Configure beacon origin allowlist for web applications
- How-to guide
- 3-min read
Use the beacon origin allowlist to specify the origins from which your application beacon endpoints should accept cross-origin RUM beacons.
Same- and cross-origin beacons
The RUM JavaScript sends RUM beacons to report the captured data to Dynatrace. Depending on the injection method, there are two default setups:
-
Auto-injected applications > same-origin beacons
When the RUM JavaScript is injected automatically, RUM beacons are sent back to the web or application server that hosts the auto-injected application; OneAgent provides a beacon endpoint.
By default, the beacons of auto-injected applications are same-origin beacons since the protocol, host, and port of the beacon requests and the page where they're issued are identical.
If you opted for one of the alternative beacon endpoint setups—where the beacons of an auto-injected application are sent to the Dynatrace SaaS infrastructure or an instrumented server on a different domain—RUM beacons are cross-origin beacons.
-
Agentless applications > cross-origin beacons
When agentless monitoring is used, RUM beacons are sent to a beacon endpoint that is part of the Dynatrace SaaS infrastructure.
For agentless applications, the RUM beacons are cross-origin beacons since they're sent to a different domain.
Browsers adhere to the same-origin policy that, by default, allows scripts to issue requests only to the same origin. To send cross-origin requests, Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) needs to be used, which allows servers to specify origins that are permitted to access the server. Therefore, cross-origin RUM beacons need to use CORS. In this case:
- The browser adds an
Originheader to the cross-origin beacon. - By default, the beacon endpoint adds an
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader to each response that allows the origin provided in theOriginheader.
Using the beacon origin allowlist, you can specify from which origins your beacon endpoints should accept RUM beacons.
Specify beacon origins for CORS
Create a beacon origin rule to specify from which origins the OneAgent and Dynatrace SaaS infrastructure should accept RUM beacons.
Right after you add the first beacon origin rule, applications that don't match that rule will stop collecting RUM data unless their beacons are sent to the same origin and handled by OneAgent.
To add a beacon origin rule
-
Go to Settings > Web and mobile monitoring > Beacon origins for CORS.
-
Select Add item.
-
Provide the correct pattern for the origin you want to specify.
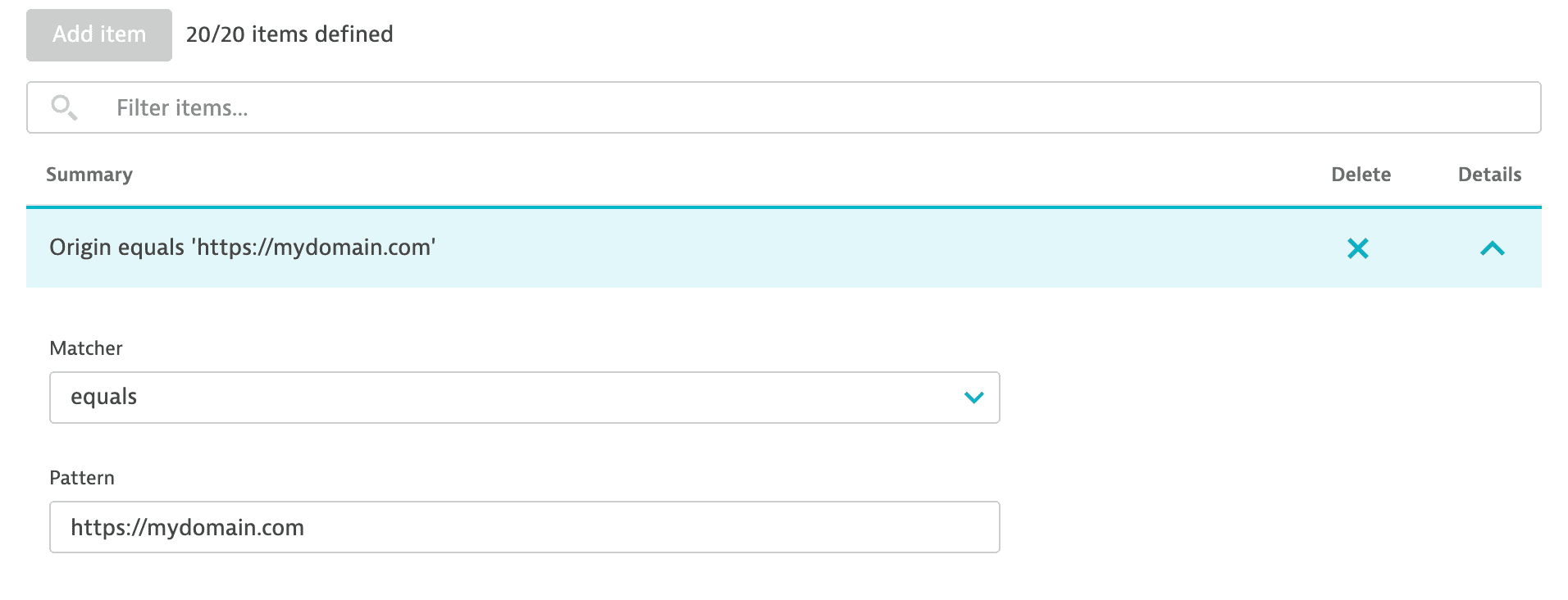
You can add up to 20 beacon origin rules per environment.
Application of beacon origin allowlist in different scenarios
![]()
This flowchart shows how Dynatrace applies the beacon origin allowlist in different scenarios. Use it to understand whether a specific beacon origin is allowed.
- If the beacon origin allowlist is empty, RUM beacons from any origin are accepted by all beacon endpoints.
- If an origin is on the allowlist, a RUM beacon from that origin is accepted. In the cross-origin case, the origin is copied to the
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader of the response, and the beacon response returns the200 OKHTTP status code. - If an origin is not on the allowlist, a cross-origin RUM beacon from that origin is rejected. The beacon fails with the
403 Forbiddenstatus code and a message such asValue in Origin Header is not allowed. - OneAgent doesn't apply the beacon origin allowlist to same-origin beacons.