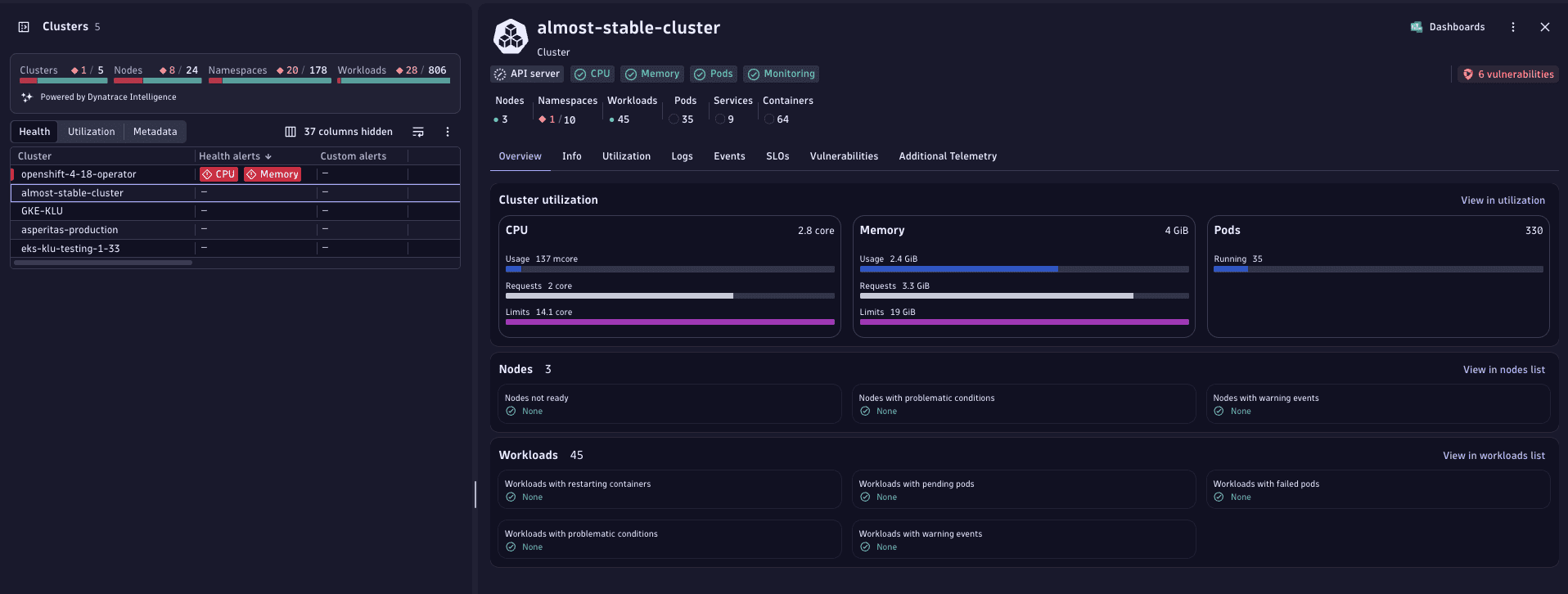
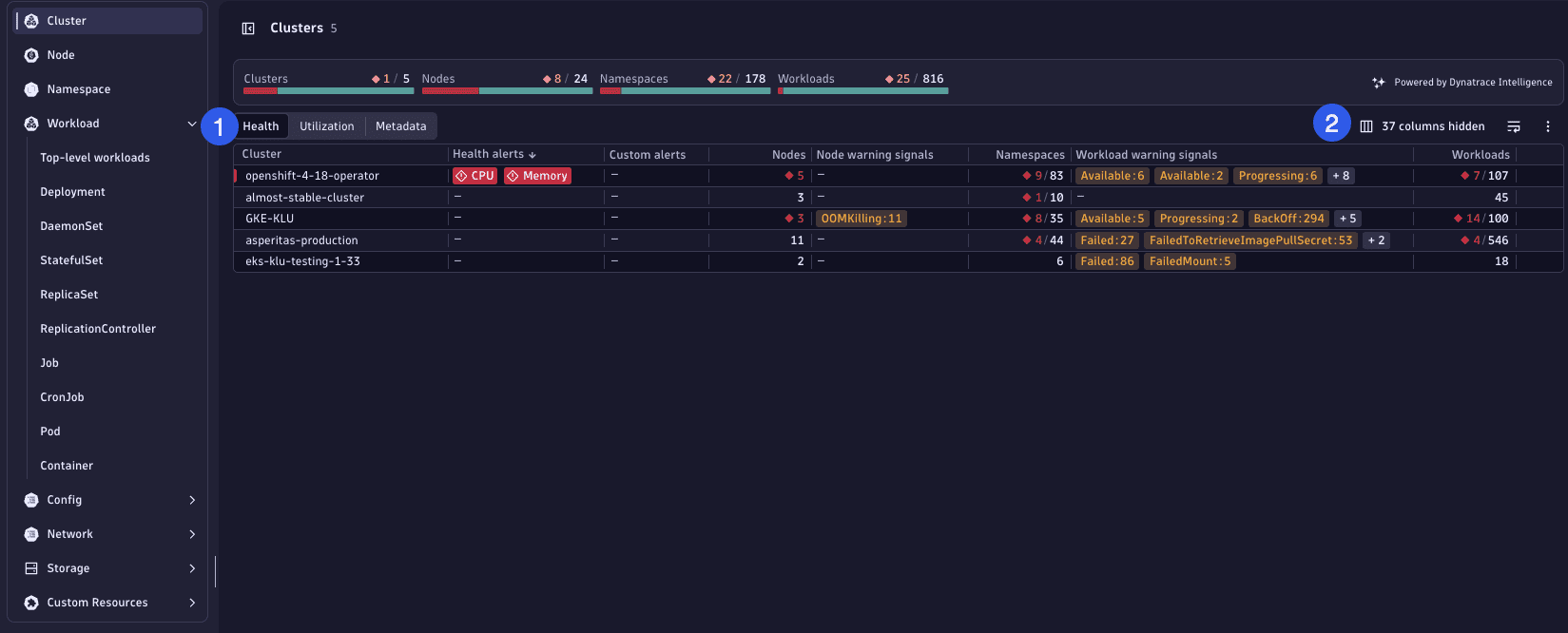
Example
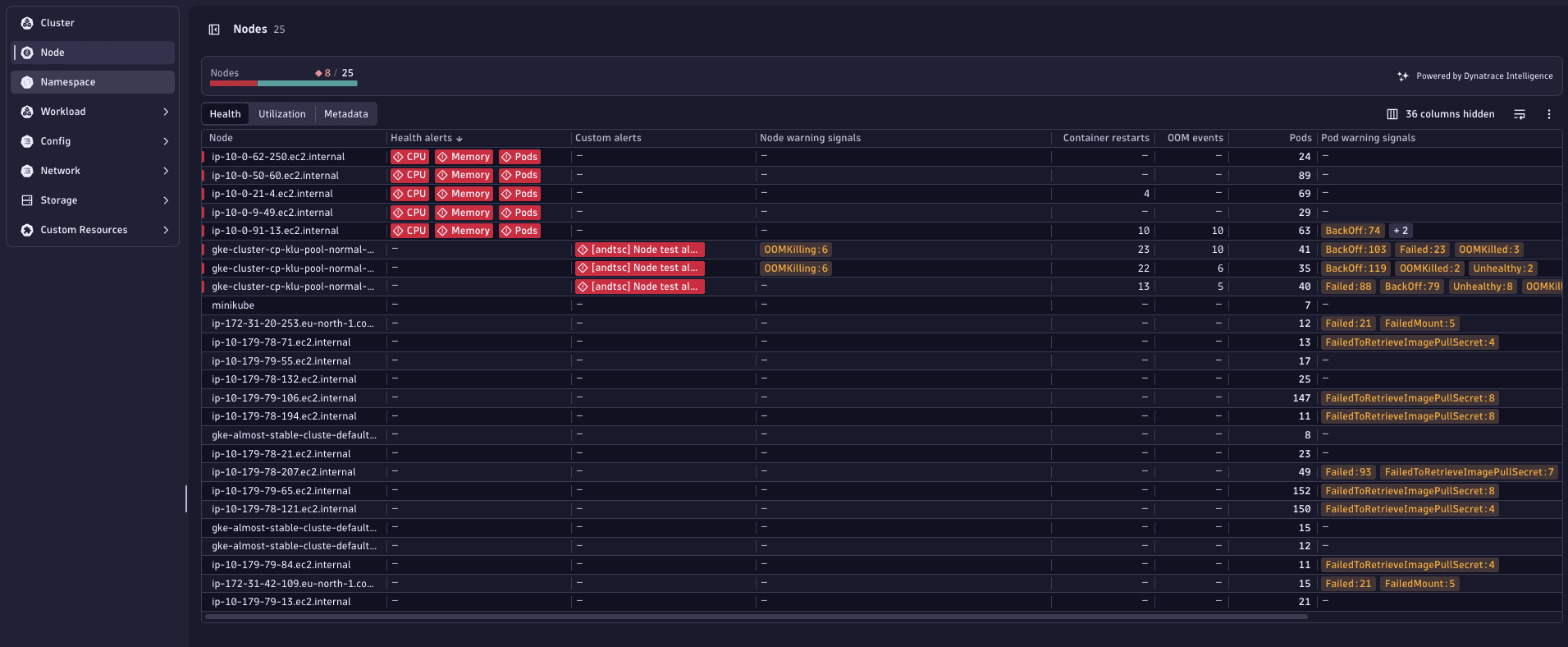
In this example, you can see that 8 nodes out of 24 are currently considered unhealthy.
-
Select the red numbers displayed within the health status area to drill down to the list of currently unhealthy nodes.
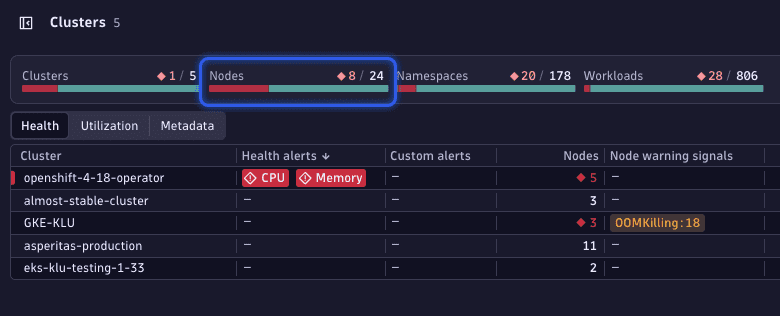
-
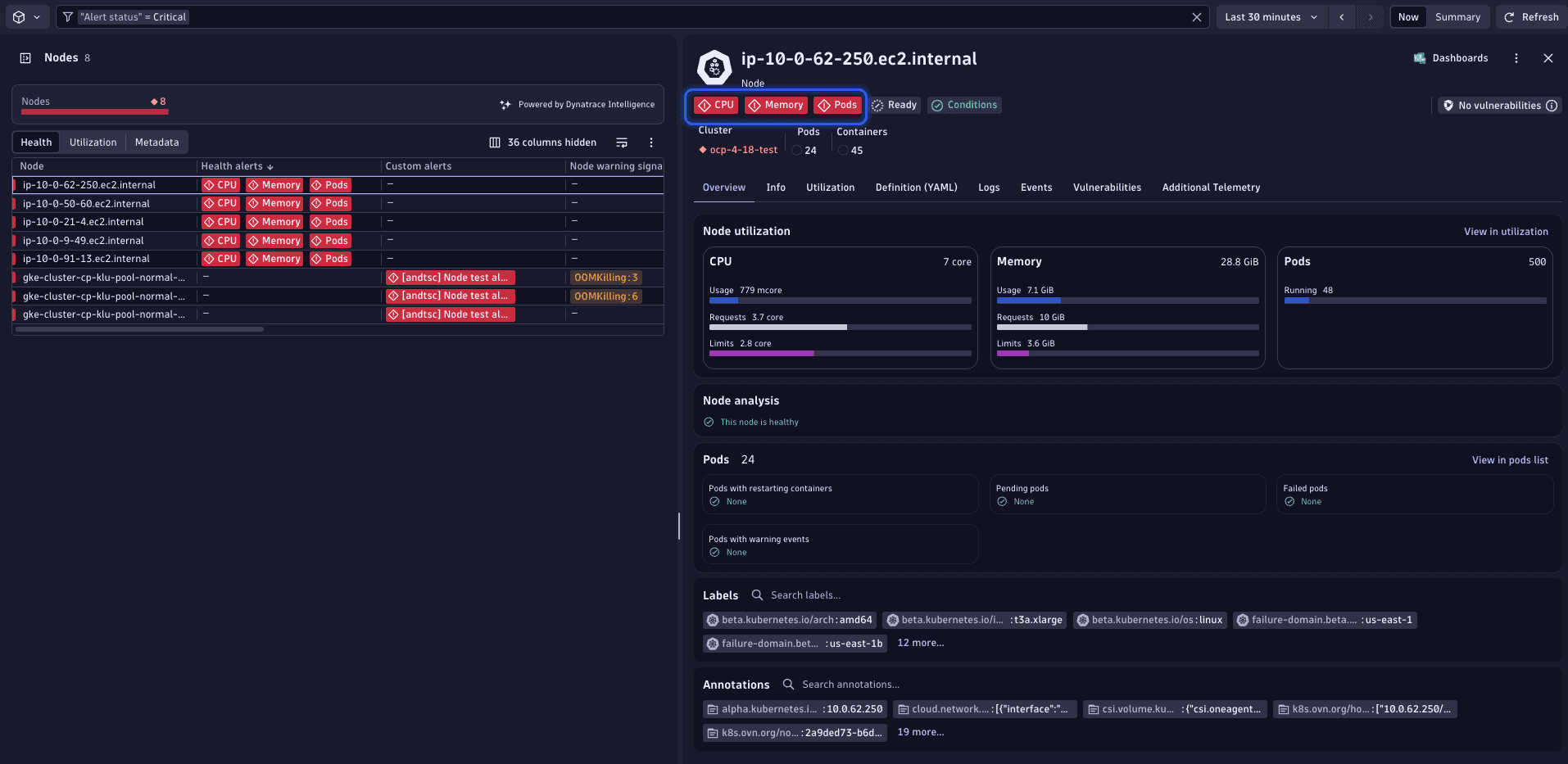
Select any node to open the details view of the problematic node, including key metrics and events that led to their current state.
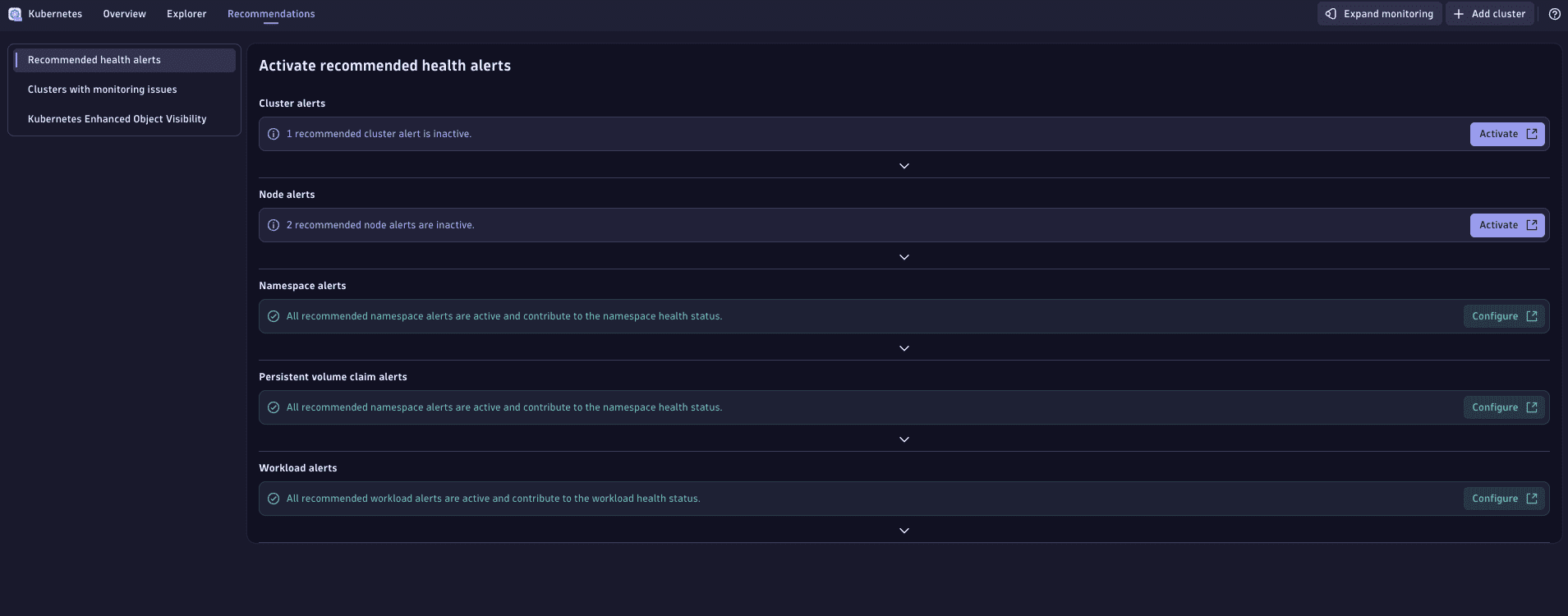
The Recommendations tab presents best-practice Kubernetes health alerts for clusters, nodes, namespaces, persistent volume claims, and workloads. It highlights which alerts are active, partially active, or inactive across your environment.
Select Activate or Configure to open the settings where you can apply the recommended alert configuration.
Warning signals
In addition to health status,  Kubernetes surfaces active problematic conditions of workloads and nodes, as well as warning signals that occurred in the last 10 minutes. These warning signals combine both problematic conditions and warning events, providing insight into potential upcoming problems or existing misconfigurations.
Kubernetes surfaces active problematic conditions of workloads and nodes, as well as warning signals that occurred in the last 10 minutes. These warning signals combine both problematic conditions and warning events, providing insight into potential upcoming problems or existing misconfigurations.
While they may not always represent active health issues at the moment, frequent Unhealthy signals, for instance, might indicate misconfigured readiness probes, inappropriate CPU limits, or unusually high workload.
Sorting and filtering of warning signals
There are two types of warning signals. They're organized as follows:
- Problematic conditions affect the health of the node or workload (for example,
DiskPressure,MemoryPressure).- Listed first
- Sorted alphabetically within each category
- Warning events are less critical, and often signal temporary issues (for example,
OOMKilled,PodEviction).- Listed after problematic conditions
- Sorted by their frequency
 Kubernetes provides several interaction options:
Kubernetes provides several interaction options:
-
Context menu actions:
- Go to affected nodes or Go to affected workloads: Navigates directly to the nodes or workloads experiencing the selected condition. This opens a filtered view displaying only the affected nodes or workloads.
- Explore events: Opens a detailed log view showing the events associated with the warning signal.
- Filter for: Automatically applies a filter to show only the entities impacted by the specific condition or event.
-
Filtering from the menu bar: You can apply filters directly from the menu bar by selecting either general categories such as Any problematic condition or individual signals like
MemoryPressure:TrueorFailedMount. Once filtered, the view updates to focus on the entities affected by the selected filter.
| Column | Content | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Node warning signals | Combines events emitted by nodes and problematic node conditions | DiskPressure, MemoryPressure, NodeNotReady |
| Pod warning signals | Combines events emitted by pods and conditions affecting pods | BackOff, PodEviction, OOMKilled |
| Workload warning signals | Combines events emitted by namespaces, workloads, and pods, along with workload conditions | CPUThrottlingHigh, ContainerRestarts, PodsPending |
Use cases
Reference
Go to the following reference pages for more information about permissions, available alerts, and default settings for new environments.
Related topics
Dive deeper into  Kubernetes with the following resources:
Kubernetes with the following resources:
- Playground environment: Test the app in a sandbox environment.
- 0 to Full Observability in Kubernetes in under 3 minutes: A quick video tutorial on how to install Dynatrace Operator.
- Blog post: Unlock the Power of DevSecOps with Newly Released Kubernetes Experience for Platform Engineering

Explore in Dynatrace Hub
Automated change impact analysis for your deployment and release processes.
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes