Create a new request naming rule
- Reference
- Published Mar 05, 2019
This use case shows you how to use the Request naming API to create a new request naming rule.
Service request naming enables you to consolidate or refine requests across multiple services. Additionally, you can synchronize these rules across multiple Dynatrace environments.
Let's assume we have two requests from Drupal (the open-source CMS) named /node/1 and /node/1/edit. The last parts of both names (/1 and /1/edit) don't carry any valuable information. We can remove those parts and consolidate the two separate requests into one named /node. To achieve this, we need a request naming rule to rename every request where the URL begins with /node into simply /node, thereby consolidating them.
The configuration for such a rule looks like this:
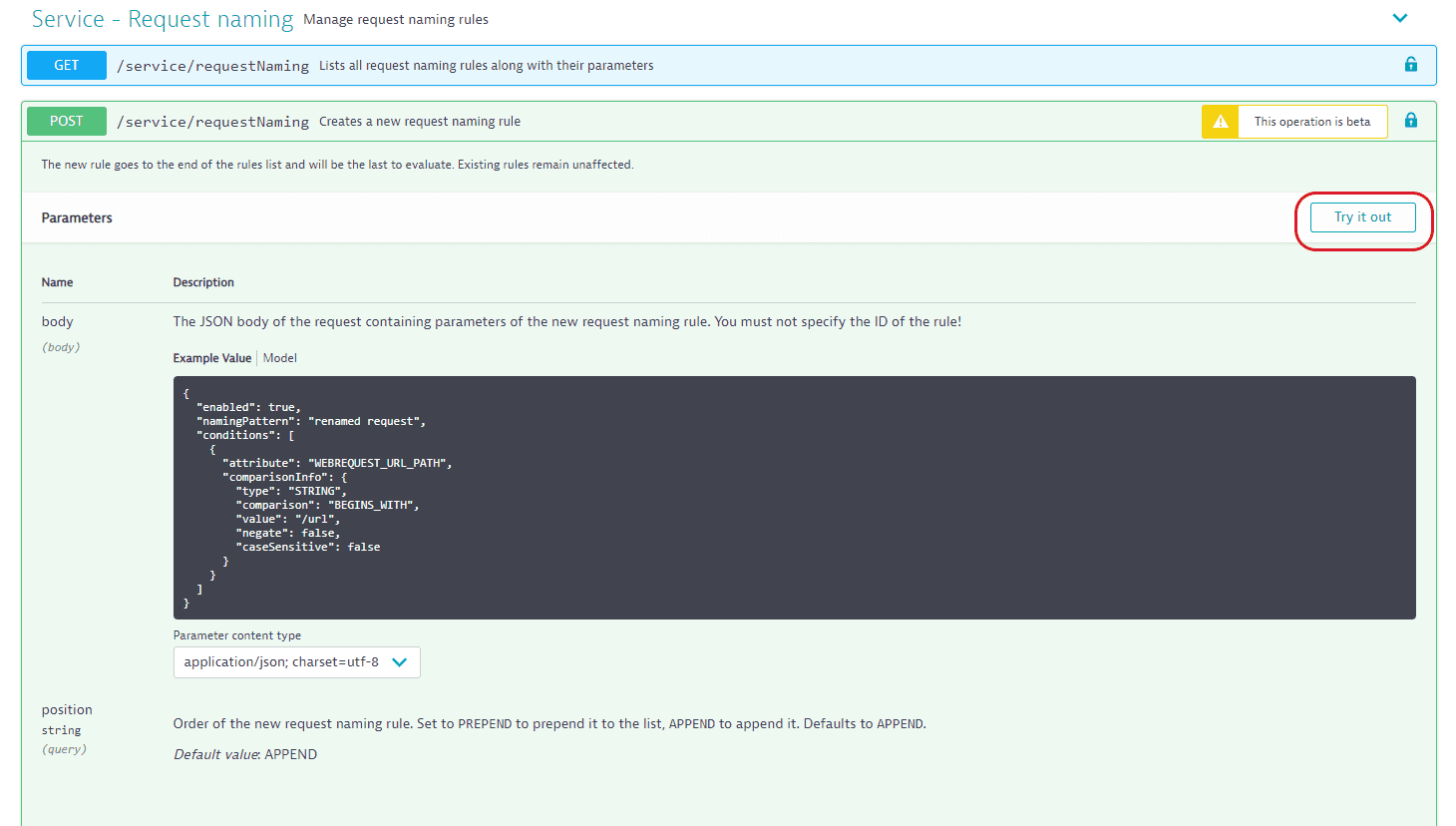
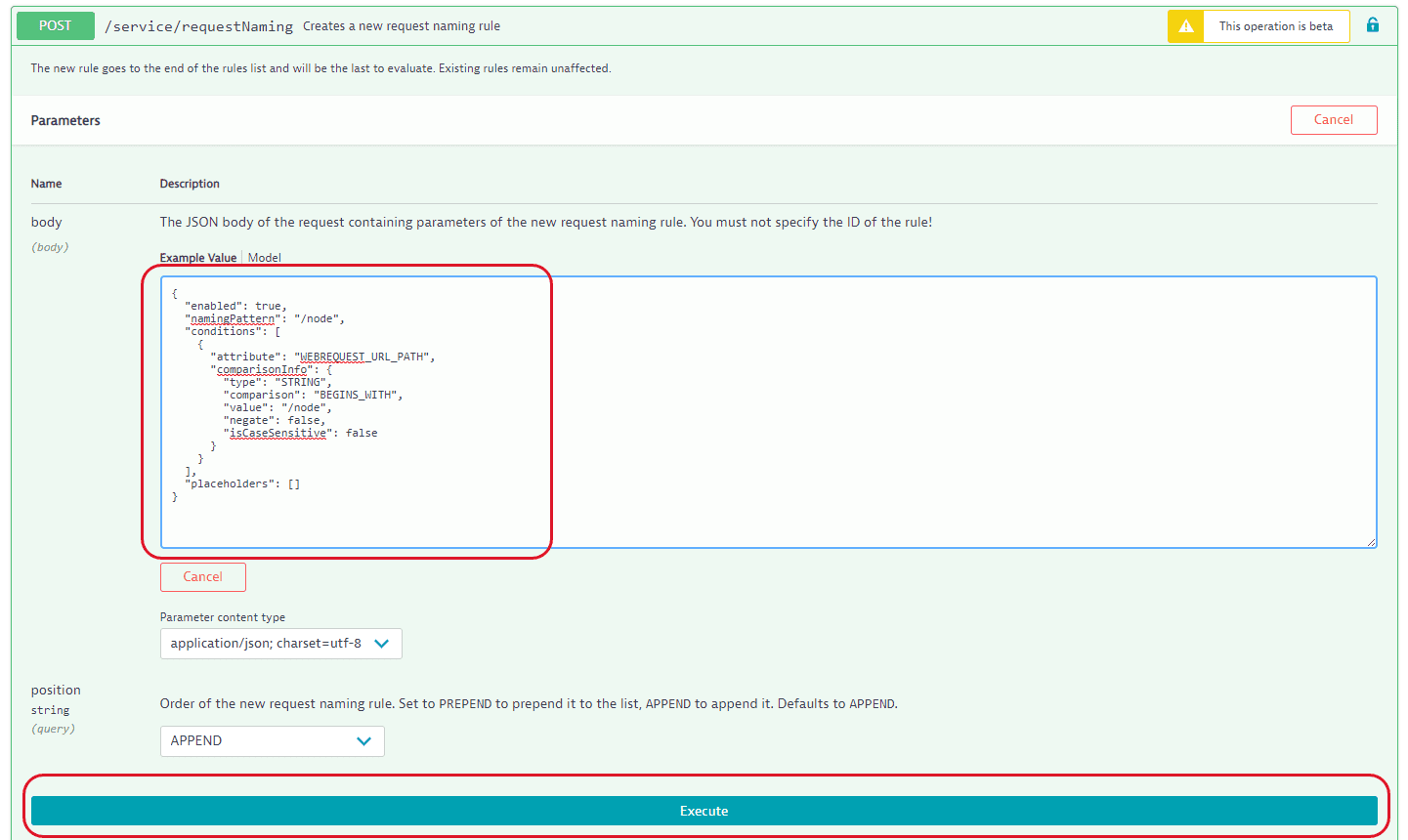
{"enabled": true,"namingPattern": "/node","conditions": [{"attribute": "WEBREQUEST_URL_PATH","comparisonInfo": {"type": "STRING","comparison": "BEGINS_WITH","value": "/node","negate": false,"isCaseSensitive": false}}],"placeholders": []}
The important components are:
- conditions—defines which requests will be renamed.
- namingPattern—defines the resulting name.
You can find descriptions of other fields in the Parameters section of the POST a new request naming rule topic.
Now let's submit this configuration in an API call. How you execute REST calls is up to you—you can use any REST client or you can write a script like the one provided below. You can also use the Dynatrace API Explorer to familiarize yourself with endpoints and execute all the required requests.
- Generate a new access token for the Dynatrace API. Be sure to assign Read configuration and Write configuration scopes to it.
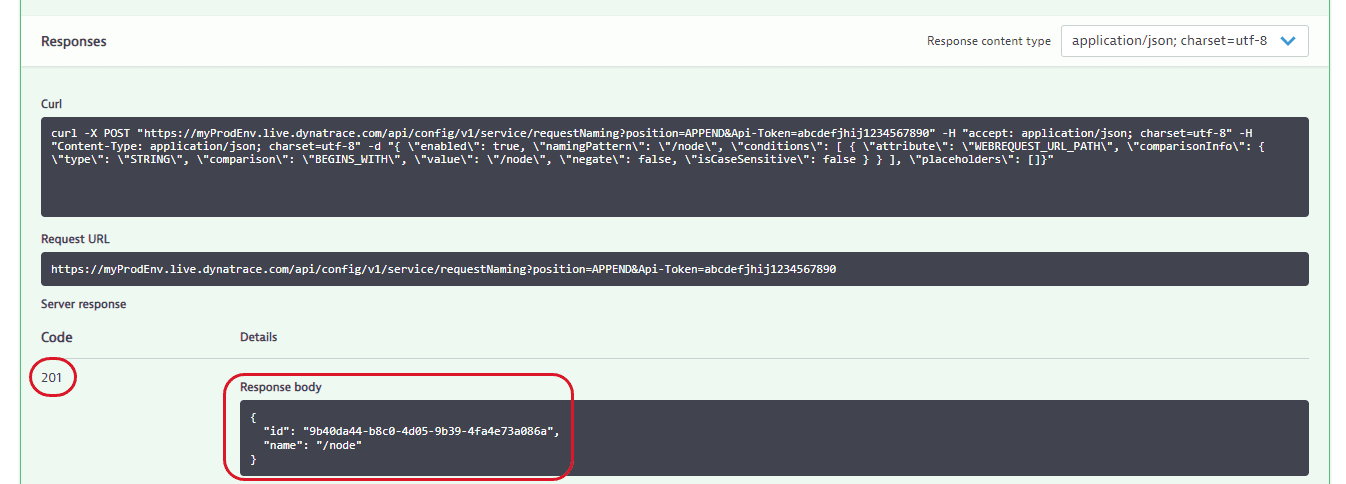
- Execute the POST a new request naming rule request with the token you created in the first step and the JSON configuration of the request naming rule from an example above as a payload.