AWS EC2 ecosystem overview
- Latest Dynatrace
- Explanation
- 5-min read
- Published Jan 28, 2026
AWS EC2 Instance Ecosystem provides a focused, hierarchical visualization of your EC2 instances and their surrounding resource ecosystem. This view enables you to understand how your EC2 instances are organized across regions, availability zones, and subnets, along with their relationships to attached EBS volumes, associated Lambda functions, and connected DynamoDB tables.
By presenting a clear structural hierarchy from region down to individual EC2 instances and their directly related resources, this view helps you quickly identify how your compute resources are distributed and connected, making it easier to troubleshoot issues, optimize instance placement, and ensure proper architectural design within your EC2 ecosystem.
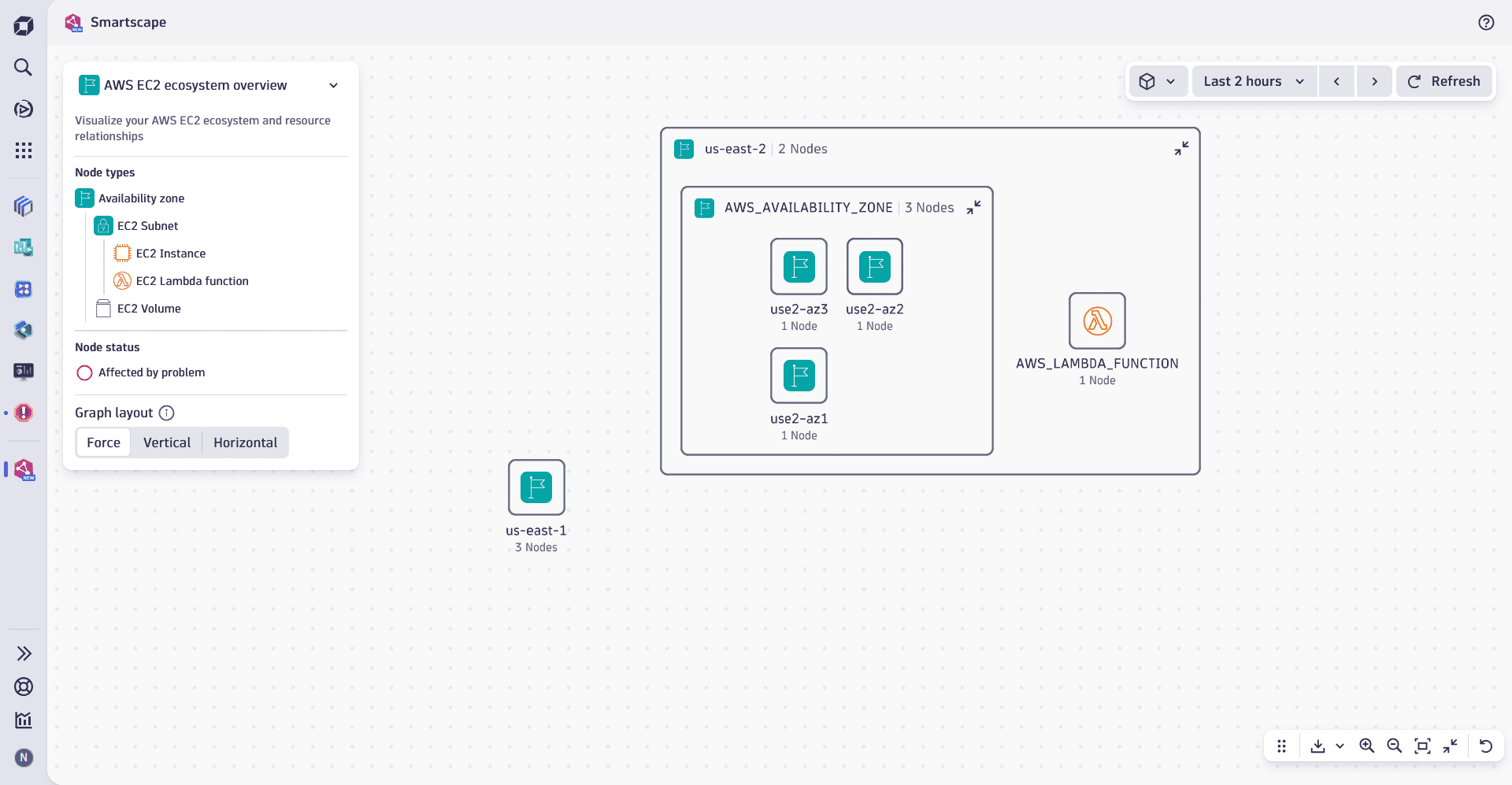
Constituent entities overview
AWS EC2 Instance Ecosystem breaks down your EC2 environment into clear, hierarchical layers to help you visualize its structure. The layers consist of:
- Nodes
- Groups
Nodes and groups
Nodes, the highest level of the view, showcase AWS Regions. Each region contains Availability Zones, Lambda functions, and DynamoDB tables, with additional resources nested within the availability zones. The structure can be visualized as follows:
- AWS Region
- AWS Availability Zone
- AWS EC2 Subnet
- AWS EC2 Instance
- AWS Lambda Function
- AWS EC2 Instance
- AWS EC2 Volume
- AWS EC2 Subnet
- AWS Lambda Function
- AWS DynamoDB Table
- AWS Availability Zone
Groups found on different hierarchy levels can contain entities of the same type or level. You can expand or collapse any group to improve visibility and focus on the relevant entities.
Use cases
You can use the AWS EC2 Instance Ecosystem to:
- Visualize and understand the distribution of EC2 instances across regions, availability zones, and subnets to ensure proper high-availability configurations.
- Identify which resources are deployed in specific availability zones to assess potential single-point-of-failure risks.
- Review your subnet organization and EC2 placement to validate network segmentation and security zone configurations.
- Investigate infrastructure dependencies during troubleshooting to identify which resources might be affected by regional or zonal issues.
- Plan capacity and disaster recovery by understanding the full scope of resources within specific regions or availability zones.
Best practice tips
To use the AWS EC2 Instance Ecosystem effectively, we recommend that you:
- Focus on specific areas by selecting a segment that defines your area of responsibility, such as specific regions, availability zones, or EC2 instances relevant to your team.
- Use the topology graph to verify that your EC2 instances, subnets, and availability zones are correctly organized and associated with their intended regions.
- Drill down into any region, availability zone, subnet, or EC2 instance to continue your exploration or investigation and access detailed health-relevant signals, metrics, events, and logs.
- Review the distribution of instances across availability zones to ensure your architecture maintains high availability and fault tolerance.
Related topics
 Smartscape
Smartscape