Calculate your consumption of Runtime Vulnerability Analytics (RVA) (DPS)
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
- 5-min read
- Published Aug 12, 2025
This page describes how the Runtime Vulnerability Analytics DPS capability is consumed and billed. For an overview of the capability, including its main features, see Runtime Vulnerability Analytics (RVA).
How consumption is calculated: GiB-hour
The unit of measure for Runtime Vulnerability Analytics is the GiB-hour (also referred to as "memory-gibibyte-hour" in your rate card).
Dynatrace is built for dynamic cloud-native environments where hosts and services are rapidly spun up and destroyed. Therefore, billing granularity for GiB hour consumption is calculated in four 15-minute intervals per hour. When a host or container is monitored for fewer than 15 minutes in an interval, GiB-hour consumption is rounded up to 15 minutes before consumption is calculated.
How consumption is calculated for hosts
Each instance that Runtime Vulnerability Analytics runs on consumes GiB-hours based on the monitored host's physical or virtual RAM, calculated in 15-minute intervals.
The RAM of each VM or host is rounded to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB (which equates to 256 MiB) before monitoring consumption is calculated. A 4 GiB minimum is applied to GiB-hour consumption for physical and virtual hosts.
For example, a host with 8.3 GiB memory is counted as an 8.5 GiB host, being the next multiple of 0.25 GiB, while a host with 2 GiB memory is counted as a 4 GiB host (no rounding needed, but application of the 4GiB minimum).
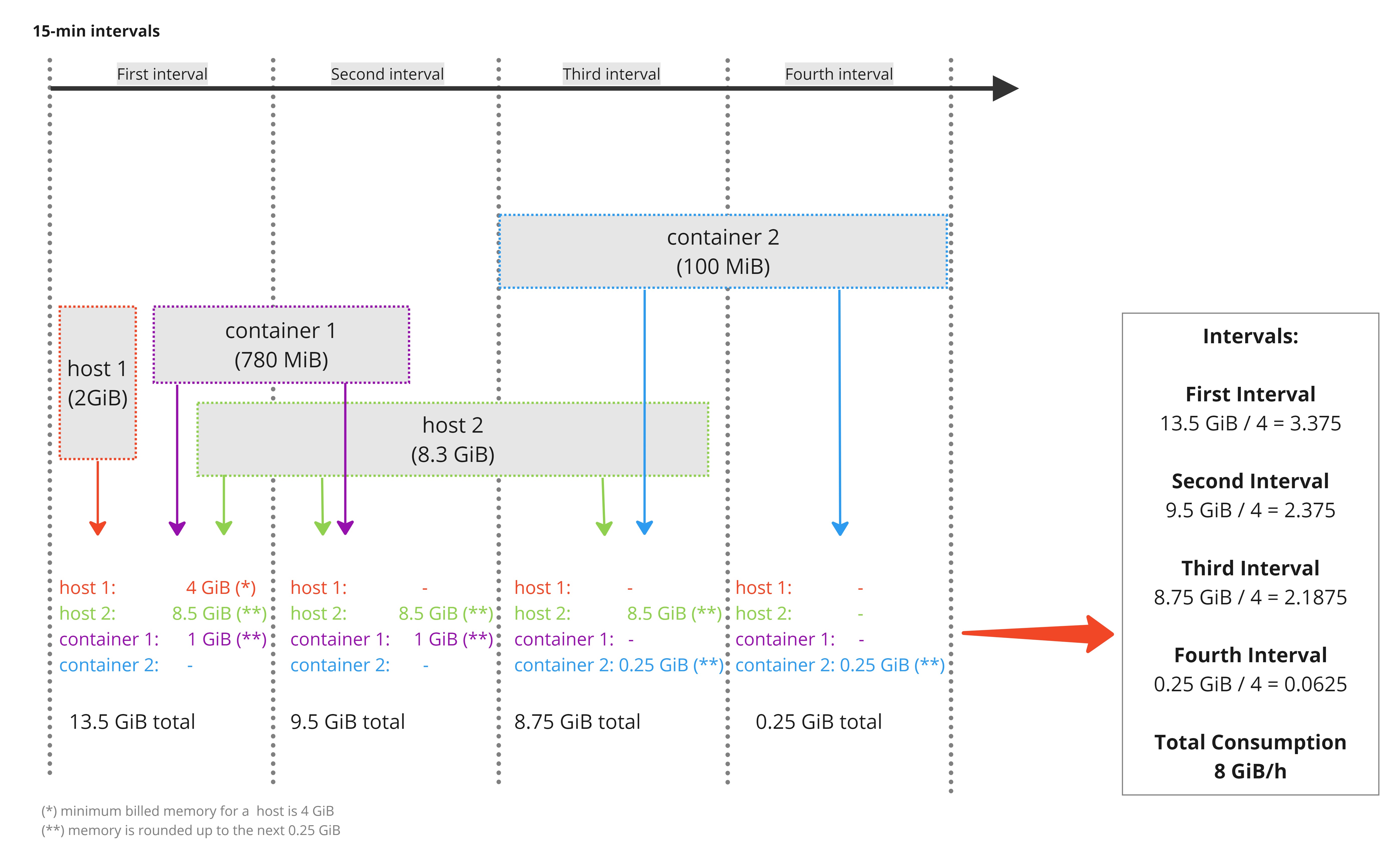
In the example above, each interval is divided by 4 in order to reach the GiB-hour consumption unit of measure.
- Host 1: Runs in the first interval with 2 GiB memory (counted as 4 GiB due to the Host Minimum) = 1.0 GiB/h
- Host 2: Runs from in the first, second, and third interval with 8.3 GiB memory (rounded to 8.5 GiB) = 6.375 GiB/h
- Container 1: Runs from in the first and second interval with 780 MiB memory (rounded to 1 GiB) = 0.5 GiB/h
- Container 2: Runs in the third and fourth interval with 100 MiB memory (rounded to 0.25 GiB) = 0.125 GiB/h
Total = 8.0 GiB/h
How consumption is calculated for containers (application-only monitoring)
Memory-size calculations for containers monitored in an application-only approach are based on either:
- The container's used memory. This method is used if you have OneAgent version 1.275+ (for Kubernetes containers) or 1.283+ (for serverless containers).
- Customer-defined memory limits. This method is used with all previous OneAgent versions. If no memory limit is set, the memory of the underlying virtual machine is used instead.
Automatic container detection needs to be manually enabled for existing tenants.
The following exceptions apply to the memory-size calculations:
- For Azure App Services running on the App Service (Dedicated) plan for Windows:
- Instances are counted as hosts and the defined memory of all instances is aggregated to determine total memory—regardless of how many applications run on those instances.
- The minimum billed memory is 256 MiB (instead of 4 GiB).
- For Azure App Service on Linux and Azure App Service for Linux Containers with OneAgent version <1.283, container instances are counted as hosts.
- Solaris Zones are counted as hosts.
- Monitored containers that are not detected as containers are counted as hosts.
In cloud-native environments, services and hosts are often short-lived. Therefore calculating monitoring consumption in 15-minute time intervals, rather than full hours, better reflects your actual usage. Containers, which are an essential mechanism in cloud-native environments, are typically smaller in memory size than hosts. Therefore, the minimum memory threshold for containers is 256 MiB, rather than 4 GiB, the minimum memory threshold for hosts. The same rounding as for hosts, to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB, also applies for containers. For example, a container with 780 MiB memory is counted as a 1 GiB container (780 MiB, which equals 0.76 GiB, being rounded up to the next multiple of 0.25 GiB).
Track your consumption
This section describes the different Dynatrace tools that you can use to track consumption and costs.
Track your consumption with Metrics
Dynatrace provides the following built-in usage metrics that help you understand and analyze your organization's consumption of Runtime Vulnerability Analytics:
- (DPS) Runtime Vulnerability Analytics billing usage
Key:
builtin:billing.runtime_vulnerability_analytics.usageDimension:
Resolution: 15 min
Description: Total number of host hours consumed by Runtime Vulnerability Analytics.
- (DPS) Runtime Vulnerability Analytics billing usage per host
Key:
builtin:billing.runtime_vulnerability_analytics.usage_per_hostDimension:
Host (dt.entity.host)Resolution: 15 min
Description: The total number of host hours consumed by Runtime Vulnerability Analytics, split by host.
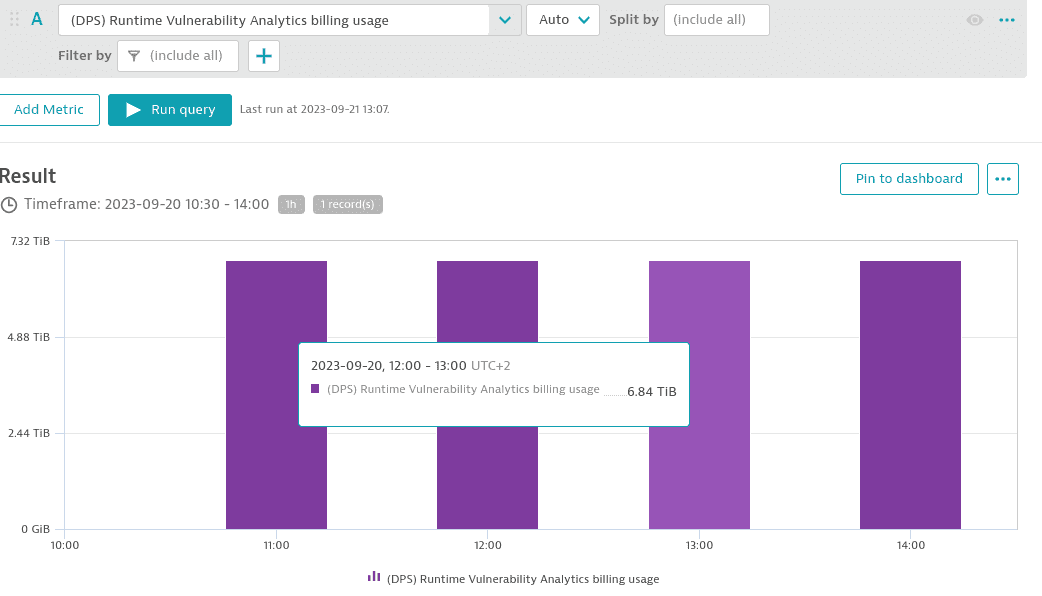
You can monitor the total memory-GiB-hour consumption aggregated across all Runtime Vulnerability Analytics monitored hosts for different intervals (15 min, hour, day, or week) for any selected timeframe using the metric builtin:billing.runtime_vulnerability_analytics.usage.
The example below shows memory-GiB-hour consumption in 1-hour intervals.
Between 11:00 and 14:00, 6.84 memory-TiB-hours were consumed each hour.
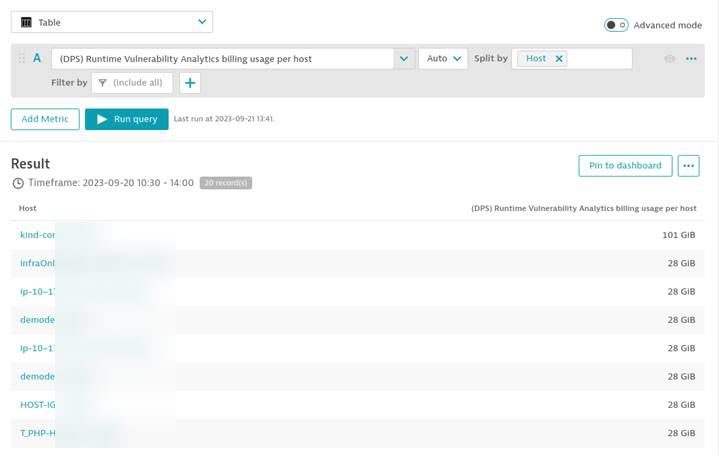
You can split the total host-hour consumption using the metric builtin:billing.runtime_vulnerability_analytics.usage_per_host.
The example below shows the list of all hosts that reported consumption.
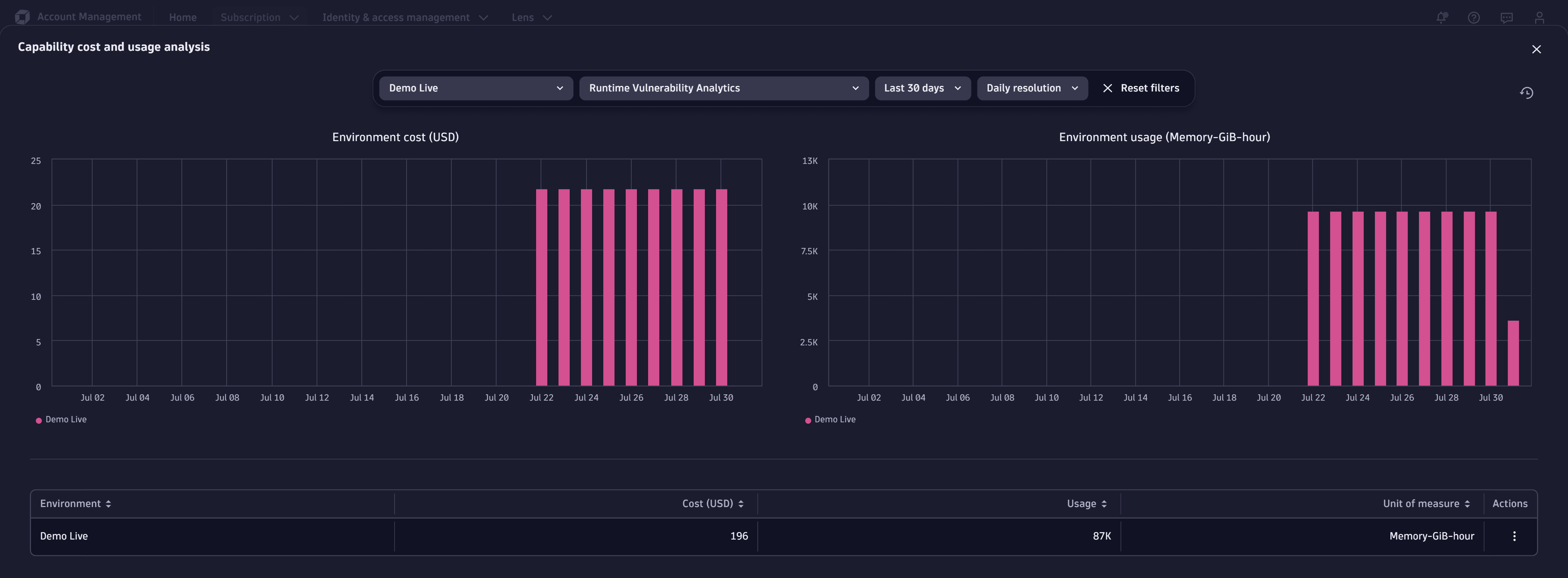
Track your consumption and costs in Account Management
You can also track your usage in Account Management.
- Go to Account Management > Subscription > Overview.
- In Cost and usage details, select Usage summary.
- Search for
Runtime Vulnerability Analyticsand select View details.
Track your consumption and costs via API
You can query metrics via the Environment API - Metrics API v2.