Meter bar chart
- Latest Dynatrace
- How-to guide
- 2-min read
- Published Feb 13, 2025
Use a meter bar to visualize a single numerical value as a progress bar.
Examples
Example 1
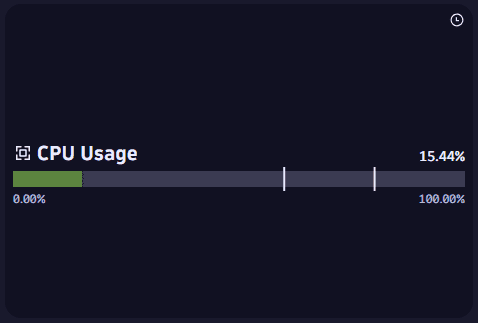
The meter bar visualization above is based on the following query, which calculates CPU as the average host CPU usage. In the Data mapping settings, Meter value is then set as CPU.
timeseries avg(dt.host.cpu.usage)| fieldsAdd CPU = arrayAvg(`avg(dt.host.cpu.usage)`)| fieldsKeep CPU
The Visual tab settings are as follows:
Example 2
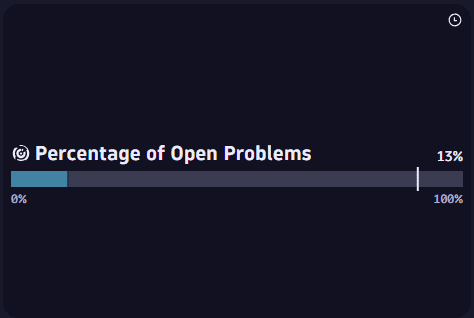
The meter bar visualization above is based on the following query, which calculates pctActive as the percentage of total problems that are open. In the Data mapping settings, Meter value is then set as pctActive.
fetch dt.davis.problems| summarize count = count(), by:{event.status}| summarize { active=toDouble(takeAny(if(event.status=="ACTIVE", count))), closed=toDouble(takeAny(if(event.status=="CLOSED", count)))}| fieldsAdd total = active + closed| fieldsAdd pctActive = (active / total) * 100| fieldsKeep pctActive
The Visual tab settings are as follows:
Chart interactions
Selection interactions
When you select a value on a chart and pin the displayed tooltip open, you can then hover over the tooltip to display a menu of selection-specific options.
The chart interactions available to you depend on your query and visualization. For example, if you select a host on a line chart and hover over the tooltip, you will see a menu of items such as:
-
Copy name—copy the name of the selected host.
-
Fields—a section with a submenu for each query field. A field submenu offers field-specific options such as:
- Copy value—copy the value of the field. Also displays the field type.
- Hide—hide the field in the chart.
- Explain value—use AI to explain the field.
- Add command to query—a section of field-specific commands that you can automatically add to your query.
- A recommended app may also be listed.
-
Visual options—opens the edit panel so you can change visualization options for the selected item.
-
Set color—opens the edit panel so you can change the color of the selected item.
-
 Go to host—opens the selection in
Go to host—opens the selection in  Infrastructure & Operations.
Infrastructure & Operations.In general, if there are recommended apps to open the selected item, the menu offers direct links to those apps, followed by an Open with option to select a different target app.
-
Open with—for details, see Drilldowns and navigation.
Title
Use the title field at the top of the options panel (initially Untitled tile or Untitled section) to add a title to your dashboard tile or notebook section.
- You can use emojis such as 😃 and 🌍 and ❤️.
- You can use variables.
Example:
- Define variables called
StatusandEmojiin your dashboard. - Set the title to
Current $Emoji status is $Status. - Set
StatustoGood. - Set
Emojito🌍.
The title will be displayed as Current 🌍 status is Good.
Visualization
If you aren't sure that you chose the right visualization, use the visualization selector to try different visualizations.
Data mapping
The data mapping section shows how a column of your result is mapped to the visualization.
Expand for general rules on data mapping settings
Expand the Data mapping section of your visualization settings to see how data in your result is mapped to your visualization, and to adjust those settings if needed.
-
Mandatory fields are marked with an asterisk (
*). Example: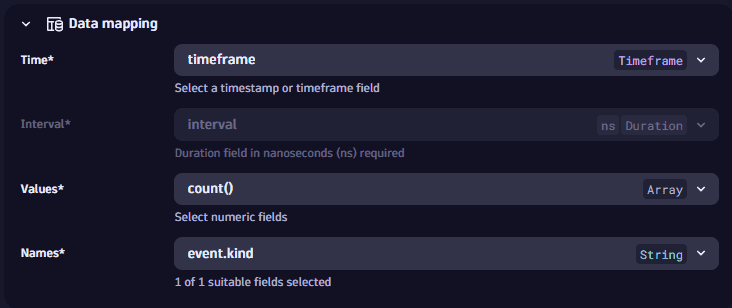
-
Data types are displayed next to field names in dropdowns and mapped fields.
-
Units are displayed when there’s only one assigned.
-
Result fields are grouped into Suitable and Unsuitable. Fields are marked as unsuitable if they cannot be used to display data in the visualization. Example:
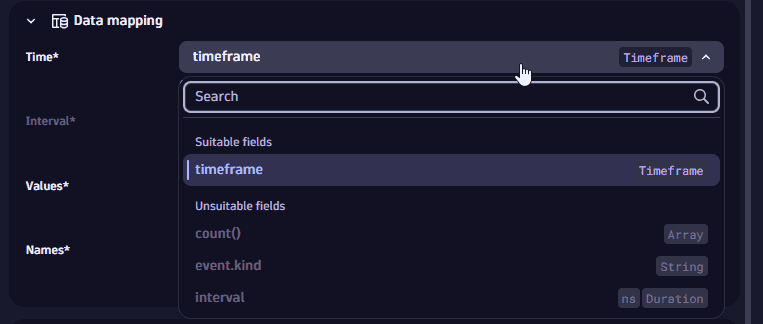
-
Automatic application of data mapping default settings:
Dynatrace version 1.319+
- Already existing tiles and sections are considered to be user-defined. Their data mapping configurations aren't updated automatically.
- Newly created tiles and sections apply a data mapping setting by default. If you don't modify these settings manually, these settings might change if a new execution of the tile/section modifies the results and there are fields missing or new fields that better suit the data mapping.
Visualization-specific data mapping settings
For a meter chart, the data mapping section includes:
- Meter value: the numeric value you want to represent as a meter.
Meter bar
Show label
To display a string above the bar, turn on Show label and enter the string.
Show icon
To display an icon above the bar, turn on Show icon and select an icon from the list. When Show label and Show icon are both selected, the icon is displayed before the label.
Min value
Determines where the meter bar starts on the left.
- Auto—starts the meter at
0 - Custom—specifies a different meter start point
Max value
Determines where the meter bar ends on the right.
- Auto
- If the meter value is less than
100, the right end of the meter =100 - If the meter value is greater than
100, the right end of the meter is the meter value
- If the meter value is less than
- Custom—specifies a different meter end point
Color
-
To set the basic color of the bar, select the desired color from the Bar color menu (or open the Bar color menu and enter the hex code for the color).
-
You can add one or more Custom colors to define the colors to display when the meter reaches certain values.
For each custom color, enter the meter value and set the corresponding color to use when the meter value reaches that value. A vertical line is displayed on the bar for each custom color value.
ExampleSuppose you want your meter to remain green normally, but turn yellow if it reaches
80, and turn red if it reaches90:- Set Bar color to the desired shade of green
- Select Color and add a custom color row with the value
80and the desired shade of yellow selected. If the meter value reaches80, the bar will turn yellow. - Select Color again and add a custom color row with the value
90and the desired shade of red selected. If the meter value reaches90, the bar will turn red.
Units and formats
To override the default units and formats in a dashboard or notebook visualization
-
Select to edit the visualization tile.
-
Select the Visual tab.
-
Select Units and formats.
-
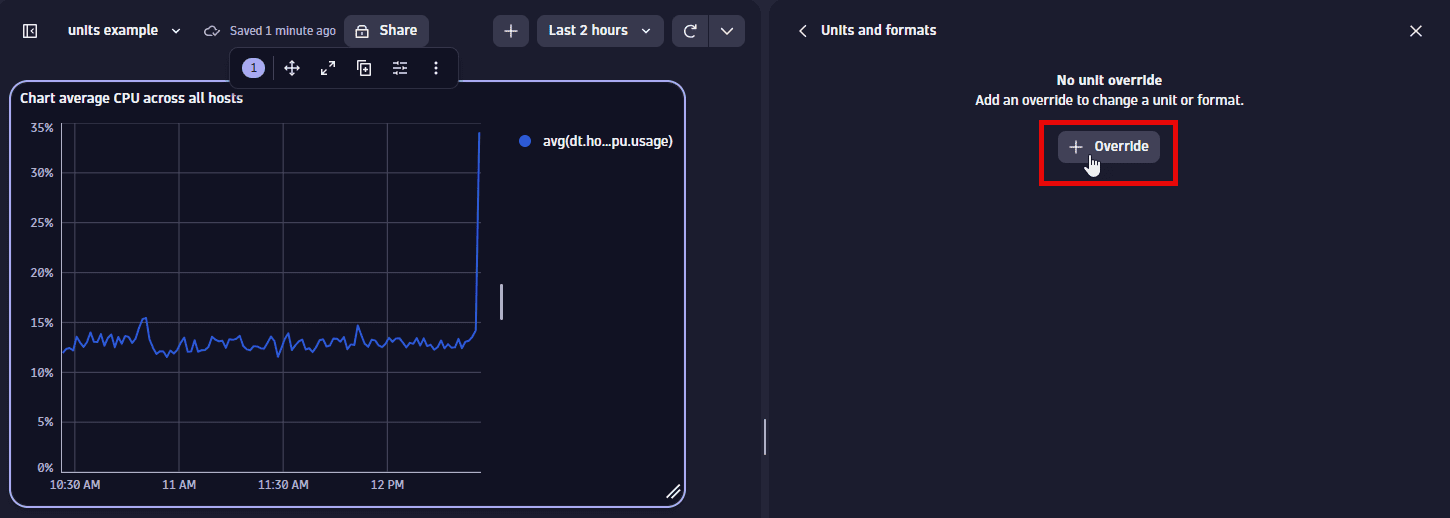
Select Override.
-
Select Override
-
In the dropdown list, select the item for which you want to add a unit override.
This is a numeric column of the underlying DQL result, so it varies according to the query. For example:
- A
fetch eventsquery returns events. The dropdown list here lets you select a numeric field (such astransfer_size) from the results. - A
timeseries avg(dt.host.cpu.usage)query returns a single timeseries foravg(dt.host.cpu.usage). That timeseries is then the only selectable option in the list.
- A
-
Define the override.
- Default unit: The base unit in which the values were captured. It's
Noneif it was not included in the DQL result, or its automatically defined by the unit passed from the DQL result. This field doesn't lead to any conversion. - Displayed unit: Once you define a default unit, you can use Displayed unit for conversion. For example, if the DQL result defined your numeric value in the result as
Bytes, Displayed unit now offers a suitable list of byte conversions such asKilobyteandMegabyte. Unlike the Default unit, the Displayed unit is always a numeric conversion. - Decimals displays the default number of decimals (degree of precision) to display. To see it in action, change the Decimals selection and observe the change in the visualization.
- Suffix displays the suffix to display after the unit. To see it in action, enter a string and observe the change in the visualization. When you don't find the unit you're looking for, you can use Suffix to display the desired unit.
- Default unit: The base unit in which the values were captured. It's
-
Turn on Abbreviate large numbers if you want to display large figures in abbreviated form. For example,
1053becomes1.1K.
To reset to defaults (discard override settings for the selected item), select the trash can next to the item.
Example for dashboards
This example uses a line chart, but the options apply to other visualizations.
-
In
 Dashboards, create a dashboard.
Dashboards, create a dashboard. -
Select and, in the Snippets section of the menu, select Metrics > Chart average CPU across all hosts.
-
In the section edit panel, select the Visual tab and select Line.
-
Select Units and formats.
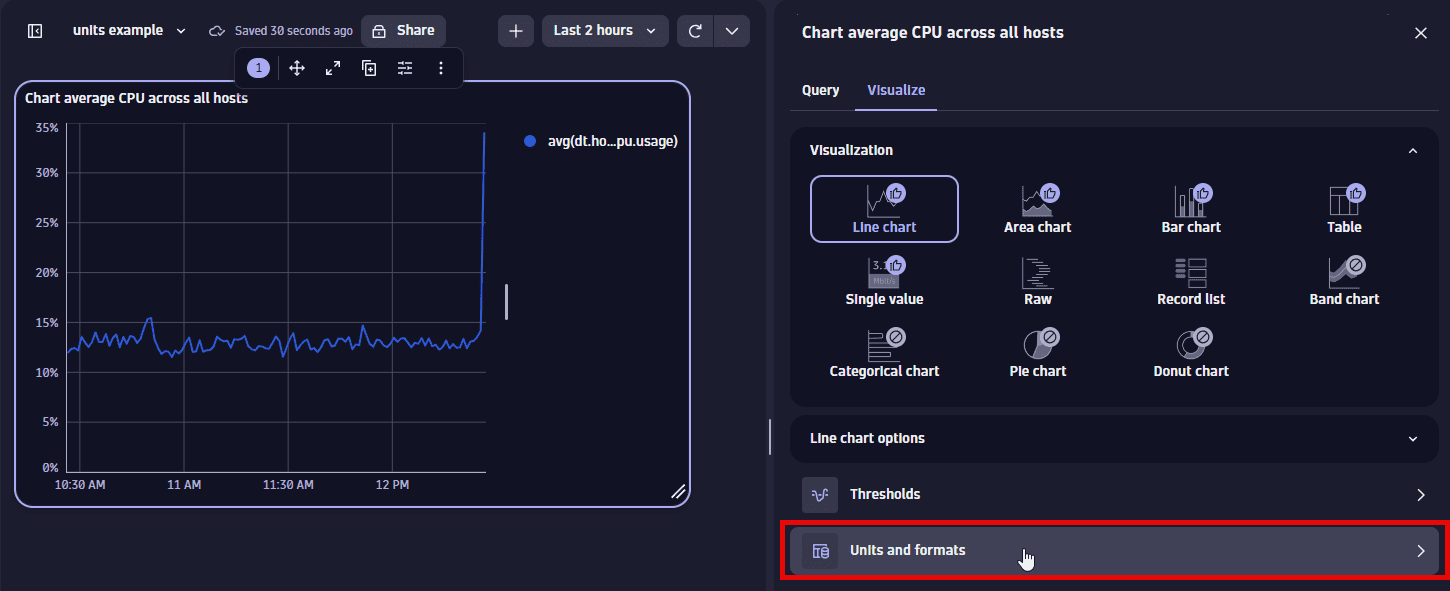
-
Select Override.
-
In the dropdown list, select the metric for which you want to add an override. There's only one metric to select in this example.
-
Define the override for the displayed metric. You can observe your changes in the Y-axis of the chart.
-
Default unit displays
Percent (%), which is the default unit for the selected metric. Try a different setting, such asOneto instead display the result as a fraction of 1. -
Displayed unit displays
Auto. You can change it to a different unit, such asOneto instead display the result as a fraction of 1.Only linear and static conversions are supported. For example, you cannot convert
Degree Celsius(°C)intoDegree Fahrenheit(°F), or convertUsd(US$)intoEur(€). -
Decimals displays the default number of decimal points (degree of precision) to display. To see it in action, change the Decimals selection and observe the change in the visualization.
For example, change this:
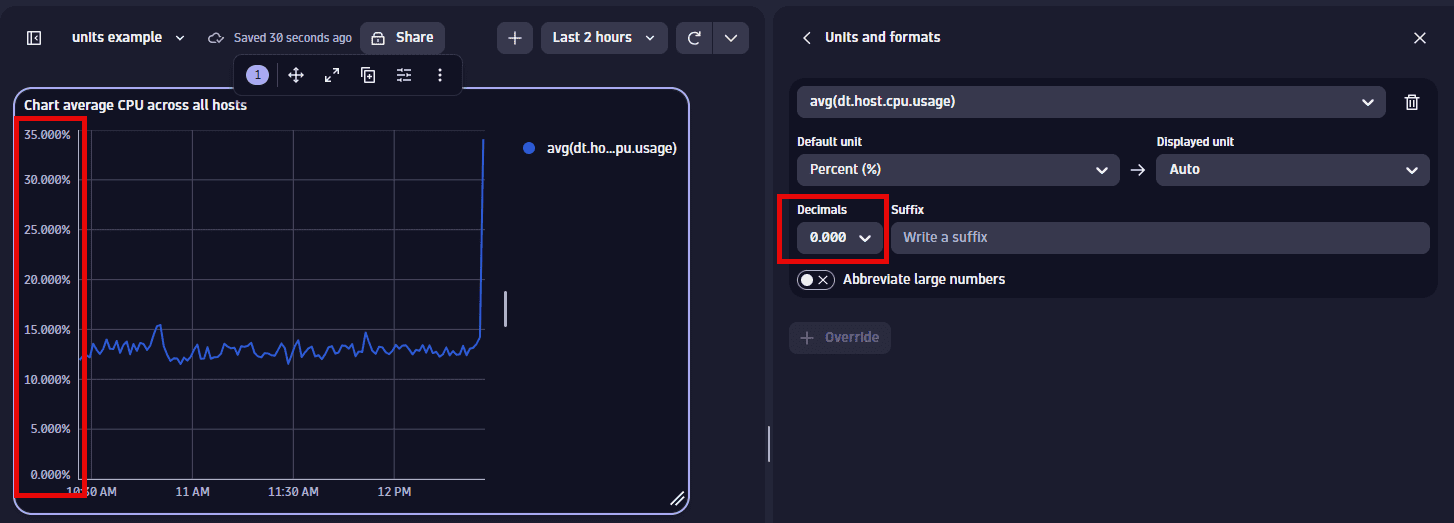
To this:
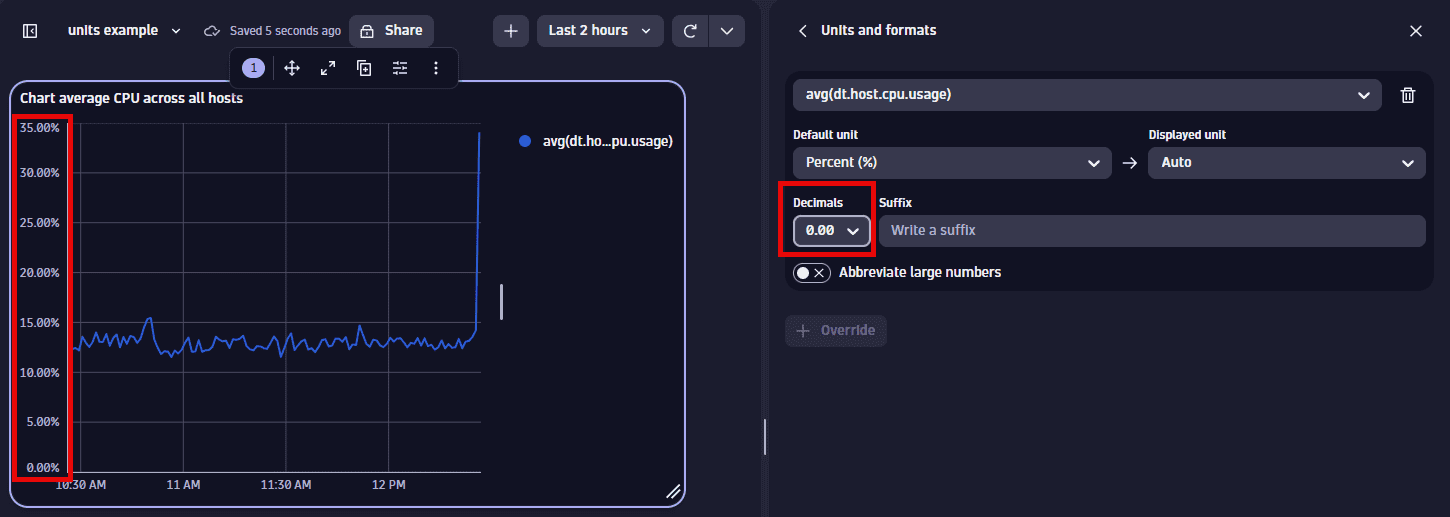
-
Suffix displays the optional suffix to display after the unit. To see it in action, enter a string and observe the change in the visualization.
-
To reset to defaults (discard override settings for the selected metric), select the trash can next to the metric.