User actions in web frontends
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
A user action represents a significant operation within the frontend and its implications. This page explains the concept for web frontends in the New RUM Experience and how it differs from RUM Classic.
User action types
User actions in web frontends can be grouped into three types:
-
Navigation user actions: When a soft navigation occurs, which results in a view change, a new user action is created automatically. Navigations are usually triggered by a user interaction, but a user interaction is not required for a user action to be created.
-
Request user actions: If a click user interaction is followed by an XHR or fetch request, a user action is created.
-
API user actions: You can also create user actions using
dynatrace.userAction.create() in the JavaScript API. There are no prerequisites for triggering a user action this way.
How user actions end
A user action ends automatically based on certain conditions, or you can close it manually via the API.
Default end behavior
While a user action is active, the RUM JavaScript keeps track of XHR and fetch requests, DOM mutations, and resource timings to determine when the user action ends. A user action ends when one of the following conditions is met:
- The user action reaches a duration of 50 s.
- The user leaves the page.
- A new user action is created. In this case, the current user action is interrupted and associated with the new one through the
user_action.interrupted_by_instance_idattribute. - When all of the following conditions apply during the last 100 ms:
- No XHR or fetch requests occurred.
- No DOM mutations occurred.
- No new request was added to the W3C Resource Timing API. Note that requests are only added once they have finished.
Ending user actions via the API
You can close user actions via the API using UserActionTracker.finish().
By default, API-created user actions follow the default end behavior. To disable auto-closing, use UserActionTracker.autoClose(), or set the autoClose option to false when creating the user action.
Example
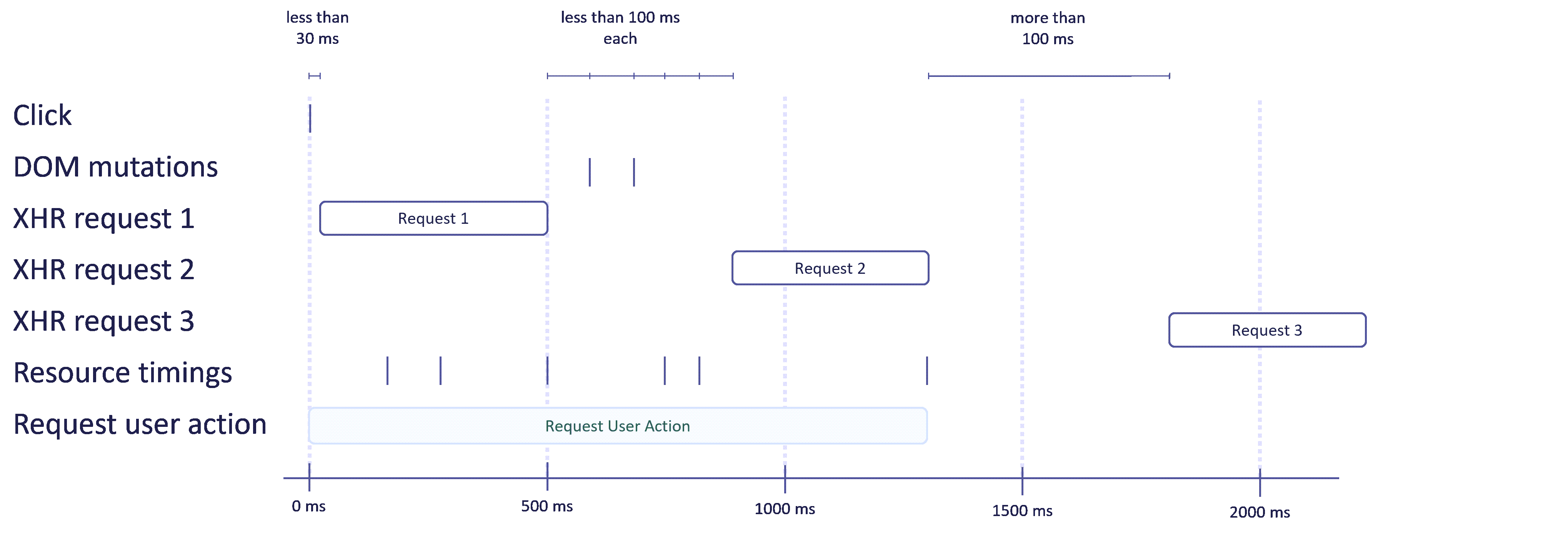
The diagram below illustrates the lifecycle of a user action, using a request user action as an example.
- The user clicks somewhere on the page.
- If an XHR or fetch request occurs within 30 ms, a new user action starts.
- As long as DOM mutations, XHR or fetch requests, or resource timings are reported within 100 ms of the previous report, the user action is extended.
- If more than 100 ms pass without any report, the user action is closed and sent.
Comparison to user actions in RUM Classic
RUM Classic also provides a user action concept, but it differs in several ways from user actions in the New RUM Experience. The table below highlights the key differences.
New RUM Experience
RUM Classic
User action triggers
Click
Click, keypress, scroll, touch, etc.
Maximum action duration
50 s
180 s
Consideration of DOM mutations for default end behavior
Considers all DOM mutations.
Considers only the visible area, and only if the Visually complete and Speed index setting is enabled.
Support for asynchronous JavaScript executions
Fully supported
Only partially supported, and only if timed action support is enabled.
API support
Granular control
Basic support